Abstract
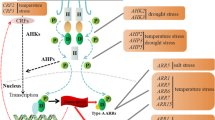
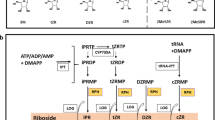
Cytokinins (CKs) are a complex group of compounds. The complexity of CKs is not just present at the level of chemical structures, but as a family of compounds. CKs occur in plants as nucleotides, nucleosides (ribosides) that are produced during de novo biosynthesis, free bases, and conjugates that are in stored/inactivated forms. Almost all organisms make cytokinins. CKs are structural components of the tRNA, and they are located next to the anticodon loop beginning with U of a subset of tRNAs in most eukaryotes and bacteria. The biosynthesis of CKs uses several pathways, and there is evidence that its biosynthesis is also regulated by other growth regulators such as auxins, strigolactones and abscisic acid. Its signaling pathway involves a phosphotransfer signal cascade. Despite advances made so far in the knowledge of CKs, there is still a long way to go. In this review, we summarize the most up-to-date knowledge on the biosynthesis of CKs and the signaling pathway that leads to the response to the presence of CKs in plant tissue, and we identify areas that require more research to complete our understanding of the role of the CKs in plants.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HMBDP:
-
4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl diphosphate
- 6-BA:
-
6-Benciladenine
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- APT:
-
Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase
- iPMP:
-
Adenosine-5′-monophosphate
- AHK:
-
Arabidopsis histidine kinase
- AHP:
-
Arabidopsis histidine-containing phosphotransfer protein
- ARR:
-
Arabidopsis response regulators
- ABC:
-
ATP-binding cassette
- ARF3:
-
AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR3
- CHASE:
-
Cyclases/histidine kinases associated sensory extracellular
- CKX:
-
CYTOKININ OXIDASE/DEHYDROGENASE
- CRE1:
-
Cytokinin response1
- DZ:
-
Dihydrozeatin
- DMAPP:
-
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- ENTs:
-
Equilibrative nucleoside transporters
- GeBP/GPL:
-
Glabrous1 enhancer-binding protein
- HPt:
-
Histidine phosphotransfer
- AHK:
-
Hybrid his kinases
- iP:
-
Hydroxymethylbutenyl diphosphate isopentenyladenine
- iPRDP:
-
Isopentenyladenosine-5′-diphosphate
- iPRTP:
-
Isopentenyladenosine-5′-triphosphate
- IPT:
-
ISOPENTENYL TRANSFERASE
- KIN:
-
Kinetin
- LOG:
-
LONELY GUY
- mT:
-
meta-Topolin
- MEP:
-
Methylerythritol phosphate
- MVA:
-
Mevalonate
- Ot:
-
ortho-Topolin
- PUPs:
-
Purine permeases
- SPY:
-
Spindly
- SL:
-
Strigolactone
- UGT:
-
Uridine diphosphate glycosyltransferase
- WOL:
-
Wooden leg1
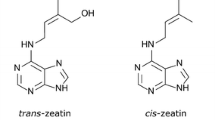
- Z:
-
Zeatin
- cZ:
-
cis-Zeatin
- tZ:
-
trans-Zeatin
- tZRPs:
-
tZ-Riboside 5′-phosphates
References
Akiyoshi DE, Klee H, Amasino RM et al (1984) T-DNA of Agrobacterium tumefaciens encodes an enzyme of cytokinin biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 81:5994–5998. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.81.19.5994
Albacete A (2017) Quantification of cytokinin levels and responses in abiotic stresses. In: Dandekar T, Naseem M (eds) Auxins and cytokinins in plant biology: methods and protocols. Springer, New York, pp 101–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6831-2_8
Albacete A, Martínez-Aldújar C, Ghanem ME et al (2009) Rootstock-mediated changes in xylem ionic and hormonal status are correlated with delayed leaf senescence, and increased leaf area and crop productivity in salinized tomato. Plant Cell Environ 32:928–938. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.01973.x
Aldesuquy H, Baka Z, Mickky B (2014) Kinetin and spermine mediated induction of salt tolerance in wheat plants: leaf area, photosynthesis and chloroplast ultrastructure of flag leaf at ear emergence. Egypt J Basic Appl Sci 1:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbas.2014.03.002
Al-Hakimi AMA (2007) Modification of cadmium toxicity in pea seedlings by kinetin. Plant Soil Environ 53:129–135
Allen M, Qin W, Moreau F, Moffatt B (2002) Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase isoforms of Arabidopsis and their potential contributions to adenine and cytokinin metabolism. Physiol Plant 115:56–68. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3054.2002.1150106.x
Anantharaman V, Aravind L (2001) The CHASE domain: a predicted ligand-binding module in plant cytokinin receptors and other eukaryotic and bacterial receptors. Trends Biochem Sci 26:579–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-0004(01)01968-5
Aremu A, Placková L, Bairu M et al (2014) Endogenous cytokinin profiles of tissue-cultured and acclimatized ´Williams´ bananas subjected to different aromatic cytokinin treatments. Plant Sci 214:88–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.09.012
Argueso CT, Raines T, Kieber JJ (2010) Cytokinin signaling and transcriptional networks. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:533–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2010.08.006
Argyros RD, Mathews DE, Chiang YH et al (2008) Type B response regulators of Arabidopsis play key roles in cytokinin signaling and plant development. Plant Cell 20:2102–2116. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.059584
Barry GF, Rogers SG, Fraley RT, Brand L (1984) Identification of a cloned cytokinin biosynthesis gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 81:4776–4780. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.81.15.4776
Bartrina I, Jensen H, Novák O et al (2017) Gain-of-function mutants of the cytokinin receptors AHK2 and AHK3 regulate plant organ size, flowering time and plant longevity. Plant Physiol 173:1783–1797. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.01903
Beinsberger SEI, Valcke RLM, Deblaere RY et al (1991) Effects of the introduction of Agrobacterium tumefaciens T-DNA ipt gene in Nicotiana tabacum L. cv. Petit havana SR1 plant cells. Plant Cell Physiol 32:489–496. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a078106
Beveridge CA, Murfet IC, Kerhoas L et al (1997) The shoot controls zeatin riboside export from pea roots. Evidence from the branching mutant rms4. Plant J 11:339–345. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1997.11020339.x
Bielach A, Podlesáková K, Marhavy P et al (2012) Spatiotemporal regulation of lateral root organogenesis in Arabidopsis by cytokinin. Plant Cell 24:3967–3981. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.103044
