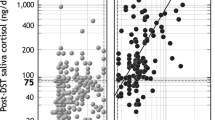
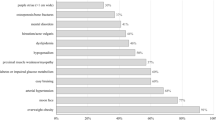
Abstract
This short review summarizes the use of late-night salivary cortisol measurement in the diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome, in the evaluation of patients with adrenal incidentalomas, and in monitoring of post-operative patients, with a focus on the different assay methodologies currently in common use. The focus is on recent studies identified by literature searches using Ovid Medline and Google Scholar as well as analysis of several recent review articles on the topic. Measurement of late night salivary cortisol (LNSC) has an excellent sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome regardless of the assay methodology used. Immunoassays have the advantage of simplicity, low cost, and small sample volume requirement, while liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry has the advantage of a high specificity for cortisol and the ability to measure cortisone. The overnight dexamethasone suppression test appears to be superior to LNSC measurement in the evaluation of patients with adrenal incidentalomas. LNSC measurement is an excellent approach to monitor post-operative Cushing’s disease patients for surgical failure or recurrence. Salivary cortisol is most useful as the initial test when Cushing’s syndrome is suspected and for periodic patient monitoring after pituitary surgery for Cushing’s disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raff H, Findling JW (2003) A physiologic approach to diagnosis of the Cushing syndrome. Ann Intern Med 138:980–991
Carroll T, Raff H, Findling JW (2008) Late-night salivary cortisol measurement in the diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 4:344–350
Findling JW, Raff H (2006) Cushing’s syndrome: important issues in diagnosis and management. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:3746–3753
Findling JW, Raff H (2001) Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 30:729–747
Findling JW, Raff H (1999) Newer diagnostic techniques and problems in Cushing’s disease. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 28:191–210
Findling JW, Raff H (2005) Screening and diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 34:385–402
Raff H (2009) Utility of salivary cortisol measurement in Cushing’s syndrome and adrenal insufficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:3647–3655
Raff H (2004) Role of salivary cortisol determinations in the diagnosis of Cushing syndrome. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diab 11:271–275
Carroll TB, Findling JW (2010) The diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 11:147–153
Alexandraki KI, Grossman AB (2010) Novel insights in the diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome. Neuroendocrinology 92:35–43
Yao KJ, Moss HB, Kirillova GP (1998) Determination of salivary cortisol by nonisotopic immunoassay. Clin Biochem 31:187–190
Gatti R, Antonelli G, Prearo M, Spinella P, Cappellin E, De Palo EF (2009) Cortisol assays and diagnostic laboratory procedures in human biological fluids. Clin Biochem 42:1205–1217
Carrozza C, Corsello SM, Paragliola RM, Ingraudo F, Palumbo S, Locantore P, Sferrazza A, Pontecorvi A, Zuppi C (2010) Clinical accuracy of midnight salivary cortisol measured by automated electrochemiluminescence immunoassay method in Cushing’s syndrome. Ann Clin Biochem 47:228–232
Beko G, Varba I, Glaz E, Sereg M, Feldman K, Toth M, Racz K, Patocs A (2010) Cutoff values of midnight salivary cortisol for the diagnosis of overt hypercortisolism are highly influenced by methods. Clin Chim Acta 411:364–367
Yaneva M, Kirilov G, Zacharieva S (2009) Midnight salivary cortisol, measured by highly sensitive electrochemiluminescence immunoassay, for the diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome. Central Eur J Med 4:59–64
Chiu SK, Collier CP, Clark AF, Wynn-Edwards KE (2003) Salivary cortisol on ROCHE Elecsys immunoassay system: pilot biological variation studies. Clin Biochem 36:211–214
