Abstract
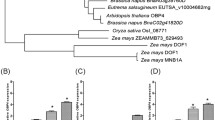
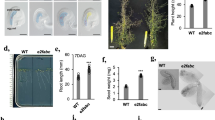
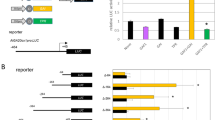
An emerging view of plant cell cycle regulators, including the E2F transcription factors, implicates them in the integration of cell proliferation and development. Arabidopsis encodes six E2F proteins that can act as activators or repressors of E2F-responsive genes. E2FA, E2FB and E2FC interact with the retinoblastoma-like RBR protein and bind to DNA together with their DP partners. In contrast, E2FD, E2FE and E2FF (also known as DEL2, DEL1 and DEL3) are atypical E2Fs that possess duplicated DNA binding regions, lack trans-activating and RBR-binding domains and are believed to act as transcriptional inhibitors/repressors. E2FE/DEL1 has been shown to inhibit the endocycle and E2FF/DEL3 appears to control cell expansion but the role of E2FD/DEL2 has not been reported so far. In this study, we investigated the expression of E2FD/DEL2 and analysed the accumulation of its product. These studies revealed that E2FD/DEL2 accumulation is subject to negative post-translational regulation mediated by the plant hormone auxin. Moreover, the analysis of mutant and transgenic plants characterized by altered expression of E2FD/DEL2 has revealed that this atypical E2F can affect plant growth by promoting cell proliferation and repressing cell elongation. Overexpression of E2FD/DEL2 increased the expression of E2FA, E2FB and E2FE/DEL1 whereas its inactivation led to the up-regulation of genes encoding repressors of cell division. These results suggest that E2FD/DEL2 is part of a regulatory network that controls the balance between cell proliferation and development in Arabidopsis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albani D, Mariconti L, Ricagno S, Pitto L, Moroni C, Helin K, Cella R (2000) DcE2F, a functional plant E2F-like transcriptional activator from Daucus carota. J Biol Chem 275:19258–19267
Andersen SU, Buechel S, Zhao Z, Ljung K, Novák O, Busch W, Schuster C, Lohmann JU (2008) Requirement of B2-type cyclin-dependent kinases for meristem integrity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 20:88–100
Axelos M, Curie C, Bardet C, Lescure B (1992) A protocol for transient expression in Arabidopsis thaliana protoplasts isolated from cell suspension cultures. Plant Physiol Biochem 30:123–128
Beemster GT, Fiorani F, Inzé D (2003) Cell cycle: the key to plant growth control? Trends Plant Sci 8:154–158
Birnbaum K, Shasha DE, Wang JY, Jung JW, Lambert GM, Galbraith DW, Benfey PN (2003) A gene expression map of the Arabidopsis root. Science 302:1956–1960
Bisova K, Krylov DM, Umen JG (2005) Genome-wide annotation and expression profiling of cell cycle regulatory genes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol 137:475–491
Boudolf V, Barrôco R, de Almeida Engler J, Verkest A, Beeckman T, Naudts M, Inzé D, De Veylder L (2004) B1-type cyclin-dependent kinases are essential for the formation of stomatal complexes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 16:945–955
Brady SM, Orlando DA, Lee J-Y, Wang JY, Koch J, Dinneny JR, Mace D, Ohler U, Benfey PN (2007) A high-resolution root spatiotemporal map reveals dominant expression patterns. Science 318:801–806
Christensen J, Cloos P, Toftegaard U, Klinkenberg D, Bracken AP, Trinh E, Heeran M, Di Stefano L, Helin K (2005) Characterization of E2F8, a novel E2F-like cell-cycle regulated repressor of E2F-activated transcription. Nucleic Acids Res 33:5458–5470
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
de Bruin A, Maiti B, Jakoi L, Timmers C, Buerki R, Leone G (2003) Identification and characterization of E2F7, a novel mammalian E2F family member capable of blocking cellular proliferation. J Biol Chem 278:42041–42049
De Veylder L, Beeckman T, Beemster GT, de Almeida Engler J, Ormenese S, Maes S, Naudts M, Van Der Schueren E, Jacqmard A, Engler G, Inzé D (2002) Control of proliferation, endoreduplication and differentiation by the Arabidopsis E2Fa-DPa transcription factor. EMBO J 21:1360–1368
del Pozo JC, Boniotti MB, Gutierrez C (2002) Arabidopsis E2Fc functions in cell division and is degraded by the ubiquitin-SCF(AtSKP2) pathway in response to light. Plant Cell 14:3057–3071