Bilyeu KD, Cole JL, Laskey JG et al (2001) Molecular and biochemical characterization of a cytokinin oxidase from maize. Plant Physiol 125:378–386. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.125.1.378
Bishopp A, Lehesranta S, Vatén A et al (2011) Phloem-transported cytokinin regulates polar auxin transport and maintains vascular pattern in the root meristem. Curr Biol 21:927–932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2011.04.049
Blackwell JR, Horgan R (1994) Cytokinin biosynthesis by extracts of Zea mays. Phytochemistry 35:339–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(00)94760-5
Brenner WG, Ramireddy E, Heyl A, Schmülling T (2012) Gene regulation by cytokinin in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 3:8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2012.00008
Brownlee BG, Hall RH, Whitty CD (1975) 3-methyl-2-butenal: an enzymatic degradation product of the cytokinin, N6-(∆2-isopentenyl) adenine. Can J Biochem 53:37–41
Brzobohaty B, Moore I, Kristoffersen P et al (1993) Release of active cytokinin by a ∆-glucosidase localized to the maize root meristem. Science 262:1051–1054. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.8235622
Bürkle L, Cedzich A, Döpke C et al (2003) Transport of cytokinins mediated by purine transporters of the PUP family expressed in phloem, hydathodes, and pollen of Arabidopsis. Plant J 34:13–26. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01700.x
Caesar K, Thamm AM, Witthöft J et al (2011) Evidence for the localization of the Arabidopsis cytokinin receptors AHK3 and AHK4 in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Exp Bot 62:5571–5580. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err238
Cai L, Zhang L, Fu Q, Xu Z-F (2018) Identification and expression analysis of cytokinin metabolic genes IPTs, CYP735A and CKXs in the biofuel plant Jatropha curcas. PeerJ 6:e4812. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4812
Cao ZY, Ma YN, Sun LH et al (2017) Direct determination of six cytokinin nucleotide monophosphates in coconut flesh by reversed-phase liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 65:9909–9915. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03798
Cassina L, Tassi E, Morelli E et al (2011) Exogenous cytokinin treatments of an Ni hyper-accumulator, Alyssum murale, grown in a serpentine soil: implications for phytoextraction. Int J Phytoremediation 13:90–101. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2011.568538
Cassina L, Tassi E, Pedron F et al (2012) Using a plant hormone and a thioligand to improve phytoremediation of Hg-contaminated soil from a petrochemical plant. J Hazard Mater 231:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.06.031
Chen C (1997) Cytokinin biosynthesis and interconversion. Physiol Plant 101:665–673. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1997.tb01051.x
Chen CM, Kristopeit SM (1981) Metabolism of cytokinin: deribosylation of cytokinin ribonucleoside by adenosine nucleosidase from wheat germ cells. Plant Physiol 68:1020–1023. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.68.5.1020
Chen P, Jiao X, Zhang Y et al (2019) The crystal structure of the phytopathogenic bacterial sensor PcrK reveals different cytokinin recognition mechanism from the plant sensor AHK4. J Struct Biol 208:69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2019.08.001
Cheng ZJ, Wang L, Sun W et al (2013) Pattern of auxin and cytokinin responses for shoot meristem induction results from the regulation of cytokinin biosynthesis by AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR3. Plant Physiol 161:240–251. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.203166
Corbesier L, Prinsen E, Jacqmard A et al (2003) Cytokinin levels in leaves, leaf exudate and shoot apical meristem of Arabidopsis thaliana during floral transition. J Exp Bot 54:2511–2517. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erg276
Corot A, Roman H, Douillet O et al (2017) Cytokinins and abscisic acid act antagonistically in the regulation of the bud outgrowth pattern by light intensity. Front Plant Sci 8:1724
Davière J-M, Achard P (2017) Organ communication: cytokinins on the move. Nat Plants 17:116. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2017.116
Davies WJ, Zhang J (1991) Root signals and the regulation of growth and development of plants in drying soil. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 42:55–76. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pp.42.060191.000415
Dobrev PI, Hoyerová K, Petrášek J (2017) Analytical determination of auxins and cytokinins. In: Dandekar T, Naseem M (eds) Auxins and cytokinins in plant biology: methods and protocols. Springer, New York, pp 31–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6831-2_2
Domagalska MA, Leyser O (2011) Signal integration in the control of shoot branching. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio 12:211. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3088
Dun EA, de Saint GA, Rameau C, Beveridge CA (2012) Antagonistic action of strigolactone and cytokinin in bud outgrowth control. Plant Physiol 158:487–498. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.186783
Durán-Medina Y, Díaz-Ramírez D, Marsch-Martínez N (2017) Cytokinins on the move. Front Plant Sci 8:146. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00146
Entsch B, Letham D (1979) Enzymic glucosylation of the cytokinin, 6-benzylaminopurine. Plant Sci Lett 14:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4211(79)90061-0
Entsch B, Parker CW, Letham DS, Summons RE (1979) Preparation and characterization, using high-performance liquid chromatography of an enzyme forming glucosides of cytokinins. Biochim Biophys Acta Enzymol 570:124–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2744(79)90207-9
Entsch B, Parker C, Letham D (1983) An enzyme from lupin seeds forming alanine derivatives of cytokinins. Phytochemistry 22:375–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(83)83008-8
Falk A, Rask L (1995) Expression of a zeatin-O-glucoside-degrading [beta]-glucosidase in Brassica napus. Plant Physiol 108:1369–1377. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.4.1369
Ferreira FJ, Kieber JJ (2005) Cytokinin signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:518–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2005.07.013
Foo E, Morris SE, Parmenter K et al (2007) Feedback regulation of xylem cytokinin content Is conserved in pea and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 143:1418–1428. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.093708
