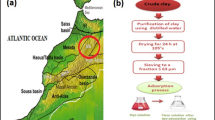
Abstract
The present study aims to investigate the adsorption behavior of methylene blue (MB) using purified Moroccan clay/alginate beads and optimize the process conditions using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Composite alginate beads were synthesized via the drop method, and their performance as adsorbents for MB removal was assessed under varying pH levels, adsorbent dosage, and initial MB concentration using the Box-Behnken design. The results revealed that the optimal conditions for achieving 100% MB removal were pH 11.8, adsorbent mass of 4.9 g, and MB concentration of 191 ppm. The adsorption process was well described by the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Langmuir isotherm model, suggesting that the process involves monolayer adsorption. Moreover, the regenerated adsorbent exhibited satisfactory adsorption performance after five cycles. These findings demonstrate the potential of purified Moroccan clay/alginate beads as an efficient, reusable adsorbent for MB removal from water solutions, contributing to the development of sustainable solutions for dye removal in wastewater treatment applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gul S, Gul H, Gul M et al (2022) Enhanced adsorption of rhodamine B on biomass of cypress/false cypress (Chamaecyparis lawsoniana) fruit: optimization and kinetic study. Water (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/w14192987
Sehar S, Rasool T, Syed HM et al (2022) Recent advances in biodecolorization and biodegradation of environmental threatening textile finishing dyes. 3 Biotech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03247-7
Belghiti M, Tanji K, El Mersly L et al (2022) Fast and non-selective photodegradation of basic yellow 28, malachite green, tetracycline, and sulfamethazine using a nanosized ZnO synthesized from zinc ore. React Kinet Mech Catal 135:2265–2278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-022-02232-8
Dave S, Das J, Varshney B, Sharma VP (2022) Dyes and pigments: interventions and how safe and sustainable are colors of life!!! In: environmental science and engineering. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 1–20
Mehta M, Sharma M, Pathania K et al (2021) Degradation of synthetic dyes using nanoparticles: a mini-review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:49434–49446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15470-5
Garg S, Roy A (2022) Phytoremediation: an alternative approach for removal of dyes. In: phytoremediation: biotechnological strategies for promoting invigorating environs. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 369–386
Rajoria B, Roy A (2022) Bacterial and fungal degradation of dyes: a remedial source. In: development in wastewater treatment research and processes: microbial degradation of xenobiotics through bacterial and fungal approach. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 23–43
Shamsheer B, Mughal TA, Yousaf Z et al (2021) Green synthesis of dyes and appliance on silk by using metamordating technique. Pak J Sci Ind Res Ser B Biol Sci 64:116–125. https://doi.org/10.52763/pjsir.biol.sci.64.2.2021.116.125
Kumar L, Bharadvaja N (2020) Microorganisms: a remedial source for dye pollution. In: removal of toxic pollutants through microbiological and tertiary treatment: new perspectives. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 309–333
Corso CR, Almeida EJR, Santos GC et al (2012) Bioremediation of direct dyes in simulated textile effluents by a paramorphogenic form of Aspergillus oryzae. Water Sci Technol 65:1490–1495. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2012.037
Bilal M, Ali J, Bibi K et al (2022) Remediation of different dyes from textile effluent using activated carbon synthesized from Buxus Wallichiana. Ind Crops Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115267
Singh I, Gupta S, Gautam HK et al (2021) Antimicrobial, radical scavenging, and dye degradation potential of nontoxic biogenic silver nanoparticles using Cassia fistula pods. Chem Pap 75:979–991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01355-3
Usefzay O, Yari S, Amiri P, Hasanein P (2022) Evaluation of protective effects of methylene blue on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Biomed Pharmacother 150:113023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113023
Vel C, Hern A (2023) Photocatalytic reduction of methylene blue induced by a commercial titanium precursor in homogeneous phase. J Photochem Photobiol A: Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2023.114552
Klyuev SV, Klyuev AV, Vatin NI (2021) Innovations and technologies in construction, BUILDINTECH BIT 2021. Springer International Publishing, Cham
Xiao X, Zhang F, Feng Z et al (2015) Adsorptive removal and kinetics of methylene blue from aqueous solution using NiO/MCM-41 composite. Phys E Low-Dimens Syst Nanostruct 65:4–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2014.08.006
