Abstract
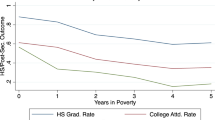
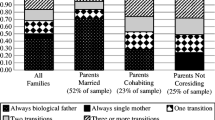
This research uses data from waves I and IV of the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health (Add Health, N = 9,631) to consider whether and how family instability in early or later childhood affects college enrollment and completion of a Bachelor’s degree by age 24. Explanatory factors include maternal selection into unstable unions, household resources available in adolescence, and adolescents’ academic achievement, behavior, and attitudes in high school. The association of later family instability with college enrollment and completion is largely explained by household resources in adolescence. The association of early family instability with college enrollment is partially explained by each set of factors, and its association with college completion, given enrollment, is explained by pre-existing maternal characteristics. The results demonstrate that early family instability has enduring consequences for eventual status attainment and that the mechanisms that connect family instability to educational outcomes vary by the timing of family structure change.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman, B. P., Kogos, J., Youngstrom, E., Schoff, K., & Izard, C. (1999). Family instability and the problem behaviors of children from economically disadvantaged families. Developmental Psychology, 35(1), 258–268.
Alexander, K. L., & Entwisle, D. R. (1988). Factors affecting achievement test scores and marks received by black and white first graders. The Elementary School Journal, 88, 449–471.
Amato, P. R. (2010). Research on divorce: Continuing trends and new developments. Journal of Marriage and The Family, 72(3), 650–666.
Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979). The ecology of human development: Experiments by nature and design. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Brooks, D. (2011). The wrong inequality. New York: The New York Times.
Bureau of Labor Statistics. (2013). Education pays. Retrieved May 3, 2013, from http://www.bls.gov/emp/ep_chart_001.htm.
Cavanagh, S. E. (2008). Family structure history and adolescent adjustment. Journal of Family Issues, 29(7), 944–980.
Cavanagh, S. E., Crissey, S. R., & Raley, R. K. (2008). Family structure history and adolescent romance. Journal of Marriage and Family, 70(3), 698–714.
Cavanagh, S. E., & Fomby, P. (2012). School context, family instability, and the academic careers of adolescents. Sociology of Education, 85(1), 81–97.
Cavanagh, S. E., & Huston, A. C. (2006). Family instability and children’s early problem behavior. Social Forces, 85(1), 551–581.
Cavanagh, S. E., & Huston, A. C. (2008). The timing of family instability and children’s social development. Journal of Marriage and Family, 70(5), 1258–1270.
Cavanagh, S. E., Schiller, K. S., & Riegle-Crumb, C. (2006). Marital transitions, parenting, and schooling: Exploring the link between family-structure history and adolescents’ academic status. Sociology of Education, 79(4), 329–354.
Cherlin, A. (2009). The marriage-go-round: The state of marriage and the family in America today. New York: Knopf.
Conley, D. (2009). Being black, living in the red (2nd ed.). Berkeley: University of California Press.
Cooper, C. E., McLanahan, S. S., Meadows, S. O., & Brooks-Gunn, J. (2009). Family structure transitions and maternal parenting stress. Journal of Marriage and Family, 71(3), 558–574.
Cooper, C. E., Osborne, C. A., Beck, A. N., & McLanahan, S. S. (2011). Partnership instability, school readiness, and gender disparities. Sociology of Education, 84(3), 246–259.
Crosnoe, R. (2009). Low-income students and the socioeconomic composition of public high schools. American Sociological Review, 74, 709–730.
Crosnoe, R., & Needham, B. (2004). Holism, contextual variability, and the study of friendships in adolescent development. Child Development, 75(1), 264–279.
Donahue, K. L., D’Onofrio, B. M., Bates, J. E., Lansford, J. E., Dodge, K. A., & Pettit, G. S. (2010). Early exposure to parents’ relationship instability: Implications for sexual behavior and depression in adolescence. Journal of Adolescent Health, 47(6), 547–554.
Duncan, G. J., & Magnuson, K. A. (2005). Can family socioeconomic resources account for racial and ethnic test score gaps? The Future of Children, 15(1), 35–54.