del Pozo JC, Diaz-Trivino S, Cisneros N, Gutierrez C (2006) The balance between cell division and endoreplication depends on E2FC-DPB, transcription factors regulated by the ubiquitin-SCF-SKP2A pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18:2224–2235
Dewitte W, Murray JA (2003) The plant cell cycle. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:235–264
Di Stefano L, Jensen MR, Helin K (2003) E2F7, a novel E2F featuring DP-independent repression of a subset of E2F-regulated genes. EMBO J 22:6289–6298
Dimova DK, Dyson NJ (2005) The E2F transcription network: old acquaintances with new faces. Oncogene 24:2810–2836
Gutierrez C (2005) Coupling cell proliferation and development in plants. Nat Cell Biol 7:535–541
Hajdukiewicz P, Svab Z, Maliga P (1994) The small, versatile pPZP family of Agrobacterium binary vectors for plant transformation. Plant Mol Biol 25:989–994
Inzé D, De Veylder L (2006) Cell cycle regulation in plant development. Annu Rev Genet 40:77–105
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Kinross KM, Clark AJ, Iazzolino RM, Humbert PO (2006) E2F4 regulates fetal erythropoiesis through the promotion of cellular proliferation. Blood 108:886–895
Kosugi S, Ohashi Y (2002) E2Ls, E2F-like repressors of Arabidopsis that bind to E2F sites in a monomeric form. J Biol Chem 277:16553–16558
Lammens T, Boudolf V, Kheibarshekan L, Zalmas LP, Gaamouche T, Maes S, Vanstraelen M, Kondorosi E, La Thangue NB, Govaerts W, Inzé D, De Veylder L (2008) Atypical E2F activity restrains APC/CCCS52A2 function obligatory for endocycle onset. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:14721–14726
Magyar Z, De Veylder L, Atanassova A, Bako L, Inzé D, Bogre L (2005) The role of the Arabidopsis E2FB transcription factor in regulating auxin-dependent cell division. Plant Cell 17:2527–2541
Maiti B, Li J, de Bruin A, Gordon F, Timmers C, Opavsky R, Patil K, Tuttle J, Cleghorn W, Leone G (2005) Cloning and characterization of mouse E2F8, a novel mammalian E2F family member capable of blocking cellular proliferation. J Biol Chem 280:18211–18220
Mariconti L, Pellegrini B, Cantoni R, Stevens R, Bergounioux C, Cella R, Albani D (2002) The E2F family of transcription factors from Arabidopsis thaliana. Novel and conserved components of the retinoblastoma/E2F pathway in plants. J Biol Chem 277:9911–9919
McClellan KA, Slack RS (2007) Specific in vivo roles for E2Fs in differentiation and development. Cell Cycle 6:2917–2927
Menges M, Murray JA (2002) Synchronous Arabidopsis suspension cultures for analysis of cell-cycle gene activity. Plant J 30:203–212
Menges M, de Jager SM, Gruissem W, Murray JA (2005) Global analysis of the core cell cycle regulators of Arabidopsis identifies novel genes, reveals multiple and highly specific profiles of expression and provides a coherent model for plant cell cycle control. Plant J 41:546–566
Naouar N, Vandepoele K, Lammens T, Casneuf T, Zeller G, van Hummelen P, Weigel D, Rätsch G, Inzé D, Kuiper M, De Veylder L, Vuylsteke M (2009) Quantitative RNA expression analysis with Affymetrix Tiling 1.0R arrays identifies new E2F target genes. Plant J 57:184–194
Oono Y, Ooura C, Rahman A, Aspuria ET, Hayashi K, Tanaka A, Uchimiya H (2003) p-Chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid impairs auxin response in Arabidopsis root. Plant Physiol 133:1135–1147
Ramirez-Parra E, Gutierrez C (2007) E2F regulates FASCIATA1, a chromatin assembly gene whose loss switches on the endocycle and activates gene expression by changing the epigenetic status. Plant Physiol 144:105–120
Ramirez-Parra E, Lopez-Matas MA, Frundt C, Gutierrez C (2004) Role of an atypical E2F transcription factor in the control of Arabidopsis cell growth and differentiation. Plant Cell 16:2350–2363
Robbens S, Khadaroo B, Camasses A, Derelle E, Ferraz C, Inze D, Van de Peer Y, Moreau H (2005) Genome-wide analysis of core cell cycle genes in the unicellular green alga Ostreococcus tauri. Mol Biol Evol 22:589–597
