Abstract
Aims
We investigated the effect of different growth substrates, frequently used during production of Arabidopsis thaliana seeds, on the endophytic assemblage of this plant.
Methods
Arabidopsis thaliana was grown on sand and on a mixture of sand and potting soil. Seeds harvested on both substrates were sown again on the same substrate until the radicle emerged and until there were 3 week-old leaves. Cultivable soil bacteria and endophytic bacteria from seeds, radicles and leaves were isolated and identified using 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Total bacterial assemblages were investigated using a direct DNA extraction from soil, seeds, radicles and leaves, and pyrosequencing of the V5-V7 hypervariable region of the 16S rRNA gene.
Results
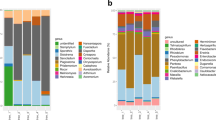
Despite differences in the soil bacterial assemblages, seed and radicle endophytic assemblages were similar. The leaf endophytic assemblage was mainly derived from the environment and not from the seed. The endophytic genera most abundant in the cultivable assemblage coincide with the genera frequently detected in the total assemblage.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that plants can select their seed endophytes. During plant growth, bacteria seem to be recruited from the environment to complement the endophytic population from which the seed endophytes of the next generation can again be selected.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amann RI, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (1995) Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol Rev 59:143–169
Belimov AA, Hontzeas N, Safronova VI, Demchinskaya SV, Piluzza G, Bullitta S, Glick BR (2005) Cadmium-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria associated with the roots of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern.). Soil Biol Biochem 37:241–250
Benson DR, Dawson JO (2007) Recent advances in the biogeography and genecology of symbiotic Frankia and its host plants. Physiol Plant 130:318–330
Berg G, Smalla K (2009) Plant species and soil type cooperatively shape the structure and function of microbial communities in the rhizosphere. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 68:1–13
Biswas JC, Ladha JK, Dazzo FB, Yanni YG, Rolfe BG (2000) Rhizobial inoculation influences seedling vigor and yield of rice. Agron J 92:880–886
Bodenhausen N, Horton MW, Bergelson J (2013) Bacterial communities associated with the leaves and the roots of Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS One 8(2):e56329
Boehm MJ, Wu TY, Stone AG, Kraakman B, Iannotti DA, Wilson GE, Madden LV, HAJ H (1997) Cross-polarized magic-angle spinning C-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic characterization of soil organic matter relative to culturable bacterial species composition and sustained biological control of Pythium root rot. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:162–168
Bokulich NA, Thorngate JH, Richardson PM, Mills DA (2014) Microbial biogeography of wine grapes is conditioned by cultivar, vintage, and climate. PNAS 111:E139–E148
Buckley D, Schmidt T (2002) Exploring the diversity of soil - a microbial rainforest. In: Staley J, Reysenbach A (eds) Biodiversity of microbial life. Wiley, New York, pp. 183–208
Bulgarelli D, Rott M, Schlaeppi K, Ver Loren van Themaat E, Ahmadinejad N, Assenza F, Rauf P, Huettel B, Reinhardt R, Schmelzer E, Peplies J, Gloeckner F, Amann R, Eickhorst T, Schulze-Lefert P (2012) Revealing structure and assembly cues for Arabidopsis root-inhabiting bacterial microbiota. Nature 488:91–95
Bulgarelli D, Schlaeppi K, Spaepen S, Ver Loren van Themaat E, Schulze-Lefert P (2013) Structure and functions of the bacterial microbiota of plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64:807–838
Burd GI, Dixon DG, Glick BR (2000) Plant growth promoting bacteria that decrease heavy metal toxicity in plants. Can J Microbiol 46:237e245
Cankar K, Kraigher H, Ravnikar M, Rupnik M (2005) Bacterial endophytes from seeds of Norway spruce (Picea abies L. Karts). FEMS Microbiol Lett 244:341–345
Chelius MK, Triplett EW (2001) The diversity of archaea and bacteria in association with the roots of Zea mays L. Microb Ecol 41:252–263
Chi F, Shen S, Cheng H, Jing Y, Yanni YG, Dazzo FB (2005) Ascending migration of endophytic rhizobia, from roots to leaves, inside rice plants and assessment of benefits to rice growth physiology. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(11):7271–7278
Compant S, Reiter B, Sessitsch A, Nowak J, Clement C, Ait Barka E (2005) Endophytic colonization of Vitis vinifera L. by plant growth-promoting bacterium burkholderia sp. strain PsJN. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1685–1693
Croes S, Weyens N, Janssen J, Vercampt H, Carleer R, Vangronsveld J (2013) Bacterial communities associated with Brassica napus L. grown on trace element-contaminated and non-contaminated fields: a genotypic and phenotypic comparison. Microb Biotechnol 6(4):371–384