Fusconi A (2013) Regulation of root morphogenesis in arbuscular mycorrhizae: what role do fungal exudates, phosphate, sugars and hormones play in lateral root formation? Ann Bot 113:19–33. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mct258
Gadallah MAA, El-Enany AE (1999) Role of kinetin in alleviation of copper and zinc toxicity in Lupinus termis plants. Plant Growth Regul 29:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006245628188
Galichet A, Hoyerová K, Kamínek M, Gruissem W (2008) Farnesylation directs AtIPT3 subcellular localization and modulates cytokinin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 146:1155. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.107425
Galuszka P, Frébort I, Šebela M et al (2001) Cytokinin oxidase or dehydrogenase? Mechanism of cytokinin degradation in cereals. Eur J Biochem 268:450–461. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1033.2001.01910.x
Galuszka P, Frébortová J, Werner T et al (2004) Cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase genes in barley and wheat: cloning and heterologous expression. Eur J Biochem 271:3990–4002. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04334.x
Gelová Z, ten Hoopen P, Novák O et al (2017) Antibody-mediated modulation of cytokinins in tobacco: organ-specific changes in cytokinin homeostasis. J Exp Bot 69:441–454. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erx426
Ghosh A, Shah Md, Jui ZS et al (2018) Evolutionary variation and expression profiling of isopentenyl transferase gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana L. and Oryza sativa L. Plant Gene 15:15–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plgene.2018.06.002
Gillissen B, Bürkle L, André B et al (2000) A new family of high-affinity transporters for adenine, cytosine, and purine derivatives in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 12:291–300. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.12.2.291
Girke C, Daumann M, Niopek-Witz S, Möhlmann T (2014) Nucleobase and nucleoside transport and integration into plant metabolism. Front Plant Sci 5:443. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00443
Gordon SP, Chickarmane VS, Ohno C, Meyerowitz EM (2009) Multiple feedback loops through cytokinin signaling control stem cell number within the Arabidopsis shoot meristem. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 106:16529–16534. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0908122106
Greenboim-Wainberg Y, Maymon I, Borochov R et al (2005) Cross talk between gibberellin and cytokinin: the Arabidopsis GA response inhibitor SPINDLY plays a positive role in cytokinin signaling. Plant Cell 17:92–102. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.104.028472
Grefen C, Harter K (2004) Plant two-component systems: principles, functions, complexity and cross talk. Planta 219:733–742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1316-4
Guttikonda SK, Trupti J, Bisht NC et al (2010) Whole genome co-expression analysis of soybean cytochrome P450 genes identifies nodulation-specific P450 monooxygenases. BMC Plant Biol 10:243. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-243
Han Y, Zhang C, Yang H, Jiao Y (2014) Cytokinin pathway mediates APETALA1 function in the establishment of determinate floral meristems in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 111:6840. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1318532111
Hansen CE, Meins F, Milani A (1985) Clonal and physiological variation in the cytokinin content of tobacco-cell lines differing in cytokinin requirement and capacity for neoplastic growth. Differentiation 29:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-0436.1985.tb00284.x
Hansen CE, Meins F, Aebi R (1987) Hormonal regulation of zeatin-riboside accumulation by cultured tobacco cells. Planta 172:520–525. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393869
Heyl A, Wulfetange K, Pils B et al (2007) Evolutionary proteomics identifies amino acids essential for ligand-binding of the cytokinin receptor CHASE domain. BMC Evol Biol 7:62–72. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-7-62
High KE, Ashton P, Nelson M et al (2019) New approaches using mass spectrometry to investigate changes to cytokinin and abscisic acid (ABA) concentrations in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 135:108–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.04.017
Higuchi M, Pischke MS, Mähönen AP et al (2004) In planta functions of the Arabidopsis cytokinin receptor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 101:8821–8826. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0402887101
Hirose N, Makita N, Yamaya T, Sakakibara H (2005) Functional characterization and expression analysis of a gene, OsENT2, encoding an equilibrative nucleoside transporter in rice suggest a function in cytokinin transport. Plant Physiol 138:196–206. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.060137
Hirose N, Takei K, Kuroha T et al (2008) Regulation of cytokinin biosynthesis, compartmentalization and translocation. J Exp Bot 59:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erm157
Hou B, Lim EK, Higgins GS, Bowles DJ (2004) N-glucosylation of cytokinins by glycosyltransferases of Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 279:47822–47832. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M409569200
Hutchison CE, Kieber JJ (2002) Cytokinin signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 14:S47–S59. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.010444
Hutchison CE, Li J, Argueso C et al (2006) The Arabidopsis histidine phosphotransfer proteins are redundant positive regulators of cytokinin signaling. Plant Cell 18:3073–3087. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.045674
Hwang I, Sheen J, Müller B (2012) Cytokinin signaling networks. Annu Rev Plant Biol 63:353–380. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042811-105503
Inoue T, Higuchi M, Hashimoto Y et al (2001) Identification of CRE1 as a cytokinin receptor from Arabidopsis. Nature 409:1060–1063. https://doi.org/10.1038/35059117
Ishida K, Yamashino T, Yokoyama A, Mizuno T (2008) Three type-B response regulators, ARR1, ARR10 and ARR12, play essential but redundant roles in cytokinin signal transduction throughout the life cycle of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 49:47–57. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcm165
