Abstract
Context
The high risk of vertebral fractures (VFs) in acromegaly patients despite normal bone mineral density (BMD) is well known. The reasons for this paradoxical finding of skeleton fragility are poorly understood due to the limited data on bone histomorphometry in acromegaly.
Objective
This study aimed to analyze histomorphometric parameters including bone microarchitecture in acromegaly patients with VFs and normal BMD compared to normal subjects, and also to evaluate the differences between active and controlled acromegaly patients.
Patients and methods
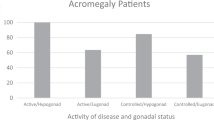
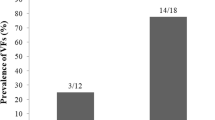
Forty-seven acromegaly patients (17 active, 30 controlled), median (range) age 57 years (30–88) were evaluated for bone turnover, morphometric VFs and BMD by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry at lumbar spine and hip; 12 patients with VFs and normal BMD underwent iliac crest bone biopsy; 12 biopsies were taken at the autopsy in healthy sex and age—matched control subjects.
Results
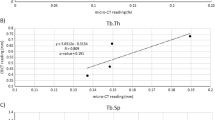
The histomorphometric evaluation of acromegaly fractured patients was compared with that of normal controls and showed significantly reduced median (range) levels of bone volume/tissue volume (BV/TV: 15.37% (7.93–26.75) vs. 18.61% (11.75–27.31), p = 0.036), trabecular thickness (TbTh: 77.6 µm (61.7–88.3) vs. 82.7 µm (72.3–92.0) p = 0.045), with increased trabecular separation (TbSp: 536.4 µm (356.2–900.6) vs. 370.3 µm (377.1–546.3) p = 0.038) and increased cortical thickness (1268 μm (752–2521) vs. 1065 μm (851–1205) p = 0.025) and porosity (11.9% (10.2–13.3) vs. 4.8% (1.6–8.8) p = 0.0008). While active acromegaly patients showed histomophometric features of increased bone turnover, patients with controlled disease presented normal bone turnover with significantly lower osteoblastic activity, expressed as osteoblast number (p = 0.001), active osteoblasts and vigor (p = 0.014) in the presence of reduced osteocyte number (p = 0.008) compared to active disease.
Conclusions
The apparent paradox of bone fragility in acromegaly patients with a normal BMD can be explained by increased cortical thickness and porosity and reduced trabecular thickness with increased trabecular separation. These structural and microarchitectural abnormalities persist in the controlled phase of acromegaly despite bone turnover normalization. The main determinant of bone disease after hormonal control is severe osteoblastic dysfunction.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander L, Appleton D, Hall R, Ross WM, Wilkinson R (1980) Epidemiology of acromegaly in the Newcastle region. Clin Endocrinol 12:71–79
Carroll PV, Jenkins PJ (2016) Acromegaly, In: Chrousos G, Dungan K, Feingold KR, Grossman A, Hershman JM, Koch C, Korbonits M, De Groot, L.J., New M, Purnell J, Rebar R, Singer F, Vinik A (eds) Endotext South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc; 2000
Giustina A, Mazziotti G, Canalis E (2008) Growth hormon, insulin like growth factors and the skeleton. Endocr Rev 29:35–59
Mazziotti G, Maffezzoni F, Giustina A: Vitamin D-binding protein: one more piece in the puzzle of acromegalic osteopathy? Endocrine 52(2):183–186 (2016)
Mazziotti G, Biagioli E, Maffezzoni F, Spinello M, Serra V, Maroldi R, Floriani I, Giustina A (2015) Bone turnover, bone mineral density, and fracture risk in acromegaly: a meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100:384–394
Bonadonna S, Mazziotti G, Nuzzo M, Bianchi A, Fusco A, De Marinis L, Giustina A (2005) Increased prevalence of radiological spinal deformities in active acromegaly: a cross-sectional study in post-menopausal women. J Bone Miner Res 20:1837–1844
Mazziotti G, Bianchi A, Bonadonna S, Cimino S, Patelli I, Fusco A, Pontecorvi A,, De Marinis L, Giustina A (2008) Prevalence of fractures in men with acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 9:4649–4655