Hansen AM, Garde AH, Christensen JM, Eller NH, Netterstrøm B (2003) Evaluation of a radioimmunoassay and establishment of a reference interval for salivary cortisol in healthy subjects in Denmark. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 63:303–310
Baid SK, Sinaii N, Wade M, Rubino D, Nieman LK (2007) Radioimmunoassay and tandem mass spectrometry measurement of bedtime salivary cortisol levels: a comparison of assays to establish hypercortisolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:3102–3107
Vogeser M, Durner J, Seliger E, Auernhammer C (2006) Measurement of late-night salivary cortisol with an automated immunoassay system. Clin Chem Lab Med 44:1441–1445
Sakihara S, Kageyhama K, Oki Y, Doi M, Iwasaki Y, Takayasu S, Moriyama T, Terui K, Nibawara T, Hirata Y, Hashimoto K, Suda T (2010) Evaluation of plasma, salivary, and urinary cortisol levels for diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome. Endocr J 57:331–337
Perogamvros I, Owen LJ, Newell-Price J, Ray DW, Trainer PJ, Keevil B (2009) Simultaneous measurement of cortisol and cortisone in human saliva using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: application in basal and stimulated conditions. J Chromatogr B 877:3771–3775
Lee S, Kwon S, Shin HJ, Lim HS, Singh RJ, Lee KR, Kim YJ (2010) Simultaneous quantitative analysis of salivary cortisol and cortisone in Korean adults using LC-MS/MS. BMB Reports 43:506–511
Jonsson BAG, Malmberg B, Amilon A, Garde AH, Orbaek P (2003) Determination of cortisol in human saliva using liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 784:63–68
Turpeinen U, Valimaki MJ, Hamalainen E (2009) Determination of salivary cortisol by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 69:592–597
Owen LJ, Haslam S, Adaway JE, Wood P, Glenn C, Keevil BG (2010) A simplified liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry assay, using on-line solid-phase extraction, for the quantitation of cortisol in saliva and comparison with a routine DELFIA method. Ann Clin Biochem 47:131–136
Nelson EA, Palombo EA, Knowles SR (2008) Comparison of evaporation techniques for the preparation of salivary cortisol for analysis by liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Biochem 41:1413–1416
Kataoka H, Matsuura E, Mitani K (2007) Determination of cortisol in human saliva by automated in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Pharmaceut Biomed Anal 44:160–165
Zerikly RK, Amiri L, Faiman C, Gupta M, Singh RJ, Nutter B, Kennedy L, Hatipoglu B, Weil RJ, Hamrahian AH (2010) Diagnostic characteristics of late-night salivary cortisol using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:4555–4559
DePalo EF, Antonelli G, Benetazzo A, Prearo M, Gatti R (2009) Human saliva cortisone and cortisol simultaneous analysis using reverse phase HPLC technique. Clin Chim Acta 405:60–65
Raff H, Sluss PM (2008) Pre-analytical issues for testosterone and estradiol assays. Steroids 73:1297–1304
Broderick JE, Arnold D, Kudielka BM, Kirschbaum C (2004) Salivary cortisol sampling compliance: comparison of patients and healthy volunteers. Psychoneuroendocrinology 29:636–650
Perogamvros I, Keevil BG, Ray DW, Trainer PJ (2010) Salivary cortisone is a potential biomarker for serum free cortisol. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:4951–4958
Raff H (2008–2009) Cushing’s syndrome: diagnosis using late-night salivary cortisol measurement. Clin Lab Int (CLI) 12:6–8 (Dec 2008–Jan 2009)
Kivlighan KT, Granger DA, Schwartz EB, Nelson V, Curran M, Shirtcliff EA (2004) Quantifying blood leakage into the oral mucosa and its effects on the measurement of cortisol, dehydroepiandrosterone, and testosterone in saliva. Horm Behav 46:39–46
Nunes ML, Vattaut S, Corcuff JB, Rault A, Loiseau H, Gatta B, Valli N, Letenneur L, Tabarin A (2009) Late-night salivary cortisol for diagnosis of overt and subclinical Cushing’s syndrome in hospitalized and ambulatory patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:456–462