Jin SH, Ma XM, Kojima M et al (2013) Overexpression of glucosyltransferase UGT85A1 influences trans-zeatin homeostasis and trans-zeatin responses likely through O-glucosylation. Planta 237:991–999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1818-4
Jiskrová E, Novák O, Pospísilová H et al (2016) Extra-and intracellular distribution of cytokinins in the leaves of monocots and dicots. New Biotechnol 33:735–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2015.12.010
Jones B, Gunneras SA, Petersson SV et al (2010) Cytokinin regulation of auxin synthesis in Arabidopsis involves a homeostatic feedback loop regulated via auxin and cytokinin signal transduction. Plant Cell 22:2956–2969. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.110.074856
Jung B, Flörchinger M, Traub M et al (2009) Uridine-ribohydrolase is a key regulator in the uridine degradation pathway of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21:876–891. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.062612
Kakimoto T (1996) CKI1, a histidine kinase homolog implicated in cytokinin signal transduction. Science 274:982–985. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.274.5289.982
Kakimoto T (2001) Identification of plant cytokinin biosynthetic enzymes as dimethylallyl diphosphate: ATP/ADP isopentenyltransferases. Plant Cell Physiol 42:677–685. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pce112
Kang J, Park J, Choi H et al (2011) Plant ABC transporters. Arabidopsis Book 9:e0153. https://doi.org/10.1199/tab.0153
Kang J, Lee Y, Sakakibara H, Martinoia E (2017) Cytokinin transporters: GO and STOP in signaling. Trends Plant Sci 22:455–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2017.03.003
Kasahara H, Takei K, Ueda N et al (2004) Distinct isoprenoid origins of cis-and trans-zeatin biosyntheses in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 279:14049–14054. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M314195200
Kiba T, Krapp A (2016) Plant nitrogen acquisition under low availability: regulation of uptake and root architecture. Plant Cell Physiol 57:707–714. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcw052
Kiba T, Kudo T, Kojima M, Sakakibara H (2010) Hormonal control of nitrogen acquisition: roles of auxin, abscisic acid, and cytokinin. J Exp Bot 62:1399–1409. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq410
Kiba T, Takei K, Kojima M, Sakakibara H (2013) Side-chain modification of cytokinins controls shoot growth in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 27:452–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2013.10.004
Kieber JJ, Schaller GE (2018) Cytokinin signaling in plant development. Development 145:dev149344. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.149344
Kim HJ, Chiang YH, Kieber JJ, Schaller GE (2013a) SCFKMD controls cytokinin signaling by regulating the degradation of type-B response regulators. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 110:10028–10033. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1300403110
Kim HJ, Kieber JJ, Schaller GE (2013b) The rice F-box protein KISS ME DEADLY2 functions as a negative regulator of cytokinin signalling. Plant Signal Behav 8:e26434. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.26434
Kiran NS, Polanská L, Fohlerová R et al (2006) Ectopic over-expression of the maize ∆-glucosidase Zm-p60.1 perturbs cytokinin homeostasis in transgenic tobacco. J Exp Bot 57:985–996. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erj084
Kiran N, Benková E, Reková A et al (2012) Retargeting a maize ∆-glucosidase to the vacuole-evidence from intact plants that zeatin-O-glucoside is stored in the vacuole. Phytochemistry 79:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2012.03.012
Ko D, Helariutta Y (2017) Shoot-root communication in flowering plants. Curr Biol 27:R973–R978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.06.054
Ko D, Kang J, Kiba T et al (2014) Arabidopsis ABCG14 is essential for the root-to-shoot translocation of cytokinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 111:7150–7155. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1321519111
Koda Y, Okasawa Y (1980) Cytokinin production by Asparagus shoot apex cultured in vitro. Physiol Plant 49:193–197. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1980.tb02651.x
Köllmer I, Novák O, Strnad M et al (2014) Overexpression of the cytosolic cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase (CKX7) from Arabidopsis causes specific changes in root growth and xylem differentiation. Plant J 78:359–371. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12477
Kopecná M, Blaschke H, Kopecný D et al (2013) Structure and function of nucleoside hydrolases from Physcomitrella patens and maize catalyzing the hydrolysis of purine, pyrimidine, and cytokinin ribosides. Plant Physiol 163:1568–1583. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.228775
Krall L, Raschke M, Zenk MH, Baron C (2002) The Tzs protein from Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 produces zeatin riboside 5'-phosphate from 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl diphosphate and AMP. FEBS Lett 527:315–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03258-1
Kumar V, Sharma A, Kaur P et al (2019) Pollution assessment of heavy metals in soils of India and ecological risk assessment: a state-of-the-art. Chemosphere 216:449–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.066
Kurakawa T, Ueda N, Maekawa M et al (2007) Direct control of shoot meristem activity by a cytokinin-activating enzyme. Nature 445:652–655. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05504
Kuroha T, Tokunaga H, Kojima M et al (2009) Functional analyses of LONELY GUY cytokinin-activating enzymes reveal the importance of the direct activation pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21:3152–3169. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.068676
LaCuesta M, Saiz-Fernández I, Podlesáková K et al (2018) The trans and cis zeatin isomers play different roles in regulating growth inhibition induced by high nitrate concentrations in maize. Plant Growth Regul 85:199–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-018-0383-7
Lairson LL, Henrissat B, Davies GJ, Withers SG (2008) Glycosyltransferases: structures, functions, and mechanisms. Annu Rev Biochem 77:521–555. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.061005.092322
Landrein B, Formosa-Jordan P, Malivert A et al (2018) Nitrate modulates stem cell dynamics in Arabidopsis shoot meristems through cytokinins. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 15:1382–1387. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1718670115