Wassenaar MJ, Biermasz NR, Hamdy NA, Zillikens MC, Van Meurs JB, Rivadeneira F, Hofman A, Uitterlinden AG, Stokkel MP, Roelfsema F, Kloppenburg M, Kroon HM, Romijn JA, Pereira AM (2011) High prevalence of vertebral fractures despite normal bone mineral density in patients with long term controlled acromegaly. Eur J Endocrinol 164:475–483
Lim SV, Marenzana M, Hopkinson M, List EO, Kopchick JJ, Pereira M, Javaheri B, Roux JP, Chavassieux P, Korbonits M, Chenu C (2015) Excessive growth hormone expression in male GH transgenic mice adversely alters bone architecture and mechanical strength. Endocrinology 156:13562–13571
Riggs L, Randall RV, Wanner HW, Jowsey J, Kelly PJ, Singh M (1972) The nature of metabolic bone disorder in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 34:911–918
Halse J, Melsen F, Mosekilde L (1981) Iliac crest bone mass and remodelling in acromegaly. Acta Endocrinol 97:18–22
Ueland T, Ebbesen EN, Thomsen JS, Mosekilde L, Brixen K, Flyvbjerg A, Bollerslev J (2002) Decreased trabecular bone biomechanical competence, apparent density, IGF-II and IGFBP-5 content in acromegaly. Eur J Clin Invest 32:122–128
Madeira M, Neto LV, de Paula Paranhos Neto F, Barbosa Lima IC, Carvalho de Mendonça LM, Gadelha MR, Fleiuss de Farias ML (2013) Acromegaly has a negative influence on trabecular bone, but not on cortical bone, as assessed by high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98(4):1734–1741
Hong AR et al (2016) Trabecular bone score as a skeletal fragility index in acromegaly patients. Osteoporos Int 27:1123–1129
Godang K et al (2016) Treatment of acromegaly increases BMD but reduces trabecular bone score: a longitudinal study. Eur J Endocrinol 175:155–164
Malgo F et al (2017) Bone material strength index as measured by impact microindentation is low in patients with fractures irrespective of fracture site. Osteoporos Int 28:2433–2437
Maffezzoni F, Maddalo M, Frara S, Mezzone M, Zorza I, Baruffaldi F, Doglietto F, Mazziotti G, Maroldi R, Giustina A (2016) High-resolution-cone beam tomography analysis of bone microarchitecture in patients with acromegaly and radiological vertebral fractures. Endocrine 54:532–542
Katznelson L, Laws ER Jr, Melmed S, Molitch ME, Murad MH, Utz A, Wass JA, Endocrine Society (2014) Acromegaly: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99:3933–3951
Giustina A, Chanson P, Bronstein MD, Klibanski A, Lamberts S, Casanueva FF, Trainer P, Ghigo E, Ho K, Melmed S (2010) A consensus on criteria for cure of acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:3141–3148
Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Gordon CM, Hanley DA, Heaney RP, Murad MH, Weaver CM, Endocrine Society (2011) Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:1911–1930
WHO Assessment of fracture risk and its application to screening for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Report of a WHO Study Group. Geneva, World Health Organization, 1994 (WHO Technical Report Series, No. 843)
Genant HK, Jergas M, Palermo L, Nevitt M, Valentin RS, Black D, Cummings SR (1996) Comparison of semiquantitative visual and quantitative morphometric assessment of prevalent and incident vertebral fractures in osteoporosis The Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. J Bone Miner Res 11:984–996
Dalle Carbonare L, Matte’ A, Valenti MT, Siciliano A, Mori A, Schweiger V, Zampieri G, Perbellini L, De Franceschi L (2015) Hypoxia-reperfusion affects osteogenic lineage and promotes sickle cell bone disease. Blood 126:2320–2328
Dempster DW, Compston JE, Drezner MK, Glorieux FH, Kanis JA, Malluche H, Meunier PJ, Ott SM, Recker RR, Parfitt AM (2013) Standardized nomenclature, symbols, and units for bone histomorphometry: a 2012 update of the report of the ASBMR Histomorphometry Nomenclature Committee. J Bone Miner Res 28:1–16
Ominsky MS, Boyd SK, Varela A, Jolette J, Felx M, Doyle N, Mellal N, Smith SY, Locher K, Buntich S, Pyrah I, Boyce RW (2017) Romosozumab improves bone mass and strength while maintaining bone quality in ovariectomized cynomolgus monkeys. J Bone Miner Res 32:788–801
