Abstract
Exposure to low, non-freezing temperatures develops freezing tolerance in many plant species. Such process is called cold acclimation. Molecular changes undergone during cold acclimation are orchestrated by signalling networks including MAP kinases. Structure and function of chloroplasts are affected by low temperatures. The aim of this work was to study how the MAP kinases MPK3 and MPK6 are involved in the chloroplast performance upon a long period of cold acclimation. We used Arabidopsis thaliana wild type and mpk3 and mpk6 mutants. Adult plants were acclimated during 7 days at 4 °C and then measurements of PSII performance and chloroplast ultrastructure were carried out. Only the mpk6 acclimated plants showed a high freezing sensitivity. No differences in the PSII function were observed in the plants from the three genotypes exposed to non-acclimated or acclimated conditions. The acclimation of wild-type plants produced severe alterations in the ultrastructure of chloroplast and thylakoids, which was more accentuated in the mpk plants. However, only the mpk6 mutant was unable to internalize the damaged chloroplasts into the vacuole. These results indicate that cold acclimation induces alterations in the chloroplast architecture leading to preserve an optimal performance of PSII. MPK3 and MPK6 are necessary to regulate these morphological changes, but besides, MPK6 is needed to the vacuolization of the damaged chloroplasts, suggesting a role in the chloroplast recycling during cold acclimation. The latter could be quite relevant, since it could explain why this mutant is the only one showing an extremely low freezing tolerance.

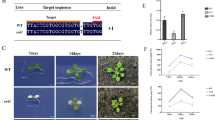
taken from 18 different plants from every genotype in three independent experiments. Different letters denote significant differences based on Tukey’s test (p < 0.05)




taken from plants exposed to NA (upper panel) or AC conditions (lower panel). Bars = 2 μm in all images. b Chloroplast length/width ratio. This was calculated from fifteen chloroplasts measured from four cells for each genotype and acclimation condition using ImageJ. c Ultrastructure of thylakoid membranes. Representative cross-sections of chloroplasts are shown for NA and AC wild type, mpk3 and mpk6. Bars = 500 nm in all images. d Scattered plot of the average grana diameter and height values (n = 75) from six chloroplasts measured by ImageJ in the three genotypes. Bars represent the respective standard errors of the mean (SEM). Different letters denote significant differences based on Tukey’s test (p < 0.05)
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Acclimated
- Atg :
-
Autophagy-defective mutant
- CBF:
-
C-repeat binding factor
- FB1:
-
Fumonisin B1
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MAPKK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase
- MAPKKK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase
- MKK2:
-
Upstream MAPKK of MPK4/MPK6
- MPK3, MPK4 or MPK6:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3, 4 or 6, respectively
- NA:
-
Non-acclimated
- PAMPs:
-
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns
- SEM:
-
Standard error of the mean
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- UV-B:
-
Ultraviolet B rays
References
Adams WW, Muller O, Cohu CM, Demmig-Adams B (2013) May photoinhibition be a consequence, rather than a cause, of limited plant productivity? Photosynth Res 117:31–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-013-9849-7
Armbruster U, Labs M, Pribil M, Viola S, Xu W, Scharfenberg M, Hertle AP, Rojahn U, Jensen PE, Rappaport F, Joliot P, Dörmann P, Wanner G, Leister D (2013) Arabidopsis CURVATURE THYLAKOID1 proteins modify thylakoid architecture by inducing membrane curvature. Plant Cell 25:2661–2678. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.113118
Asai T, Tena G, Plotnikova J, Willmann MR, Chiu WL, Gomez-Gomez L, Boller T, Ausubel FM, Sheen J (2002) MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 415:977–983. https://doi.org/10.1038/415977a
Chow WS, Kim E-H, Horton P, Anderson JM (2005) Granal stacking of thylakoid membranes in higher plant chloroplasts: the physicochemical forces at work and the functional consequences that ensue. Photochem Photobiol Sci 4:1081–1090. https://doi.org/10.1039/b507310n
Colcombet J, Hirt H (2008) Arabidopsis MAPKs: a complex signalling network involved in multiple biological processes. Biochem J 413:217–226. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20080625
Deng X, Hu ZA, Wang HX, Wen XG, Kuang TY (2003) A comparison of photosynthetic apparatus of the detached leaves of the resurrection plant Boea hygrometrica with its non-tolerant relative Chirita heterotrichia in response to dehydration and rehydration. Plant Sci 165:851–861. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(03)00284-X
Ensminger I, Busch F, Huner NPA (2006) Photostasis and cold acclimation: sensing low temperature through photosynthesis. Physiol Plant 126:28–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2006.00627