Leyser O (2018) Auxin signaling. Plant Physiol 176:465–479. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00765
Li G, Liu K, Baldwin SA, Wang D (2003) Equilibrative nucleoside transporters of Arabidopsis thaliana cDNA cloning, expression pattern, and analysis of transport activities. J Biol Chem 278:35732–35742. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M304768200
Li YJ, Wang B, Dong RR, Hou BK (2015) AtUGT76C2, an Arabidopsis cytokinin glycosyltransferase is involved in drought stress adaptation. Plant Sci 236:157–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.04.002
Lim E-K, Bowles D (2004) A class of plant glycosyltransferases involved in cellular homeostasis. EMBO J 23:2915–2922. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600295
Liu CJ, Zhao Y, Zhang K (2019) Cytokinin transporters: multisite players in cytokinin homeostasis and signal distribution. Front Plant Sci 10:693. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00693
Lomin SN, Myakushina YA, Arkhipov DV et al (2018) Studies of cytokinin receptor–phosphotransmitter interaction provide evidences for the initiation of cytokinin signalling in the endoplasmic reticulum. Funct Plant Biol 45:192–202. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP16292
Lukatkin AS, Gracheva NV, Grishenkova NN et al (2007) Cytokinin-like growth regulators mitigate toxic action of zinc and nickel ions on maize seedlings. Russ J Plant Physiol 54:381–387. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443707030132
Lutts S, Lefèvre I (2015) How can we take advantage of halophyte properties to cope with heavy metal toxicity in salt-affected areas? Ann Bot 115:509–528. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcu264
Manandhar S, Funnell KA, Woolley DJ, Cooney J (2018) Interaction between strigolactone and cytokinin on axillary and adventitious bud development in Zantedeschia. J Plant Physiol Pathol 6:1. https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-955X.1000172
Markovich O, Steiner E, Kouril S et al (2017) Silicon promotes cytokinin biosynthesis and delays senescence in Arabidopsis and sorghum. Plant Cell Environ 40:1189–1196. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12913
Matsumoto-Kitano M, Kusumoto T, Tarkowski P et al (2008) Cytokinins are central regulators of cambial activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 105:20027–20031. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0805619105
Matsuo S, Kikuchi K, Fukuda M et al (2012) Roles and regulation of cytokinins in tomato fruit development. J Exp Bot 63:5569–5579. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers207
Miller CO (1961) A kinetin-like compund in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 47:170–174. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.47.2.170
Miller CO, Skoog F, Okumura FS et al (1955a) Structure and synthesis of kinetin. J Am Chem Soc 77:2662–2663. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01614a108
Miller CO, Skoog F, Von Saltza MH, Strong FM (1955b) Kinetin, a cell division factor from deoxyribonucleic acid. J Am Chem Soc 77:1392. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01610a105
Miyawaki K, Matsumoto-Kitano M, Kakimoto T (2004) Expression of cytokinin biosynthetic isopentenyltransferase genes in Arabidopsis: tissue specificity and regulation by auxin, cytokinin, and nitrate. Plant J 37:128–138. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1345-313X.2003.01945.x
Miyawaki K, Tarkowski P, Matsumoto-Kitano M et al (2006) Roles of Arabidopsis ATP/ADP isopentenyltransferases and tRNA isopentenyltransferases in cytokinin biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 103:16598–16603. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0603522103
Moffatt B, Pethe C, Laloue M (1991) Metabolism of benzyladenine is impaired in a mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana lacking adenine phosphoribosyltransferase activity. Plant Physiol 95:900–908. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.95.3.900
Mok DWS, Mok MC (2001) Cytokinin metabolism and action. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52:89–118. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.52.1.89
Mok M, Mok D, Arsden KE, Shaw G (1987) The biological activity and metabolism of a novel cytokinin metabolite, O-xylosylzeatin, in callus tissue of Phaseolus vulgaris and P. lunatus. J Plant Physiol 130:423–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(87)80207-9
Mok DWS, Martin RC, Shan X, Mok MC (2000) Genes encoding zeatin O-glycosyltransferases. Plant Growth Regul 32:285–287. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010712102890
Morris SE, Turnbull CGN, Murfet IC, Beveridge CA (2001) Mutational analysis of branching in pea. Evidence that Rms1 and Rms5 regulate the same novel signal. Plant Physiol 126:1205–1213. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.126.3.1205
Mortier V, Wasson A, Jaworek P et al (2014) Role of LONELY GUY genes in indeterminate nodulation on Medicago truncatula. New Phytol 202:582–593. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12681
Mougel C, Zhulin IB (2001) CHASE: an extracellular sensing domain common to transmembrane receptors from prokaryotes, lower eukaryotes and plants. Trends Biochem Sci 26:582–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-0004(01)01969-7
Müller B, Sheen J (2007a) Advances in cytokinin signaling. Science 318:68–69. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1145461
Müller B, Sheen J (2007b) Arabidopsis cytokinin signaling pathway. Science's STKE 2007:5
Müller B, Sheen J (2008) Cytokinin and auxin interaction in root stem-cell specification during early embryogenesis. Nature 453:1094–1097. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06943
Müller D, Waldie T, Miyawaki K et al (2015) Cytokinin is required for escape but not release from auxin mediated apical dominance. Plant J 82:874–886. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12862
Murai M (1994) Cytokinin biosynthesis in tRNA and cytokinin incorporation into plant RNA. In: Mok DWS, Mok MC (eds) Cytokinins, chemistry, activity, and function. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Fl, pp 87–99
Nelson D, Werck-Reichhart D (2011) A P450-centric view of plant evolution. Plant J 66:194–211. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04529.x