Song SG, Kim SH (2011) Pruritus ani. J Korean Soc Coloproctol 27:54–57. https://doi.org/10.3393/jksc.2011.27.2.54
Ge ITK, Nugraha MW, Ahmad Kamal N, Sambudi NS (2019) Composite of kaolin/sodium alginate (SA) beads for methylene blue adsorption. ASEAN J Chem Eng 19:100–109. https://doi.org/10.22146/ajche.51457
Waghchaure RH, Adole VA, Jagdale BS (2022) Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue, rhodamine B, methyl orange and Eriochrome black T dyes by modified ZnO nanocatalysts: a concise review. Inorg Chem Commun 143:109764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109764
Thiam A, Tanji K, Assila O et al (2020) Valorization of date pits as an effective biosorbent for remazol brilliant blue adsorption from aqueous solution. J Chem 2020:14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4173152
Rohmah AA, Purnomo AS, Safitri WN (2022) Biodecolorization of methylene blue by using bacillus subtilis immobilized into SA-PVA-bentonite matrix in mineral salt medium and non-nutritious medium. Indones J Chem 22:1637–1650. https://doi.org/10.22146/ijc.76080
Fahoul Y, Zouheir M, Tanji K, Kherbeche A (2022) Synthesis of a novel ZnAl2O4/CuS nanocomposite and its characterization for photocatalytic degradation of acid red 1 under UV illumination. J Alloys Compd 889:161708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.161708
Bellouk H, El Mrabet I, Tanji K et al (2022) Performance of coagulation-flocculation followed by ultra-violet/ultrasound activated persulfate/hydrogen peroxide for landfill leachate treatment. Sci African 17:e01312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2022.e01312
Tanji K, El Mrabet I, Fahoul Y et al (2023) Experimental and theoretical investigation of enhancing the photocatalytic activity of Mg doped ZnO for nitrophenol degradation. React Kinet Mech Catal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-023-02385-0
Chkirida S, Zari N, Achour R et al (2021) Highly synergic adsorption/photocatalytic efficiency of alginate/bentonite impregnated TiO2 beads for wastewater treatment. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 412:113215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2021.113215
Madhava Rao M, Ramesh A, Purna Chandra Rao G, Seshaiah K (2006) Removal of copper and cadmium from the aqueous solutions by activated carbon derived from Ceiba pentandra hulls. J Hazard Mater 129:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.08.018
Benhouria A, Islam MA, Zaghouane-Boudiaf H et al (2015) Calcium alginate-bentonite-activated carbon composite beads as highly effective adsorbent for methylene blue. Chem Eng J 270:621–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.02.030
Anfar Z, Zbair M, Ahsaine HA et al (2018) Well-designed WO3/Activated carbon composite for Rhodamin. Removal: synthesis, characterization, and modeling using response surface methodology. Fuller Nanotub Carbon Nanostruct 26:389–397. https://doi.org/10.1080/1536383X.2018.1440386
Foroutan R, Peighambardoust SJ, Peighambardoust SH et al (2021) Adsorption of crystal violet dye using activated carbon of lemon wood and activated carbon/fe3 o4 magnetic nanocomposite from aqueous solutions: a kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. Molecules 26:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082241
Shak A, Dawood S, Sen TK (2017) Performance and dynamic modelling of mixed biomass-kaolin packed bed adsorption column for the removal of aqueous phase methylene blue (MB) dye. Desalin Water Treat 82:67–80. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.20963
Gao LH, Goldfarb JL (2021) Characterization and adsorption applications of composite biochars of clay minerals and biomass. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:44277–44287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13858-x
Keskin Avci S, Erucar I (2018) Porous Materials. Compr Energy Syst 2–5:182–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809597-3.00218-2
Birniwa AH, Abubakar AS, Mahmud HNME et al (2022) Application of agricultural wastes for cationic dyes removal from wastewater BT - textile wastewater treatment: sustainable bio-nano materials and macromolecules, volume 1. In: Khadir A (ed) Muthu SS. Springer Nature Singapore, Singapore, pp 239–274
Dotto GL, Pinto LAA (2011) Adsorption of food dyes onto chitosan: optimization process and kinetic. Carbohydr Polym 84:231–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.11.028
Jeon YS, Lei J, Kim J-H (2008) Dye adsorption characteristics of alginate/polyaspartate hydrogels. J Ind Eng Chem 14:726–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2008.07.007
de Souza FM, dos Santos OAA (2020) Adsorption of Diuron from aqueous solution onto commercial organophilic clay: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. Environ Technol 41:603–616. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1505967
Adeyemo AA, Adeoye IO, Bello OS (2017) Adsorption of dyes using different types of clay: a review. Appl Water Sci 7:543–568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0322-y