Fiil BK, Petersen K, Petersen M, Mundy J (2009) Gene regulation by MAP kinase cascades. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:615–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2009.07.017
Fristedt R, Willig A, Granath P, Crèvecoeur M, Rochaix JD, Vener AV (2009) Phosphorylation of photosystem II controls functional macroscopic folding of photosynthetic membranes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21:3950–3964. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.069435
Gan P, Liu F, Li R, Wang S, Luo J (2019) Chloroplasts- beyond energy capture and carbon fixation: Tuning of photosynthesis in response to chilling stress. Int J Mol Sci 20:5046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205046
Grigorova B, Vassileva V, Klimchuk D, Vaseva I, Demirevska K, Feller U (2012) Drought, high temperature, and their combination affect ultrastructure of chloroplasts and mitochondria in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) leaves. J Plant Interact 7:204–213. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2011.654134
Havaux M, Strasser RJ, Greppin H (1991) A theoretical and experimental analysis of the q P and q N coefficients of chlorophyll fluorescence quenching and their relation to photochemical and nonphotochemical events. Photosynth Res 27:41–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00029975
Ichimura K, Mizoguchi T, Yoshida R, Yuasa T, Shinozaki K (2000) Various abiotic stresses rapidly activate Arabidopsis MAP kinases ATMPK4 and ATMPK6. Plant J 24:655–665. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00913.x
Iermak I, Szabó M, Zavafer A (2020) Special issue in honour of Prof. Reto J. Strasser-Analysis of OJIP transients during photoinactivation of photosystem II indicates the presence of multiple photosensitizers in vivo and in vitro. Photosynthetica 58:497–506. https://doi.org/10.32615/ps.2019.166
Izumi M, Ishida H, Nakamura S, Hidema J (2017) Entire photodamaged chloroplasts are transported to the central vacuole by autophagy. Plant Cell 29:377–394. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.16.00637
Kalaji HM, Schansker G, Brestic M, Bussotti F, Calatayud A, Ferroni L, Goltsev V, Guidi L, Jajoo A, Li P, Losciale P, Mishra VK, Misra AN, Nebauer SG, Pancaldi S, Penella C, Pollastrini M, Suresh K, Tambussi E, Yanniccari M, Zivcak M, Cetner MD, Samborska IA, Stirbet A, Olsovska K, Kunderlikova K, Shelonzek H, Rusinowski S, Bąba W (2017) Frequently asked questions about chlorophyll fluorescence, the sequel. Photosynth Res 132:67–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-016-0318-y
Kim SH, Kim HS, Bahk S, An J, Yoo Y, Kim JY, Chung WS (2017) Phosphorylation of the transcriptional repressor MYB15 by mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 is required for freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res 45:6613–6627. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx417
Kolber Z, Zehr J, Falkowski PG (1988) Effects of growth irradiance and nitrogen limitation on photosynthetic energy conservation in photosystem II. Plant Physiol 88:923–929. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.88.3.92
Kutík J, Hola D, Kocova M, Rothova O, Haisel D, Wilhelmova N, Tichá I (2004) Ultrastructure and dimensions of chloroplasts in leaves of three maize (Zea mays L.) inbred lines and their F-1 hybrids grown under moderate chilling stress. Photosynthetica 4242:447–455. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHOT.0000046165.15048.a4
Lazár D, Nauš J (1998) Statistical properties of chlorophyll fluorescence induction parameters. Photosynthetica 35:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006886202444
Lazár D, Schansker G (2009) Models of chlorophyll a fluorescence transients. Photosynthesis in silico. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 85–123
Lee KP, Kim C, Landgraf F, Apel K (2007) EXECUTER1- and EXECUTER2-dependent transfer of stress-related signals from the plastid to the nucleus of Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:10270–10275. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0702061104
Li Z, Yue H, Xing D (2012) MAP Kinase 6-mediated activation of vacuolar processing enzyme modulates heat shock-induced programmed cell death in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 195:85–96. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04131.x
Li H, Ding Y, Shi Y, Zhang X, Zhang S, Gong Z, Yang S (2017) MPK3- and MPK6-mediated ICE1 phosphorylation negatively regulates ICE1 stability and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 43(630–642):e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2017.09.025
Li X, Brestic M, Tan D-X, Zivcak M, Zhu X, Liu S, Song F, Reiter RJ, Liu F (2018) Melatonin alleviates low PS I limited carbon assimilation under elevated CO2 and enhances the cold tolerance of offspring in chlorophyll b-deficient mutant wheat. J Pineal Res 64:e12453. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12453