Nic-Can GI, Avilez-Montalvo JR, Avilez-Montalvo RN et al. (2016) The relationship between stress and somatic embryogenesis. In: Loyola-Vargas VM, Ochoa-Alejo N (eds) Somatic embryogenesis Fundamental aspects and applications. Springer, Switzerland, pp 151–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-33705-0_9
Niemann MCE, Weber H, Hluska T et al (2018) The cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase CKX1 Is a membrane-bound protein requiring homooligomerization in the endoplasmic reticulum for its cellular activity. Plant Physiol 176:2024–2039. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00925
Nishii K, Wright F, Chen YYu, Möller M (2018) Tangled history of a multigene family: the evolution of ISOPENTENYL TRANSFERASE genes. PLoS ONE 13:e0201198. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0201198
Nishiyama R, Watanabe Y, Fujita Y et al (2011) Analysis of cytokinin mutants and regulation of cytokinin metabolic genes reveals important regulatory roles of cytokinins in drought, salt and abscisic acid responses, and abscisic acid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 23:2169–2183. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.087395
Nitschke S, Cortleven A, Iven T et al (2016) Circadian stress regimes affect the circadian clock and cause jasmonic acid-dependent cell death in cytokinin-deficient Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell 28:1616–1639. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.16.00016
Nongpiur R, Soni P, Karan R et al (2012) Histidine kinases in plants: cross talk between hormone and stress responses. Plant Signal Behav 7:1230–1237. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.21516
Nordström A, Tarkowski P, Tarkowska D et al (2004) Auxin regulation of cytokinin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana: a factor of potential importance for auxin–cytokinin-regulated development. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 101:8039–8044. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0402504101
Noriega X, Pérez FJ (2017) ABA biosynthesis genes are down-regulated while auxin and cytokinin biosynthesis genes are up-regulated during the release of grapevine buds from endodormancy. J Plant Growth Regul 36:814–823. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-017-9685-7
Osugi A, Sakakibara H (2015) How do plants respond to cytokinins and what is their importance? BMC Biol 13:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-015-0214-5
Osugi A, Kojima M, Takebayashi Y et al (2017) Systemic transport of trans-zeatin and its precursor have differing roles in Arabidopsis shoots. Nat Plants 3:17112. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2017.112
Park J, Lee Y, Martinoia E, Geisler M (2017) Plant hormone transporters: what we know and what we would like to know. BMC Biol 15:93. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-017-0443-x
Pernisová M, Grochova M, Konecny T et al (2018) Cytokinin signalling regulates organ identity via the AHK4 receptor in Arabidopsis. Development 145:dev163907. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.163907
Persson BC, Esberg B, Ólafsson Ó, Björk GR (1994) Synthesis and function of isopentenyl adenosine derivatives in tRNA. Biochimie 76:1152–1160. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-9084(94)90044-2
Poitout A, Crabos A, Petrick I et al (2018) Responses to systemic nitrogen signaling in Arabidopsis roots involve trans-zeatin in shoots. Plant Cell 30:1243–1257. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00011
Qi Z, Xiong L (2013) Characterization of a Purine Permease Family Gene OsPUP7 Involved in Growth and Development Control in Rice. J Int Plant Biol 55:1119–1135. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12101
Rahayu YS, Walch-Liu P, Neumann G et al (2005) Root-derived cytokinins as long-distance signals for NO3-induced stimulation of leaf growth. J Exp Bot 56:1143–1152. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eri107
Reid DE, Heckmann AB, Novak O et al (2016) CYTOKININ OXIDASE/DEHYDROGENASE3 maintains cytokinin homeostasis during root and nodule development in Lotus japonicus. Plant Physiol 170:1060–1074. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00650
Rivero RM, Shulaev V, Blumwald E (2009) Cytokinin-dependent photorespiration and the protection of photosynthesis during water deficit. Plant Physiol 150:1530. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.139378
Rivero RM, Gimeno J, van Deynze A et al (2010) Enhanced cytokinin synthesis in tobacco plants expressing PSARK: IPT prevents the degradation of photosynthetic protein complexes during drought. Plant Cell Physiol 51:1929–1941. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcq143
Rowe JH, Topping JF, Liu J, Lindsey K (2016) Abscisic acid regulates root growth under osmotic stress conditions via an interacting hormonal network with cytokinin, ethylene and auxin. New Phytol 211:225–239. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13882
Ruffel S, Krouk G, Ristova D et al (2011) Nitrogen economics of root foraging: transitive closure of the nitrate-cytokinin relay and distinct systemic signaling for N supply vs. demand. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 108:18524–18529. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1108684108
Sáenz L, Jones LH, Oropeza C et al (2003) Endogenous isoprenoid and aromatic cytokinins in different plant parts of Cocos nucifera (L.). Plant Growth Regul 39:205–215. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022851012878
Saito T, Opio P, Wang S et al. (2019) Association of auxin, cytokinin, abscisic acid, and plant peptide response genes during adventitious root formation in Marubakaido apple rootstock (Malus prunifolia Borkh. var. ringo Asami). Acta Physiol Plant 41:41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-019-2827-8
Sakakibara H (2006) Cytokinins: activity, biosynthesis, and translocation. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:431–449. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105231
Sakakibara H (2010) Cytokinin biosynthesis and metabolism. In: Davies PJ (ed) Plant hormones. Springer, Amsterdam, pp 95–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-2686-7_5
Sakakibara H, Kasahara H, Ueda N et al (2005) Agrobacterium tumefaciens increases cytokinin production in plastids by modifying the biosynthetic pathway in the host plant. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 102:9972–9977. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0500793102