Velic N, Stjepanovic M, Begovic L et al (2018) Valorisation of waste wood biomass as biosorbent for the removal of synthetic dye methylene blue from aqueous solutions. SEEFOR-SOUTH-EAST Eur For 9:115–122. https://doi.org/10.15177/seefor.18-13
Liu Y, Zheng Y, Wang A (2010) Response surface methodology for optimizing adsorption process parameters for methylene blue removal by a hydrogel composite. Adsorpt Sci Technol 28:913–922. https://doi.org/10.1260/0263-6174.28.10.913
Bezerra MA, Santelli RE, Oliveira EP et al (2008) Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 76:965–977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.05.019
Aydar AY (2018) Utilization of response surface methodology in optimization of extraction of plant materials. IntechOpen, Rijeka
Aljar MAA, Rashdan S, El-Fattah AA (2021) Environmentally friendly polyvinyl alcohol−alginate/ bentonite semi-interpenetrating polymer network nanocomposite hydrogel beads as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Polymers (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13224000
El Khanchaoui A, Sajieddine M, Mansori M et al (2023) Removal of single dye and dye mixture from aqueous solution with alginate-coated calcined layered double hydroxide and illite clay composite beads. Mater Res Innov. https://doi.org/10.1080/14328917.2022.2163112
Li H, Zhang SP, Liang YQ et al (2018) Trimeric surfactant modified montmorillonite immobilized in alginate beads: an efficient adsorbent for removal of Cu 2+ and methyl orange from aqueous solution. Russ J Phys Chem A 92:2802–2810. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024418130186
Wang W, Fan M, Ni J et al (2022) Efficient dye removal using fixed-bed process based on porous montmorillonite nanosheet/poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid)/sodium alginate hydrogel beads. Appl Clay Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2022.106443
Brindley GW (1981) Phyllosilicates. Mineralogy - encyclopedia of earth sciences series. Springer, Boston, pp 369–376
Pawar RR, Lalhmunsiama GP et al (2018) Porous synthetic hectorite clay-alginate composite beads for effective adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution. Int J Biol Macromol 114:1315–1324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.008
Mohapi M, Sefadi JS, Mochane MJ et al (2020) Effect of LDHs and other clays on polymer composite in adsorptive removal of contaminants: a review. Crystals 10:1–39. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10110957
Ewis D, Ba-Abbad MM, Benamor A, El-Naas MH (2022) Adsorption of organic water pollutants by clays and clay minerals composites: a comprehensive review. Appl Clay Sci 229:106686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2022.106686
Şahin Ö, Kaya M, Saka C (2015) Plasma-surface modification on bentonite clay to improve the performance of adsorption of methylene blue. Appl Clay Sci 116–117:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CLAY.2015.08.015
Komadel P (2016) Acid activated clays: materials in continuous demand. Appl Clay Sci 131:84–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.05.001
Liu D, Yang X, Zhang L et al (2022) Immobilization of biomass materials for removal of refractory organic pollutants from wastewater. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19:13830. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192113830
Schmidt LN, Horst MF, Lencina MMS et al (2022) Gels based on calcium alginate/pillared bentonite: structural characterization and their use as cadmium removal agent. J Environ Sci Heal - Part A Toxic/Hazardous Subst Environ Eng 57:218–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2022.2050124
Samaddar P, Kumar S, Kim KH (2019) Polymer hydrogels and their applications toward sorptive removal of potential aqueous pollutants. Polym Rev 59:418–464. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583724.2018.1548477
Cavallaro G, Gianguzza A, Lazzara G et al (2013) Alginate gel beads filled with halloysite nanotubes. Appl Clay Sci 72:132–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2012.12.001
Cavallaro G, Lazzara G, Rozhina E et al (2019) Organic-nanoclay composite materials as removal agents for environmental decontamination. RSC Adv 9:40553–40564. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra08230a
Liu L, Wan Y, Xie Y et al (2012) The removal of dye from aqueous solution using alginate-halloysite nanotube beads. Chem Eng J 187:210–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.136
Kurczewska J, Cegłowski M, Schroeder G (2019) Alginate/PAMAM dendrimer – Halloysite beads for removal of cationic and anionic dyes. Int J Biol Macromol 123:398–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.119
Ruan B, Wu P, Chen M et al (2018) Immobilization of Sphingomonas sp. GY2B in polyvinyl alcohol–alginate–kaolin beads for efficient degradation of phenol against unfavorable environmental factors. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 162:103–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.06.058