Evans, G. W., Schamberg, M. A., & McEwen, B. S. (2009). Childhood poverty, chronic stress, and adult working memory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(16), 6545–6549.
Fomby, P. (2011). Family instability and school readiness in the United Kingdom. Family Science, 2(3), 171–185.
Fomby, P., & Bosick, S. J. (in press). Family instability and the transition to adulthood. Journal of Marriage and Family.
Fomby, P., Cavanagh, S. E., & Goode, J. (2011). Family instability and school readiness in the United States and the United Kingdom. Paper presented at the National Council on Family Relations.
Fomby, P., & Cherlin, A. J. (2007). Family instability and child well-being. American Sociological Review, 72, 181–204.
Fomby, P., Mollborn, S., & Sennott, C. A. (2010). Race/ethnic differences in effects of family instability on adolescents’ risk behavior. Journal of Marriage and Family, 72(2), 234–253.
Fomby, P., & Osborne, C. (2010). The influence of union instability and union quality on children’s aggressive behavior. Social Science Research, 39(6), 912–924.
Fomby, P., & Sennott, C. (2013). Family structure instability and mobility: The consequences for adolescents’ problem behavior. Social Science Research, 42, 181–206.
Forman, E. M., & Davies, P. T. (2003). Family instability and young adolescent maladjustment: The mediating effects of parenting quality and adolescent appraisals of family security. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 32(1), 94–105.
Furstenberg, F. F. (1990). Divorce and the American family. Annual Review of Sociology, 16, 379–403.
Harris, K. M. (2009). The National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health (Add Health), waves I & II, 1994–1996; wave III, 2001–2002; wave IV, 2007–2009 [machine-readable data file and documentation]. Chapel Hill: Carolina Population Center, University of North Carolina Chapel Hill.
Harris, K. M., Halpern, C. T., Whitsel, E., Hussey, J., Tabor, J., Entzel, P., et al. (2009). The National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health: Research design (WWW document). Retrieved from http://www.cpc.unc.edu/projects/addhealth/design. Accessed 13 March 2013.
Heard, H. E. (2007a). The family structure trajectory and adolescent school performance. Journal of Family Issues, 28(3), 319–354.
Heard, H. E. (2007b). Fathers, mothers, and family structure: Family trajectories, parent gender, and adolescent schooling. Journal of Marriage and Family, 69(2), 435–450.
Heckman, J. J. (2008). Schools, skills, and synapses. Economic Inquiry, 46(3), 289–324.
Henretta, J. C., Wolf, D. A., Van Voorhis, M. F., & Soldo, B. J. (2012). Family structure and the reproduction of inequality: Parents’ contribution to children’s college costs. Social Science Research, 41(4), 876–887.
Hill, R. (1949). Families under stress: Adjustment to the crisis of war separation and reunion. New York: Harper and Brothers.
Jednorog, K., Altarelli, I., Monzalvo, K., Fluss, J., Dubois, J., Billard, C., et al. (2012). The influence of socioeconomic status on children’s brain structure. Plos One, 7(8), e42486.
Julian, T., & Kominski, R. (2011). Education and synthetic work-life earnings estimates. Washington, DC: U.S. Census Bureau.
Khatiwada, I., McLaughlin, J., Sum, A., & Palma, S. (2007). The fiscal consequences of adult educational attainment. Boston: Center for Labor Market Studies, Northeastern University.
Lareau, A. (2011). Unequal childhoods: Race, class, and family life. Second edition. A decade later (2nd ed.). Berkeley: University of California Press.
Locke, E. W., & Burgess, H. J. (1945). The family: From institution to companionship. New York: American Book Co.
Magnuson, K., & Berger, L. M. (2009). Family structure states and transitions: Associations with children’s well-being during middle childhood. Journal of Marriage and Family, 71(3), 575–591.
Mare, R. D. (1980). Social background and school continuation decisions. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 75, 295–305.
Martin, M. A. (2012). Family structure and the intergenerational transmission of educational advantage. Social Science Research, 41(1), 33–47.