Dalle Carbonare L, Ballanti P, Bertoldo F, Valenti MT, Giovanazzi B, Giannini S, Realdi G, Lo Cascio V (2008) Trabecular bone microarchitecture in mild primary hyperparathyroidism. J Endocrinol Invest 31:525–530
Courpron P, Meunier P, Bressot C, Giroux JM (1976) Amount of bone in the iliac crest biopsy. In: Meunier PJ (ed) Second international workshop on bone morphometry. Societe de la Nouvelle Imprimerie Fournie Toulouse, Lyon, pp 39–53
Meunier PJ, Edouard C, Richard D, Laurent J (1976) Histomorphometry of osteoid tissue. The hyperosteoidoses. In: Meunier PJ (ed) Second international workshop on bone morphometry. Societe de la Nouvelle Imprimerie Fournie Toulouse, Lyon, pp 249–262
Meunier P, Edouard C, Courpron P (1976) Morphometric analysis of trabecular resorption surfaces in normal iliac bone. In: Jaworski ZFG (ed) Proceedings of the first workshop on bone morphometry. University of Ottowa Press, Ottawa, pp 156–160
Melsen F, Mosekilde L (1978) Tetracyline double-labeling of iliac trabecular bone in 41 normal adults. Calcif Tissue Res 26:99
Melsen F, Melsen B, Mosekilde L, Bergmann S (1978) Histomorphometric analysis of normal bone from the iliac crest. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A 86:70–81
Mazziotti G, Bianchi A, Porcelli T, Mormando M, Maffezzoni F, Cristiano A, Giampietro A, De Marinis L, Giustina A (2013) Vertebral fractures in patients with acromegaly: a 3-year prospective study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:3402–3410
Claessen KM, Kroon HM, Pereira AM, Appelman-Dijkstra NM, Verstegen ,M.J., Kloppenburg M, Hamdy NA, Biermasz NR (2013) Progression of vertebral fractures despite long-term biochemical control of acromegaly: a prospective follow-up study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:4808–4815
Kurland ES, Rosen CJ, Cosman F, McMahon D, Chan F, Shane E, Lindsay R, Dempster D, Bilezikian JP (1997) Insulin-like growth factor-I in men with idiopathic osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:2799–2805
Mazziotti G, Marzullo P, Doga M, Aimaretti G, Giustina A (2015) Growth hormone deficiency in treated acromegaly. Trends Endocrinol Metab 26:11–21
Dutta P, Mahendran B, Reddy KS, Ahluwalia J, Vaiphei K, Kochhar RK, Gupta P, Srinivasan A, Prakash M, Mukherjee KK, Shah VN, Parthan G, Bhansali A (2015) Short-term efficacy of recombinant human GH therapy in cured acromegaly patients with GH deficiency: a single-center experience. Endocr Connect 4:65–75
Van der Klaauw AA, Bax JJ, Roelfsema F, Stokkel MP, Bleeker GB, Biermasz NR, Smit JW, Romijn JA, Pereira AM (2009) Limited effects of growth hormone replacement in patients with GH deficiency during long-term cure of acromegaly. Pituitary 12, 339–346
Altinova AE, Ozkan C, Akturk M, Gulbahar O, Yalcin M, Cakir N, Toruner FB (2016) Vitamin D-binding protein and free vitamin D concentrations in acromegaly. Endocrine 52:374–379
Ajmal A, Haghshenas A, Attarian S, Barake M, Tritos NA, Klibanski A, Miller KK, Nachtigall LB (2014) The effect of somatostatin analogs on vitamin D and calcium concentrations in patients with acromegaly. Pituitary 17:366–373
Mazziotti G, Maffezzoni F, Frara S, Giustina A (2017) Acromegalic osteopathy. Pituitary 20:63–69
Ezzat S, Melmed S, Endres D, Eyre DR, Singer FR (1993) Biochemical assessment of bone formation and resorption in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 76:1452–1457
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Disclosure
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Ethical approval
All procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carbonare, L.D., Micheletti, V., Cosaro, E. et al. Bone histomorphometry in acromegaly patients with fragility vertebral fractures. Pituitary 21, 56–64 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-017-0847-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-017-0847-1