Salemi E, Tessari U, Colombani N, Mastrocicco M (2010) Improved gravitational grain size separation method. Appl Clay Sci 48:612–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2010.03.014
Shi P, He P, Teh TKH et al (2011) Parametric analysis of shape changes of alginate beads. Powder Technol 210:60–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2011.02.023
Bakatula EN, Richard D, Neculita CM, Zagury GJ (2018) Determination of point of zero charge of natural organic materials. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:7823–7833. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1115-7
Wibowo N, Setyadhi L, Wibowo D et al (2007) Adsorption of benzene and toluene from aqueous solutions onto activated carbon and its acid and heat treated forms: influence of surface chemistry on adsorption. J Hazard Mater 146:237–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.011
Khalfaoui A, Khelifi MN, Khelfaoui A et al (2022) The adsorptive removal of bengal rose by artichoke leaves: optimization by full factorials design. Water (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142251
Whang TJ, Huang HY, Hsieh MT, Chen JJ (2009) Laser-induced silver nanoparticles on titanium oxide for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Int J Mol Sci 10:4707–4718. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10114707
El -Habacha M, Dabagh A, Lagdali S et al (2023) Methylene blue dye’s adsorption on a natural clay surface from Southeast Morocco: modeling and experimental equilibrium studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.21203/RS.3.RS-2306837/V1
Mukhopadhyay T, Dey TK, Chowdhury R, Chakrabarti A (2015) Structural damage identification using response surface-based multi-objective optimization: a comparative study. Arab J Sci Eng 40:1027–1044. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1591-3
Wang Q, Song Y (2018) Clay minerals and major elements concentrations of Zhuanglang Miocene red clay in Longzhong Basin, China. Data Br 17:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2018.01.030
Ganguli JN, Agarwal S (2012) Removal of a basic dye from aqueous solution by a natural kaolinitic clay-adsorption and kinetic studies. Adsorpt Sci Technol 30:171–182. https://doi.org/10.1260/0263-6174.30.2.171
Omer OS, Hussein BHM, Ouf AM et al (2018) An organified mixture of illite-kaolinite for the removal of Congo red from wastewater. J Taibah Univ Sci 12:858–866. https://doi.org/10.1080/16583655.2018.1540179
Gil A, Santamaría L, Korili SA et al (2021) A review of organic-inorganic hybrid clay based adsorbents for contaminants removal: synthesis, perspectives and applications. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105808
Mustapha S, Ndamitso MM, Abdulkareem AS et al (2019) Potential of using kaolin as a natural adsorbent for the removal of pollutants from tannery wastewater. Heliyon 5:e02923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02923
Bergaya F, Lagaly G (2013) Chapter 7.1—Purification of natural clays. In: Bergaya F, Lagaly GBT-D (eds) Handbook of Clay Science. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 213–221
Awasthi A, Jadhao P, Kumari K (2019) Clay nano-adsorbent: structures, applications and mechanism for water treatment. SN Appl Sci 1:1076. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0858-9
Środoń J, Drits VA, McCarty DK et al (2001) Quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis of clay-bearing rocks from random preparations. Clays Clay Miner 49:514–528. https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2001.0490604
Moon DH, Kim SJ, Nam SW, Cho HG (2021) X-ray diffraction analysis of clay particles in ancient baekje black pottery: indicator of the firing parameters. Minerals. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111239
Jozanikohan G, Abarghooei MN (2022) The Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis for the clay mineralogy studies in a clastic reservoir. J Pet Explor Prod Technol 12:2093–2106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13202-021-01449-y
Carrado KA, Decarreau A, Petit S et al (2006) Chapter 4 synthetic clay minerals and purification of natural clays. In: Bergaya F, Theng BKG, Lagaly GBT-D (eds) Handbook of clay science. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 115–139
Maged A, Kharbish S, Ismael IS, Bhatnagar A (2020) Characterization of activated bentonite clay mineral and the mechanisms underlying its sorption for ciprofloxacin from aqueous solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:32980–32997. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09267-1
Madejová J, Gates WP, Petit S (2017) Chapter 5—IR spectra of clay minerals. In: Gates WP, Kloprogge JT, Madejová J, Bergaya FBTD (eds) Infrared and Raman spectroscopies of clay minerals. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 107–149