Liu X, Zhou Y, Xiao J, Bao F (2018) Effects of chilling on the structure, function and development of chloroplasts. Front Plant Sci 9:1715. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01715
Liu Y, Dang P, Liu L, He C (2019) Cold acclimation by the CBF–COR pathway in a changing climate: Lessons from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep 38:511–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02376-3
MAPK Group (2002) Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plants: a new nomenclature. Trends Plant Sci 7:301–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1360-1385(02)02302-6
Matsubara S, Chow WS (2004) Populations of photoinactivated photosystem II reaction centers characterized by chlorophyll a fluorescence lifetime in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:18234–18239. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0403857102
Meng X, Xu J, He Y, Yang KY, Mordorski B, Liu Y, Zhang S (2013) Phosphorylation of an ERF transcription factor by Arabidopsis MPK3/MPK6 regulates plant defense gene induction and fungal resistance. Plant Cell 25:1126–1142. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.109074
Mohanta TK, Arora PK, Mohanta N, Parida P, Bae B (2015) Identification of new members of the MAPK gene family in plants shows diverse conserved domains and novel activation loop variants. BMC Genom 16:58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1244-7
Ohad I, Kyle DJ, Hirschberg J (1985) Light-dependent degradation of the QB-protein in isolated pea thylakoids. The EMBO J 4(7):1655–1659. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03833.x
Osmond CB, Grace SC (1995) Perspectives on photoinhibition and photorespiration in the field. Quintessential inefficiencies of the light and dark reactions of photosynthesis. J Exp Bot 46:1351–1362. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/46.special_issue.1351
Osmond B, Chow WS, Wyber R, Zavafer A, Keller B, Pogson BJ, Robinson SA (2017) Relative functional and optical absorption cross-sections of PSII and other photosynthetic parameters monitored in situ, at a distance with a time resolution of a few seconds, using a prototype light induced fluorescence transient (LIFT) device. Funct Plant Biol 44:985–1006. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP17024
Pribil M, Sandoval-Ibáñez O, Xu W, Sharma A, Labs M, Liu Q, Galgenmüller C, Schneider T, Wessels M, Matsubara S, Jansson S, Wanner G, Leister D (2018) Fine-tuning of photosynthesis requires CURVATURE THYLAKOID1-mediated thylakoid plasticity. Plant Physiol 176:2351–2364. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00863
Rungrat T, Awlia M, Brown T, Cheng R, Sirault X, Fajkus J, Trtilek M, Furbank B, Badger M, Tester M, Pogson BJ, Borevitz JO, Wilson P (2016) Using phenomic analysis of photosynthetic function for abiotic stress response gene discovery. Arabidopsis Book 14:e0185. https://doi.org/10.1199/tab.0185
Saucedo-García M, Guevara-García A, González-Solís A, Cruz-García F, Vázquez-Santana S, Markham JE, Lozano-Rosas MG, Dietrich CR, Ramos-Vega M, Cahoon EB, Gavilanes-Ruíz M (2011) MPK6, sphinganine and the LCB2a gene from serine palmitoyltransferase are required in the signaling pathway that mediates cell death induced by long chain bases in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 191:943–957. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03727.x
Saucedo-García M, Gavilanes-Ruíz M, Arce-Cervantes O (2015) Long-chain bases, phosphatidic acid, MAPKs, and reactive oxygen species as nodal signal transducers in stress responses in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 6:55. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00055
Schansker G, Tóth SZ, Holzwarth AR, Garab G (2014) Chlorophyll a fluorescence: beyond the limits of the QA model. Photosynth Res 120:43–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-013-9806-5
Scheller HV, Haldrup A (2005) Photoinhibition of photosystem I. Planta 221:5–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-005-1507-7
Schreiber U, Klughammer C (2013) Wavelength-dependent photodamage to Chlorella investigated with a new type of multi-color PAM chlorophyll fluorometer. Photosynth Res 114:165–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-013-9801-x
Schreiber U, Klughammer C (2021) Evidence for variable chlorophyll fluorescence of photosystem I in vivo. Photosynth Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-020-00814-y
Stirbet A (2011) On the relation between the Kautsky effect (chlorophyll a fluorescence induction) and Photosystem II: basics and applications of the OJIP fluorescence transient. J Photochem Photobiol B 104(1–2):236–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2010.12.010
Strand A, Hurry V, Henkes S, Huner N, Gustafsson P, Gardeström P, Stitt M (1999) Acclimation of Arabidopsis leaves developing at low temperatures. Increasing cytoplasmic volume accompanies increased activities of enzymes in the Calvin cycle and in the sucrose-biosynthesis pathway. Plant Physiol 119:1387–1398. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.119.4.1387