Rossignol P, Stevens R, Perennes C, Jasinski S, Cella R, Tremousaygue D, Bergounioux C (2002) AtE2F-a and AtDP-a, members of the E2F family of transcription factors, induce Arabidopsis leaf cells to re-enter S phase. Mol Genet Genomics 266:995–1003
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Schwechheimer C, Schwager K (2004) Regulated proteolysis and plant development. Plant Cell Rep 23:353–364
Sozzani R, Maggio C, Varotto S, Canova S, Bergounioux C, Albani D, Cella R (2006) Interplay between Arabidopsis activating factors E2Fb and E2Fa in cell cycle progression and development. Plant Physiol 140:1355–1366
Vandepoele K, Raes J, De Veylder L, Rouze P, Rombauts S, Inzé D (2002) Genome-wide analysis of core cell cycle genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 14:903–916
Vandepoele K, Vlieghe K, Florquin K, Hennig L, Beemster GT, Gruissem W, Van de Peer Y, Inze D, De Veylder L (2005) Genome-wide identification of potential plant E2F target genes. Plant Physiol 139:316–328
Vlieghe K, Vuylsteke M, Florquin K, Rombauts S, Maes S, Ormenese S, Van Hummelen P, Van de Peer Y, Inzé D, De Veylder L (2003) Microarray analysis of E2Fa-DPa-overexpressing plants uncovers a cross-talking genetic network between DNA replication and nitrogen assimilation. J Cell Sci 116:4249–4259
Vlieghe K, Boudolf V, Beemster GT, Maes S, Magyar Z, Atanassova A, de Almeida Engler J, De Groodt R, Inzé D, De Veylder L (2005) The DP-E2F-like gene DEL1 controls the endocycle in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Biol 15:59–63
Yadav RK, Girke T, Pasala S, Xie M, Reddy GV (2009) Gene expression map of the Arabidopsis shoot apical meristem stem cell niche. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:4941–4946
Zimmermann P, Hirsch-Hoffmann M, Hennig L, Gruissem W (2004) GENEVESTIGATOR. Arabidopsis microarray database and analysis toolbox. Plant Physiol 136:2621–2632
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Ministero dell’Università e della Ricerca (PRIN 2006 to RC and DA) and by a grant from the National Science Foundation (MCB-0110536 to LH-B). We thank Lieven De Veylder for the kind gift of the e2fd T-DNA insertion line. We are grateful to Paolo Longoni for his help with RT-PCR assays and Sharon Settlage for helpul comments. We also thank Philip Benfey for sharing time and resources for improving our experiments, as well as Jose Dinneny, Siobhan Brady, Terri Long and Anjali Iyer-Pascuzzi for their comments on the manuscript, and Leslie Eibest for the ESEM analysis at Duke University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Rosangela Sozzani and Caterina Maggio have contributed equally to this work.
Sequence data from this article can be found in the EMBL/GenBank data libraries under accession numbers: E2FD (AJ417835) and E2FE (AJ417835). The AGI locus identifiers are: E2FD/DEL2 (At5g14960), E2FE/DEL1 (At3g48160).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11103_2009_9577_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Supplemental Fig. 1 Plant phenotypes. (A) ESEM of the adaxial epidermal surface of cotyledons (upper panel) and leaves (lower panel) of 6-day-old wild-type (Col-0), e2fd and E2FD OE seedlings. Bars are 100μm. (B) Phenotype of wild-type (Col-0), e2fd and E2FD OE line 8 plants 22 days after sowing (JPG 967 kb)
11103_2009_9577_MOESM2_ESM.jpg
Supplemental Fig. 2 Immunolocalization of E2FD/DEL2 and E2FE/DEL1 in Arabidopsis tissues. Accumulation of E2FD/DEL2 (a) or E2FE/DEL1 (b) in SAM. Accumulation of E2FD/DEL2 (c) and E2FE/DEL1 (d) in young leaves and control (e). Analysis of mature leaves for accumulation of E2FD/DEL2 (f) and E2FE/DEL1 (g) and control (h). Immunolocalization of E2FD/DEL2 (i), E2FE/DEL1 (j) and control reaction (k) in unpollinated pistils. For the negative controls shown in e, h and k, treatment with the primary antibody was omitted (JPG 5190 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sozzani, R., Maggio, C., Giordo, R. et al. The E2FD/DEL2 factor is a component of a regulatory network controlling cell proliferation and development in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 72, 381–395 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-009-9577-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-009-9577-8