Rahim SNA, Sulaiman A, Hamzah F et al (2013) Enzymes encapsulation within calcium alginate-clay beads: characterization and application for cassava slurry saccharification. Procedia Eng 68:411–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2013.12.200
Hoang-Minh T, Kasbohm J, Nguyen-Thanh L et al (2019) Use of TEM-EDX for structural formula identification of clay minerals : a case study of Di Linh bentonite. Vietnam J Appl Crystallogr 52:133–147
Panda L, Das B, Rao DS, Mishra BK (2011) Application of dolochar in the removal of cadmium and hexavalent chromium ions from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 192:822–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.05.098
Aziz F, Achaby ME, Lissaneddine A et al (2020) Composites with alginate beads: a novel design of nano-adsorbents impregnation for large-scale continuous flow wastewater treatment pilots. Saudi J Biol Sci 27:2499–2508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.11.019
Barreca S, Orecchio S, Pace A (2014) The effect of montmorillonite clay in alginate gel beads for polychlorinated biphenyl adsorption: isothermal and kinetic studies. Appl Clay Sci 99:220–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2014.06.037
Viscusi G, Lamberti E, Gerardi C et al (2022) Encapsulation of grape (Vitis vinifera L.) pomace polyphenols in soybean extract-based hydrogel beads as carriers of polyphenols and pH-monitoring devices. Gels 8:734. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8110734
Thakur S, Verma A, Raizada P et al (2022) Bentonite-based sodium alginate/ dextrin cross-linked poly (acrylic acid) hydrogel nanohybrids for facile removal of paraquat herbicide from aqueous solutions. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133002
Bao Y, Ma J, Li N (2011) Synthesis and swelling behaviors of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly(AA-co-AM-co-AMPS)/MMT superabsorbent hydrogel. Carbohydr Polym 84:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.10.061
Moussout H, Ahlafi H, Aazza M et al (2020) Interfacial electrochemical properties of natural Moroccan Ghassoul (stevensite) clay in aqueous suspension. Heliyon. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03634
Râpă M, Ţurcanu AA, Matei E et al (2021) Adsorption of copper (II) from aqueous solutions with alginate/clay hybrid materials. Materials (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237187
Idris S, Iyaka YA, Ndamitso MM et al (2012) Evaluation of kinetic models of copper and lead uptake from dye wastewater by activated pride of barbados shell. Am J Chem 1:47–51. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.chemistry.20110102.10
Egbosiuba TC, Abdulkareem AS, Kovo AS et al (2020) Ultrasonic enhanced adsorption of methylene blue onto the optimized surface area of activated carbon: adsorption isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics. Chem Eng Res Des 153:315–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2019.10.016
Allouss D, Essamlali Y, Amadine O et al (2019) Response surface methodology for optimization of methylene blue adsorption onto carboxymethyl cellulose-based hydrogel beads: adsorption kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and reusability studies. RSC Adv 9:37858–37869. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra06450h
Zhao M, Liu P (2009) Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by modified expanded graphite powder. Desalination 249:331–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2009.01.037
Mourabet M, El Boujaady H, El Rhilassi A et al (2011) Defluoridation of water using Brushite: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Desalination 278:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.05.068
Singh NB, Susan ABH (2018) Polymer nanocomposites for water treatments In: polymer-based nanocomposites for energy and environmental applications: Woodhead publishing series in composites science and engineering. University of Ottawa Press, Ottawa, pp 569–595
Said KAM, Ismail NZ, Jama’in RL et al (2018) Application of freundlich and Temkin isotherm to study the removal of Pb(II) via adsorption on activated carbon equipped polysulfone membrane. Int J Eng Technol 7:91–93. https://doi.org/10.14419/ijet.v7i3.18.16683
Sun Y, Li Y, Chen B et al (2022) Methylene blue removed from aqueous solution by encapsulation of bentonite aerogel beads with cobalt alginate. ACS Omega. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c04904
Barrak I, Ayouch I, Kassab Z et al (2021) Sodium alginate encapsulated Moroccan clay as eco-friendly and efficient adsorbent for copper ions from aqueous medium. Mater Today Proc 51:2040–2046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.07.392
Pratt A (2014) Environmental applications of magnetic nanoparticles. Front Nanosci 6:259–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-098353-0.00007-5
Islam MA, Chowdhury MA, Mozumder MSI, Uddin MT (2021) Langmuir adsorption kinetics in liquid media: interface reaction model. ACS Omega 6:14481–14492. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c01449