Strasser RJ, Tsimilli-Michael M, Srivastava A (2004) Analysis of the fluorescence transient. In: George C, Papageorgiou C, Govindjee (eds.): Chlorophyll fluorescence: A signature of photosynthesis. Advances in photosynthesis and respiration series. Springer, Dordrecht, 321–362
Strauss AJ, Krüger GHJ, Strasser RJ, Van Heerden PDR (2006) Ranking of dark chilling tolerance in soybean genotypes probed by the chlorophyll a fluorescence transient OJIP. Environ Exper Bot 56:147–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2005.01.011
Suleyman IA, Murata N (2004) Environmental stress inhibits the synthesis de novo of proteins involved in the photodamage–repair cycle of Photosystem II in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Biochim Biophys Acta 1657:23–32
Suzuki K, Nagasuga K, Okada M (2008) The chilling injury induced by high root temperature in the leaves of rice seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol 49:433–442. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcn020
Teige M, Scheikl E, Eulgem T, Dóczi R, Ichimura K, Shinozaki K, Dangl JL, Hirt H (2004) The MKK2 pathway mediates cold and salt stress signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell 15:141–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2004.06.023
Van Heerden PD, Tsimilli-Michael M, Krüger GH, Strasser RJ (2003) Dark chilling effects on soybean genotypes during vegetative development: parallel studies of CO2 assimilation, chlorophyll a fluorescence kinetics O-J-I-P and nitrogen fixation. Physiol Plant 117:476–491. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3054.2003.00056.x
Walters RG, Horton P (1993) Theoretical assessment of alternative mechanisms for non-photochemical quenching of PS II fluorescence in barley leaves. Photosynth Res 36:119–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00016277
Wunder T, Xu W, Liu Q, Wanner G, Leister D, Pribil M (2013) The major thylakoid protein kinases STN7 and STN8 revisited: effects of altered STN8 levels and regulatory specificities of the STN kinases. Front Plant Sci 4:417. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00417
Yang YJ, Zhang SB, Huang W (2018) Chloroplastic ATP synthases alleviates photoinhibition of Photosystem I in tobacco illuminated at chilling temperature. Front Plant Sci 14:1648. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01648
Zavafer A, Iermak I, Cheah MH, Chow WS (2019) Two quenchers formed during photodamage of photosystem II and the role of one quencher in preemptive photoprotection. Sci Rep 9:17275. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53030-7
Zavafer A, González-Solís A, Palacios-Bahena S, Saucedo-García M, Tapia de Aquino C, Vázquez-Santana S, King-Días B, Gavilanes-Ruiz M (2020) Organized disassembly of photosynthesis during programmed cell death mediated by long chain bases. Sci Rep 10:10360. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-65186-8
Zhao Y, Wang P, Si T, Hsu C-C, Wang L, Zayed O, Yu Z, Zhu Y, Dong J, Tao WA, Zhu J-K (2017) MAP kinase cascades regulate the cold response by modulating ICE1 protein stability. Dev Cell 43:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2017.09.024
Zushi K, Kajiwara S, Matsuzoe N (2012) Chlorophyll a fluorescence OJIP transient as a tool to characterize and evaluate response to heat and chilling stress in tomato leaf and fruit. Sci Hort 148:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2012.09.022
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Laura Carmona-Salazar and Dr. Rodolfo Paredes for the transmission electron microscopy work.
Funding
This work was financed by Dirección General de Asuntos del Personal Académico (DGAPA), UNAM (grants: PAPIIT IN222815 and IN220618), Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT) (CB-2015 and 255265 to M.S.-G; CB-2014-01 and 238368 to M.G.-R) and Facultad de Química, UNAM (5000 9115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CDGC, IGPP, DCR, FRC and EAP performed the experiments; MSG, AZ and MGR analysed the data; DCR, MSG, AZ and MGR conceived the project; MSG, AZ and MGR wrote the article with contributions of all the authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Alonso Zavafer is a guest Editor in this special issue in honour to Wah Soon Chow. Despite this relationship, he did not at any stage have editor-level access to this manuscript whilst in peer review, as is the standard practice when handling manuscripts submitted by an editor to this journal. The authors have no further conflicts of interest to declare. Alonso Zavafer declares that Zavafer is a pseudonym and his legal name is Alonso Zavaleta Fernandez de Cordova.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saucedo-García, M., González-Córdova, C.D., Ponce-Pineda, I.G. et al. Effects of MPK3 and MPK6 kinases on the chloroplast architecture and function induced by cold acclimation in Arabidopsis. Photosynth Res 149, 201–212 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-021-00852-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-021-00852-0