Salama AMS, El-D A, Wareing PF (1979) Effects of mineral nutrition on endogenous cytokinins in plant of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). J Exp Bot 30:971–981. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/30.5.971
Sasaki T, Suzaki T, Soyano T et al (2014) Shoot-derived cytokinins systemically regulate root nodulation. Nat Commun 5:4983. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5983
Schäfer M, Brütting C, Meza-Canales ID et al (2015) The role of cis-zeatin-type cytokinins in plant growth regulation and mediating responses to environmental interactions. J Exp Bot 66:4873–4884. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv214
Schaller GE, Doi K, Hwang I et al. (2007) Nomenclature for two-component signaling elements of rice. Plant Physiol 143:555–557
Schaller GE, Shiu SH, Armitage JP (2011) Two-component systems and their co-option for eukaryotic signal transduction. Curr Biol 21:320–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2011.02.045
Schmülling T, Werner T, Riefler M et al (2003) Structure and function of cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase genes of maize, rice, Arabidopsis and other species. J Plant Res 116:241–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-003-0096-4
Séguéla M, Briat JF, Vert G, Curie C (2008) Cytokinins negatively regulate the root iron uptake machinery in Arabidopsis through a growth-dependent pathway. Plant J 55:289–300. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03502.x
Seo H, Kim KJ (2017) Structural basis for a novel type of cytokinin-activating protein. Sci Rep UK 7:45985. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep45985
Sheflin AM, Kirkwood JS, Wolfe LM et al (2019) High-throughput quantitative analysis of phytohormones in sorghum leaf and root tissue by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 411:4839–4848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01658-9
Shi Y, Tian S, Hou L et al (2012) Ethylene signaling negatively regulates freezing tolerance by repressing expression of CBF and type-A ARR genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24:2578–2595. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.098640
Shiono K, Hashizaki R, Nakanishi T et al (2017) Multi-imaging of cytokinin and abscisic acid on the roots of rice (Oryza sativa) using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 65:7624–7628. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02255
Simm S, Scharf KD, Jegadeesan S et al (2016) Survey of genes involved in biosynthesis, transport, and signaling of phytohormones with focus on Solanum lycopersicum. Bioinform Biol Insights 10:185–207. https://doi.org/10.4137/BBI.S38425
Singh S, Prasad SM (2014) Growth, photosynthesis and oxidative responses of Solanum melongena L. seedlings to cadmium stress: mechanism of toxicity amelioration by kinetin. Sci Hortic 176:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.06.022
Singh S, Letham S, Zhang X, Alni L (1992) Cytokinin biochemistry in relation to leaf senescence VI. Effect of nitrogenous nutrients on cytokinin levels and senescence of tobacco leaves. Physiol Plant 84:262–268. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1992.tb04663.x
Singh S, Singh A, Srivastava PK, Prasad SM (2018) Cadmium toxicity and its amelioration by kinetin in tomato seedlings vis-à-vis ascorbate-glutathione cycle. J Photochem Photobiol Biol 178:76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.10.025
Skalicky V, Kubes M, Napier R, Novák O (2018) Auxins and cytokinins-the role of subcellular organization on homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci 19:3115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103115
Skoog F, Miller CO (1957) Chemical regulation of growth and organ formation in plant tissues cultured in vitro. Symp Soc Exp Biol 11:118–131
Šmehilová M, Dobrusková J, Novák O et al (2016) Cytokinin-specific glycosyltransferases possess different roles in cytokinin homeostasis maintenance. Front Plant Sci 7:1264. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01264
Song JY, Choi EY, Lee HS et al (1995) Effect of auxin on expression of the isopentenyl transferase gene (ipt) in transformed bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) single-cell clones induced by Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58. J Plant Physiol 146:148–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(11)81981-4
Steklov M, Lomin S, Osolodkin D, Romanov G (2013) Structural basis for cytokinin receptor signaling: an evolutionary approach. Plant Cell Rep 32:781–793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1408-3
Stock AM, Robinson VL, Goudreau PN (2000) Two-component signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem 69:183–215
Strnad M (1997) The aromatic cytokinins. Physiol Plant 101:674–688. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1997.tb01052.x
Sun J, Niu QW, Tarkowski P et al (2003) The Arabidopsis AtIPT8/PGA22 gene encodes an isopentenyl transferase that is involved in de novo cytokinin biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 131:167–176. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.011494
Sun J, Hirose N, Wang X et al (2005) Arabidopsis SOI33/AtENT8 gene encodes a putative equilibrative nucleoside transporter that is involved in cytokinin transport in planta. J Int Plant Biol 47:588–603. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2005.00104.x
Svacinova J, Novak O, Plackova L et al (2012) A new approach for cytokinin isolation from Arabidopsis tissues using miniaturized purification: pipette tip solid-phase extraction. Plant Meth 8:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-4811-8-17
Swaminathan S, Bock RM (1977) Isolation and identification of cytokinins from Euglena gracilis transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry 16:1355–1360. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00626a018
Takei K, Sakakibara H, Sugiyama T (2001a) Identification of genes encoding adenylate isopentenyltransferase, a cytokinin biosynthesis enzyme, in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 276:26405–26410. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M102130200
Takei K, Sakakibara H, Taniguchi M, Sugiyama T (2001b) Nitrogen-dependent accumulation of cytokinins in root and the translocation to leaf: implication of cytokinin species that induces gene expression of maize response regulator. Plant Cell Physiol 42:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pce009
Takei K, Ueda N, Aoki K et al (2004a) AtIPT3 is a key determinant of nitrate-dependent cytokinin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 45:1053–1062. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pch119