Cardoso EM, Arregger AL, Tumilasci OR, Contreras LN (2009) Diagnostic value of salivary cortisol in Cushing’s syndrome (CS). Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 70:516–521
Mullan K, Black N, Thiraviaraj A, Bell PM, Burgess C, Hunter SJ, McCance DR, Leslie H, Sheridan B, Atkinson AB (2010) Is there value in routine screening for Cushing’s syndrome in patients with diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:2262–2265
Newsome S, Chen K, Hoang J, Wilson JD, Potter JM, Hickman PE (2008) Cushing’s syndrome in a clinic population with diabetes. Intern Med J 38:178–182
Baid SK, Rubino D, Sinaii N, Ramsey S, Frank A, Nieman LK (2009) Specificity of screening tests for Cushing’s syndrome in an overweight and obese population. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:3857–3864
Carroll T, Raff H, Findling JW (2009) Late-night salivary cortisol for the diagnosis of Cushing syndrome: a meta-analysis. Endocr Pract 15:335–342
Kidambi S, Raff H, Findling JW (2007) Limitations of nocturnal salivary cortisol and urine free cortisol in the diagnosis of mild Cushing’s syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol 157:725–731
Bardet S, Rohmer V, Boux de Casson F, Coffin C, Ronci N, Sabatier JP, Lecomte P, Audran M, Henry-Amar M, Tabarin A (2002) Bone density and biochemical bone markers in patients with adrenal incidentalomas: effect of subclinical hypercortisolism. Rev Méd Interne 23:508–517
Chiodini I (2011) Diagnosis and treatment of subclinical hypercortisolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:1223–1236
Chiodini I, Morelli V, Masserini B, Salcuni AS, Eller-Vainicher C, Viti R, Coletti F, Guglielmi G, Battista C, Carnevale V, Iorio L, Beck-Peccoz P, Arosio M, Ambrosi B, Scillitani A (2009) Bone mineral density, prevalence of vertebral fractures, and bone quality in patients with adrenal incidentalomas with and without subclinical hypercortisolism: an Italian multicenter study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:3207–3214
Morelli V, Vainicher CE, Salcuni AS, Coletti F, Iorio L, Muscogiuri G, Della Casa S, Arosio M, Ambrosi B, Beck-Peccoz P, Chiodini I (2011) Risk of new vertebral fractures in patients with adrenal incidentaloma with and without subclinical hypercortisolism: a multicenter longitudinal study. J Bone Miner Res. doi:10.1002/jbmr.398
Masserini B, Morelli V, Bergamaschi S, Ermetici F, Eller-Vainicher C, Barbieri AM, Maffini MA, Scillitani A, Ambrosi B, Beck-Peccoz P, Chiodini I (2009) The limited role of midnight salivary cortisol levels in the diagnosis of subclinical hypercortisolism in patients with adrenal incidentaloma. Eur J Endocrinol 160:87–92
Deutschbein T, Unger N, Hinrichs J, Walz MK, Mann K, Petersenn S (2009) Late-night and low-dose dexamethasone-suppressed cortisol and serum for the diagnosis of cortisol-secretion adrenal adenomas. Eur J Endocrinol 161:747–753
Sereg M, Toke J, Patocs A, Varga I, Igaz P, Szucs N, Horanyi J, Pusztai P, Czirjak S, Glaz E, Racz K, Toth M (2011) Diagnostic performance of salivary cortisol and serum osteocalcin measurements in patients with overt and subclinical Cushing’s syndrome. Steroids 76:38–42
Aghi MK, Petit J, Chapman P, Loeffler J, Klibanski A, Biller BM, Swearingen B (2008) Management of recurrent and refractory Cushing’s disease with reoperation and/or proton beam radiosurgery. Clin Neurosurg 55:141–144
Carrasco CA, Coste J, Guignat L, Groussin L, Dugué MA, Gaillard S, Bertagna X, Bertherat J (2008) Midnight salivary cortisol determination for assessing the outcome of transsphenoidal surgery in Cushing’s disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:4728–4734
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raff, H. Cushing’s syndrome: diagnosis and surveillance using salivary cortisol. Pituitary 15, 64–70 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-011-0333-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-011-0333-0