Keskin Avci S, Erucar I (2018) 2.7 Porous Materials. In : Dincer IBT-CES. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 182–203
Alvarez-Torrellas S, Boutahala M, Boukhalfa N, Munoz M (2019) Effective adsorption of methylene blue dye onto magnetic nanocomposites. Modeling and reuse studies. Appl Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214563
Patel H (2021) Review on solvent desorption study from exhausted adsorbent. J Saudi Chem Soc 25:101302. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSCS.2021.101302
Veli S, Alyüz B, Aly B (2007) Adsorption of copper and zinc from aqueous solutions by using natural clay. J Hazard Mater 149:226–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.04.109
Ely A, Baudu M, Basly J-P, Kankou MOSO (2009) Copper and nitrophenol pollutants removal by Na-montmorillonite/alginate microcapsules. J Hazard Mater 171:405–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.015
Belhouchat N, Zaghouane-Boudiaf H, Viseras C (2017) Removal of anionic and cationic dyes from aqueous solution with activated organo-bentonite/sodium alginate encapsulated beads. Appl Clay Sci 135:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.08.031
Ngah WSW, Fatinathan S (2008) Adsorption of Cu(II) ions in aqueous solution using chitosan beads, chitosan-GLA beads and chitosan-alginate beads. Chem Eng J 143:62–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.12.006
Viscusi G, Lamberti E, Gorrasi G (2022) Design of a hybrid bio-adsorbent based on Sodium Alginate/Halloysite/Hemp hurd for methylene blue dye removal: kinetic studies and mathematical modeling. Coll Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127925
Bée A, Obeid L, Mbolantenaina R et al (2017) Magnetic chitosan/clay beads: a magsorbent for the removal of cationic dye from water. J Magn Magn Mater 421:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.07.022
Oussalah A, Boukerroui A, Aichour A, Djellouli B (2019) Cationic and anionic dyes removal by low-cost hybrid alginate/natural bentonite composite beads: adsorption and reusability studies. Int J Biol Macromol 124:854–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.197
Park J-K, Lee G-M, Lee C-Y et al (2012) Analysis of siloxane adsorption characteristics using response surface methodology. Environ Eng Res 17:117–122. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2012.17.2.117
Middleton GV, Church MJ, Coniglio M, et al (2003) Encyclopedia of Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks. In: Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series. pp 1–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-3609-5
Abdullah NH, Mohamed M, Mohd Shohaimi NA et al (2021) Enhancing the decolorization of methylene blue using a low-cost super-absorbent aided by response surface methodology. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154430
Som A, Afiqah A, Siti R et al (2021) Optimisation of operating conditions during coagulation - flocculation process in industrial wastewater treatment using Hylocereus undatus foliage through response surface methodology. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17633-w
El Mrabet I, Ihssane B, Valdés H, Zaitan H (2022) Optimization of Fenton process operating conditions for the treatment of the landfill leachate of Fez city (Morocco). Int J Environ Sci Technol 19:3323–3336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03393-0
Lau YJ, Karri RR, Mubarak NM et al (2020) Removal of dye using peroxidase-immobilized Buckypaper/polyvinyl alcohol membrane in a multi-stage filtration column via RSM and ANFIS. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:40121–40134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10045-2
Akter M, Bhattacharjee M, Dhar AK et al (2021) Cellulose-based hydrogels for wastewater treatment: a concise review. Gels 7:1–28. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7010030
Weng CH, Pan YF (2007) Adsorption of a cationic dye (methylene blue) onto spent activated clay. J Hazard Mater 144:355–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.09.097
Loqman A, El Bali B, El Gaidoumi A et al (2021) The first application of moroccan perlite as industrial dyes removal. SILICON 14:2813–2838. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12633-021-01056-W
Rashid RA, Jawad AH, Ishak MAM, Kasim NN (2016) KOH-activated carbon developed from biomass waste: adsorption equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for Methylene blue uptake. Desalin Water Treat 57:27226–27236. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2016.1167630
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Iboustaten, E.M., Bertani, R., Tanji, K. et al. Adsorption behavior of methylene blue using purified moroccan clay/alginate beads: response surface methodology optimization. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 136, 1563–1588 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-023-02408-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-023-02408-w