Daniel R (2005) The metagenomics of soil. Nat Rev Microbiol 3(6):470–478
Ding G, Pronk GJ, Babin D, Heuer H, Heister K, Kögel-Knabner I, Smalla K (2013) Mineral composition and charcoal determine the bacterial community structure in artificial soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 86:15–25
Fierer N, Jackson RB (2006) The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. PNAS 103:626–631
García-Fraile P, Carro L, Robledo M, Ramírez-Bahena M, Flores-Félix J, Fernández MT, Mateos PF, Rivas R, Igual JM, Martínez-Molina E, Peix Á, Velázquez E (2012) Rhizobium promotes non-legumes growth and quality in several production steps: towards a biofertilization of edible raw vegetables healthy for humans. PLoS One 7(5):e38122
Gilbert JA, van der Lelie D, Zarraonaindia I (2014) Microbial terroir for wine grapes. PNAS 111(1):5–6
Gómez-Lama Cabanás C, Schilirò E, Valverde-Corredor A, Marcado-Blanco J (2014) The biocontrol endophytic bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens PICF7 induces systemic defense responses in aerial tissues upon colonization of olive roots. Front Microbiol 5(5):427
Gottel NR, Castro HF, Kerley M, Yang Z, Pelletier DA, Podar M, Karpinets T, Uberbacher E, Tuskan GA, Vilgalys R, Doktycz MJ, Schadt CW (2011) Distinct microbial communities within the endopshere and rhizosphere of Populus deltoides roots across contrasting soil types. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(17):5934–5944
Green SJ, Inbar E, Michel FC, Hadar Y, Minz D (2006) Succession of bacterial communities during early plant development: transition from seed to root and effect of compost amendment. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(6):3975–3983
Green SJ, Michel FC, Hadar Y, Minz D (2007) Contrasting patterns of seed and root colonization by bacteria from the genus chryseobacterium and from the family oxalobacteraceae. ISME J 1:291–299
Haichar F, Marol C, Berge O, Rangel-Castro JI, Prosser JI, Balesdent J, Heulin T, Acouak W (2008) Plant host habitat and root exudates shape soil bacterial community structure. ISME J 2:1221–1230
Hallmann J, Quadt-Hallmann A, Mahaffee WF, Kloepper JW (1997) Bacterial endophytes in agricultural crops. Can J Microbiol 43:895–914
Hardoim PR, Hardoim CCP, van Overbeek LS, van Elsas JD (2012) Dynamics of seed-borne rice endophytes on early plant growth stages. PLoS One 7(2):e30438
Hodgson S, de Cates C, Hodgson J, Morley NJ, Sutton BC, Gange AC (2014) Vertical transmission of fungal endophytes is widespread in forbs. Ecol Evol 4(8):1199–1208
Inbar E, Green SJ, Hadar Y, Minz D (2005) Competing factors of compost concentration and proximity to root affect the distribution of streptomycetes. Microb Ecol 50:73–81
Inceoğlu O, Al-Soud WA, Falcão Salles J, Semenov AV, van Elsas JD (2011) Comparative analysis of bacterial communities in a potato field as determined by pyrosequencing. PLoS One 6(8):e23321
Johnston-Monje D, Raizada MN (2011) Conservation and diversity of seed associated endophytes in Zea across boundaries of evolution, ethnography and ecology. PLoS One 6:e20396
Johnston-Monje D, Mousa WK, Lazarovits G, Raizada MN (2014) Impact of swapping soils on the endophytic bacterial communities of pre-domesticated, ancient and modern maize. BMC Plant Biol 14:233
Kaga H, Mano H, Tanaka F, Watanabe A, Kaneko S, Morisaki H (2009) Rice seeds as sources of endophytic bacteria. Microbes Environ 24:154–162
Kearse M, Moir R, Wilson A, Stones-Havas S, Cheung M, Sturrock S, Buxton S, Cooper A, Markowitz S, Duran C, Thierer T, Ashton B, Mentjies P, Drummond A (2012) Geneious basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinform 28(12):1647–1649
Kloepper JW, Schroth MN, Miller TD (1980) Effects of rhizosphere colonization by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on potato plant development and yield. Phytopathol 70:1078–1082
Kumar KV, Patra DD (2013) Effect of metal tolerant plant growth promoting bacteria on growth and metal accumulation in Zea mays plants grown in fly ash amended soil. Int J Phytoremediation 15(8):743–755
Lundberg D, Lebeis S, Herrera Paredes S, Yourstone S, Gehring J, Malfatti S, Tremblay J, Engelbrektson A, Kunin V, Glavina del Rio T, Edgar R, Eickhorst T, Ley R, Hugenholtz P, Green Tringe S, Dangl J (2012) Defining the core Arabidopsis thaliana root microbiome. Nature 488:86–90
Mastretta C, Taghavi S, van der Lelie D, Mengoni A, Galardi F, Gonelli C, Barac T, Boulet J, Weyens N, Vangronsveld J (2009) Endophytic bacteria from seeds of Nicotiana tabacum can reduce Cd phytotoxicity. Int J Phytoremediation 11:252–267
Mercado-Blanco J, Bakker PAHM (2007) Interactions between plants and beneficial pseudomonas spp.: exploiting bacterial traits for crop protection. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 92:367–389
Mergeay M, Nies D, Schlegel HG, Gerits J, Charles P, Van Gijsegem F (1985) Alcaligenes eutrophus CH34 is a facultative chemolithotroph with plasmid-bound resistance to heavy metals. J Bacteriol 162:328–334
