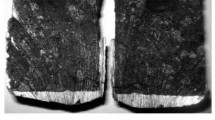
Penetration of sodium into carbon-graphite material (CGM) specimens previously modified with lithium is studied. Sodium diffusion coefficients are calculated after treating CGM with lithium vapor and values are determined for activation energy of diffusion under different conditions. The kinetic dependences obtained make it possible to determine the sodium diffusion mechanism in modified CGM. The efficiency is demonstrated of preliminary treatment with lithium vapor that makes it possible to prevent aluminum electrolyzer cathode lining surface layer breakdown during operation. The tests on CGM specimens performed make it possible to create prerequisites for developing technology for hearth surface protection from sodium penetration during electrolysis in molten cryolite-alumina.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. M. Sizyakov, V. Yu. Bazhin, R. K. Patrin, et al., “Features of high-amperage electrolyzer hearth breakdown,” Refract. Indust. Ceram., 54(3), 151 – 154 (2013).
A. V. Saitov, V. Yu. Bazhin, and R. Yu. Feshchenko, “Operational problems of a graphitized cathodic block lining in contemporary aluminum electrolyzers,” Refract. Indust. Ceram., 58(2), 126 – 129 (2017).
M. Sorlie and H. Oye, Cathodes in Aluminium Electrolysis, Aluminium-Verlag, Düsseldorf (2013).
M. B. Rapoport, Carbon-Graphite Interlayer Compounds and their Value in Aluminum Metallurgy [in Russian], TsNIItsvetmetinformatsiya, Moscow (1967).
E. S. Gorlanov, V. Yu. Bazhin, and S. N. Fedorov, “Carbide formation at a carbon-graphite lining cathode surface wettable with aluminum,” Refract. Indust. Ceram., 57(5), 292 – 296 (2016).
S. Bao, K. Tang, A. Kvithyld, T. Engh, and M. Tangstad, “Wetting of pure aluminium on graphite, SiC and Al2O3 in aluminium filtration,” Trans. Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 22(8), 1930 – 1938 (2012).
V. De Nora and T. Nguyen, “Inert anode: Challenges from fundamental research to industrial application,” Light Metals, 417 – 421 (2009).
Han-bing He, Y. Wang, Jia-ju Long, and Zhao-hui Chen, “Corrosion of NiFe2O4–10NiO–based cermet inert anodes for aluminium electrolysis,” Trans. Nonferrous Metals Society of China., 23(12), 3816 – 3821 (2013).
M. B. Rapoport, “Increase in the life of cathode blocks of aluminum electrolyzers,” Trudy VAMI, 38 (1955).
D. S. Newman, H. Justnes, and H. A. Oye, “The effect of Li on graphitic cathodes used in aluminum electrolysis,” Metall., 6, 582 – 584 (1986).
V. Yu. Bazhin and A. V. Saitov, “Improvement of the physical and operating properties of carbon-graphite lining with lithium additions,” Novye Ogneupory, No. 1, 49 – 54 (2018).
G. V. Galevskii, N. M. Kulagin, M. Ya. Mintsis, and G. A. Sirazutdinov, Aluminum Metallurgy. Technology, Electrical Supply, Automation: Hgih School Texbook [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (2008).
A. R. Ubbelohde and F. A. Lewis, Graphite and its Crystal Compounds Oxford University Press (1965).
V. Yu. Bazhin, R. Yu. Feshchenko, A. V. Saitov, and E. A. Kuznetsova, “Protection of an aluminum electrolyzer carbon-graphite lining by a lithium intercalation layer,” Refract. Indust. Ceram., 55(2), 81 – 83 (2014).
V. A. Emel’kin, M. G. Ktakherman and B. A. Pozdnyakov, “Preparation of lithium oxide with decomposition of lithium carbonate in a stream of heat carrier,” Teoret. Osnovy. Khim. Tekhnol., 43(1), 93 – 98 (2009).
E. W. Dewing, “The reaction of sodium with nongraphitic carbon: Reactions occurring in the linings of aluminium reduction cells,” Trans. Metall Soc. AIME., 227(12), 1328 – 1334 (1963).
P. Sh’yumon, Diffusion in Solids [in Russian], Metallurgiya. Moscow (1966).
B. V. Romanovskii, Bases of Chemical technology: High School Textbook [in Russian], Ekzamen, Moscow (2006).
N. K. Kondrasheva, F. D. Baitalov, and A. A. Boitsova, “Comparative assessment of structural-mechanical properties of heavy oils of Timano-Pechorskaya province,” Zapiski Gornogo Instituta, 225, 320 – 329 (2017).
O. Yu. Elagin, Production Methods for Increasing the Wear Resistance of Machine Components: Textbook [in Russian], Univer. Kniga, Logos (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Novye Ogneupory, No. 5, pp. 56 – 65, May, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saitov, A.V., Bazhin, V.Y. Features of Using Modified Carbon-Graphite Lining Materials in Aluminum Electrolyzers. Refract Ind Ceram 59, 278–286 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11148-018-0221-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11148-018-0221-5