McLanahan, S., & Percheski, C. (2008). Family structure and the reproduction of inequalities. Annual Review of Sociology, 34, 257–276.
Meadows, S. O., McLanahan, S., & Brooks-Gunn, J. (2008a). Stability and change in family structure and mental health trajectories. American Sociological Review, 73(2), 314–334.
Meadows, S. O., McLanahan, S. S., & Brooks-Gunn, J. (2008b). Stability and change in family structure and maternal health trajectories. American Sociological Review, 73(2), 314–334.
Milan, S., Pinderhughes, E. E., & Conduct Problems Prevention Research Group. (2006). Family instability and child maladjustment trajectories during elementary school. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 34(1), 43–56.
Molfese, V. J., Modglin, A., & Molfese, D. L. (2003). The role of environment in the development of reading skills: A longitudinal study of preschool and school-age measures. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 36(1), 59–67.
National Center for Education Statistics. (2011a). The condition of education 2011 (NCES 2011–033), indicator 21. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education.
National Center for Education Statistics. (2011b). The condition of education 2011 (NCES 2011–033), indicator 23. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education.
Osborne, C., Berger, L., & Magnuson, K. (2012). Family structure transitions and changes in maternal resources and well-being. Demography, 49(1), 23–47.
Osborne, C., & McLanahan, S. (2007). Partnership instability and child well-being. Journal of Marriage and Family, 69(4), 1065–1083.
Osgood, D. W., Ruth, G., Eccles, J. S., Jacobs, J. E., & Barber, B. L. (2005). Six paths to adulthood: Fast starters, parents without careers, educated partners, educated singles, working singles, and slow starters. In R. A. Settersten Jr, F. F. Furstenberg Jr, & R. G. Rumbaut (Eds.), On the frontier of adulthood: Theory, research and policy (pp. 320–355). Chicago: The University of Chicago Press.
Pong, S. L. (1998). The school compositional effect of single parenthood on 10th-grade achievement. Sociology of Education, 71(1), 23–42.
Raley, R. K., Kim, Y., & Daniels, K. (2012). Young adults’ fertility expectations and events: Associations with college enrollment and persistence. Journal of Marriage and Family, 74(4), 866–879.
Ryan, R., & Claessens, A. E. (2012). Associations between family structure changes and children’s behavior problems: The moderating effects of timing and marital birth. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the population association of America.
Steelman, L. C., & Powell, B. (1991). Sponsoring the next generation: Parental willingness to pay for higher education. American Journal of Sociology, 96(6), 1505–1529.
Sun, Y. M., & Li, Y. Z. (2009). Postdivorce family stability and changes in adolescents’ academic performance a growth-curve model. Journal of Family Issues, 30(11), 1527–1555.
Sun, Y. M., & Li, Y. Z. (2011). Effects of family structure type and stability on children’s academic performance trajectories. Journal of Marriage and Family, 73(3), 541–556.
Tomalski, P., & Johnson, M. H. (2010). The effects of early adversity on the adult and developing brain. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 23(3), 233–238.
Turley, R. N. L., & Desmond, M. (2011). Contributions to college costs by married, divorced, and remarried parents. Journal of Family Issues, 32(6), 767–790.
Watson, M. W., Fischer, K. W., Andreas, J. B., & Smith, K. W. (2004). Pathways to aggression in children and adolescents. Harvard Educational Review, 74(4), 404–430.
Wojtkiewicz, R. A., & Holtzman, M. (2011). Family structure and college graduation: Is the stepparent effect more negative than the single parent effect? Sociological Spectrum, 31(4), 498–521.
Wu, L. L. (1996). Effects of family instability, income, and income instability on the risk of a premarital birth. American Sociological Review, 61(3), 386–406.
Wu, L. L., & Thomson, E. (2001). Race differences in family experience and early sexual initiation: Dynamic models of family structure and family change. Journal of Marriage and Family, 63(3), 682–696.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fomby, P. Family Instability and College Enrollment and Completion. Popul Res Policy Rev 32, 469–494 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11113-013-9284-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11113-013-9284-7