Normander B, Prosser AI (2000) Bacterial origin and community composition in the barley phytosphere as a function of habitat and presowing conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(10):4372–4377
Paterson E, Gebbing T, Abel C, Sim A, Telfer G (2007) Rhizodeposition shapes rhizosphere microbial community structure in organic soil. New Phytol 173(3):600–610
R Core Team (2014) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL: http://www.R-project.org
Reisberg EE, Hildebrandt U, Riederer M, Hentschel U (2013) Distinct phyllosphere bacterial communities on Arabidopsis wax mutant leaves. PLoS One 8(11):e78613
Reiter B, Sessitsch A (2006) Bacterial endophytes of the wildflower crocus albiflorus analyzed by characterization of isolates and by a cultivation-independent approach. Can J Microbiol 52(2):140–149
Remans T, Nacry P, Pervent M, Girin T, Tillard P, Lepetit M, Gojon A (2006) A central role for the nitrate transporter NRT2.1 in the integrated morphological and physiological responses of the root system to nitrogen limitation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 140:909–921
Ringelberg D, Foley K, Reynolds CM (2012) Bacterial endophyte communities of two wheatgrass varieties following propagation in different growing media. Can J Microbiol 58:67–80
Rott M (2012) Structure and assembly cues of Arabidopsis root-inhabiting bacterial communities and comparative genomics of selected rhizobium members. Dissertation, University of Cologne, pp. 55–105
Schauer M, Hahn MW (2005) Diversity and phylogenetic affiliations of morphologically conspicuous large filamentous bacteria occurring in the pelagic zones of a broad spectrum of freshwater habitats. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1931–1940
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(23):7537–7541
Segata B, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D, Miropolsky L, Garrett WS, Huttenhower C (2011) Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol 12(6):R60
Siciliano SD, Fortin N, Mihoc A, Wisse G, Labelle S, Beaumier D, Ouelette D, Roy R, Whyte L, Banks K, Schwab P, Lee K, Greer C (2001) Selection of specific endophytic bacterial genotypes by plants in response to soil contamination. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2469–2475
Smeets K, Ruytinx J, Van Belleghem F, Semane B, Lin D, Vangronsveld J, Cuypers A (2008) Critical evaluation and statistical validation of a hydroponic culture system for Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:212–218
Staden R, Beal KF, Bonfield JK (1999) The staden package, 1998. Methods Mol Biol 132:115–130
Tiquia SM, Lloyd J, Herms DA, Hoitink HAJ, Michel FC (2001) Effects of mulching and fertilization on soil nutrients, microbial activity and rhizosphere bacterial community structure determined by analysis of TRFLPs of PCR-amplified 16S rRNA genes. Appl Soil Ecol 21:31–48
Truyens S, Weyens N, Cuypers A, Vangronsveld J (2013) Changes in the population of seed bacteria of transgenerationally Cd-exposed Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Biol 15:971–981
Truyens S, Jambon I, Croes S, Janssen J, Weyens N, Mench M, Carleer R, Vangrondveld J (2014) The effect of long-term Cd and Ni exposure on seed endophytes of agrostis capillaris and their potential application in phytoremediation of metal contaminated soils. Int J Phytoremediation 16:643–659
Wardle DA (1992) A comparative assessment of factors which influence microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen levels in soil. Biol Rev 67:321–358
Weyens N, Taghavi S, Barac T, van der Lelie D, Boulet J, Artois T, Carleer R, Vangronsveld J (2009) Bacteria associated with oak and ash on a TCE-contaminated site: characterization of isolates with potential to avoid evapotranspiration of TCE. Environ Sci Pollut Res 16:830–843
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Fund for Scientific Research Flanders (FWO-Vlaanderen), with Ph.D. grants for Sascha Truyens and Sofie Thijs and a post-doc grant for Nele Weyens. This work has been financially supported by the UHasselt Methusalem project 08M03VGRJ and by the European Commission under the Seventh Framework Programme for Research (FP7-KBBE-266124, GREENLAND).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Stéphane Compant.
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. A1
Rarefaction curves for soil (blue), seed (red), radicle (yellow), and leaf (green) samples. Dotted lines are samples from sand; full lines are samples from potting soil. The vertical line indicates the number of sequences (2000) subsampled from each sample for further analysis (GIF 16 kb)
Table A1
(DOCX 25 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Truyens, S., Beckers, B., Thijs, S. et al. The effects of the growth substrate on cultivable and total endophytic assemblages of Arabidopsis thaliana . Plant Soil 405, 325–336 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2761-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2761-5