Takei K, Yamaya T, Sakakibara H (2004b) Arabidopsis CYP735A1 and CYP735A2 encode cytokinin hydroxylases that catalyze the biosynthesis of trans-zeatin. J Biol Chem 279:41866–41872. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M406337200
Tanaka H, Dhonukshe P, Brewer PB, Friml J (2006) Spatiotemporal asymmetric auxin distribution: a means to coordinate plant development. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:2738–2754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-006-6116-5
Tardieu F, Simonneau T, Muller B (2018) The physiological basis of drought tolerance in crop plants: a scenario-dependent probabilistic approach. Annu Rev Plant Biol 69:733–759. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042817-040218
Taya Y, Tanaka Y, Nishimura S (1978) 5′-AMP is a direct precursor of cytokinin in Dictyostelium discoideum. Nature 271:545–547. https://doi.org/10.1038/271545a0
To JP, Kieber JJ (2008) Cytokinin signaling: two-components and more. Trends Plant Sci 13:85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2007.11.005
To JP, Haberer G, Ferreira FJ et al (2004) Type-A Arabidopsis response regulators are partially redundant negative regulators of cytokinin signaling. Plant Cell 16:658–671. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.018978
Tokunaga H, Kojima M, Kuroha T et al (2012) Arabidopsis lonely guy (LOG) multiple mutants reveal a central role of the LOG-dependent pathway in cytokinin activation. Plant J 69:355–365. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04795.x
Tounekti T, Hernández I, Müller M et al (2011) Kinetin applications alleviate salt stress and improve the antioxidant composition of leaf extracts in Salvia officinalis. Plant Physiol Biochem 49:1165–1176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2011.07.011
Tsai YC, Weir NR, Hill K et al (2012) Characterization of genes involved in cytokinin signaling and metabolism from rice. Plant Physiol 158:1666–1684. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.192765
Turner J, Mok D, Mok M, Shaw G (1987) Isolation and partial purification of an enzyme catalyzing the formation of O-xylosylzeatin in Phaseolus vulgaris embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 84:3714–3717. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.84.11.3714
VanWallendael A, Soltani A, Emery NC et al (2019) A molecular view of plant local adaptation: incorporating stress-response networks. Annu Rev Plant Biol 70:559–583. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050718-100114
Walch-Liu P, Neumann G, Bangerth F, Engels C (2000) Rapid effects of nitrogen form on leaf morphogenesis in tobacco. J Exp Bot 51:227–237. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/51.343.227
Wang R, Tischner R, Gutierrez RA et al (2004) Genomic analysis of the nitrate response using a nitrate reductase-null mutant of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 136:2512–2522. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.044610
Wang J, Ma XM, Kojima M et al (2011) N-glucosyltransferase UGT76C2 is involved in cytokinin homeostasis and cytokinin response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 52:2200–2213. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcr152
Wang J, Ma XM, Kojima M et al (2013) Glucosyltransferase UGT76C1 finely modulates cytokinin responses via cytokinin N-glucosylation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol Biochem 65:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.01.012
Wang Hx, Wang Ml, Wang Xz, Ding Yl (2019) Detection of seven phytohormones in peanut tissues by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. J Integr Agric 18:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(19)62640-7
Werner T, Schmülling T (2009) Cytokinin action in plant development. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:527–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2009.07.002
Werner T, Motyka V, Laucou V et al (2003) Cytokinin-deficient transgenic Arabidopsis plants show multiple developmental alterations indicating opposite functions of cytokinins in the regulation of shoot and root meristem activity. Plant Cell 15:2532–2550. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.014928
Wulfetange K, Lomin SN, Romanov GA et al (2011) The cytokinin receptors of Arabidopsis are located mainly to the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant Physiol 156:1808–1818. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.180539
Wybouw B, De Rybel B (2019) Cytokinin: a developing story. Trends Plant Sci 24:177–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2018.10.012
Xu J, Zha M, Li Y et al (2015) The interaction between nitrogen availability and auxin, cytokinin, and strigolactone in the control of shoot branching in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep 34:1647–1662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1815-8
Yamada H, Suzuki T, Terada K et al (2001) The Arabidopsis AHK4 histidine kinase is a cytokinin-binding receptor that transduces cytokinin signals across the membrane. Plant Cell Physiol 42:1017–1023. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pce127
Yamburenko MV, Kieber JJ, Schaller GE (2017) Dynamic patterns of expression for genes regulating cytokinin metabolism and signaling during rice inflorescence development. PLoS ONE 12:e0176060. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176060
Yokoyama A, Yamashino T, Amano YI et al (2007) Type-B ARR transcription factors, ARR10 and ARR12, are implicated in cytokinin-mediated regulation of protoxylem differentiation in roots of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 48:84–96. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcl040
Young NF, Ferguson BJ, Antoniadi I et al (2014) Conditional auxin response and differential cytokinin profiles in shoot branching mutants. Plant Physiol 165:1723–1736. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.114.239996
Yu J, Tehrim S, Wang L et al (2017) Evolutionary history and functional divergence of the cytochrome P450 gene superfamily between Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica species uncover effects of whole genome and tandem duplications. BMC Genom 18:733. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-4094-7
Žd'árská M, Zatloukalová P, Benítez M et al (2013) Proteome analysis in Arabidopsis reveals shoot- and root-specific targets of cytokinin action and differential regulation of hormonal homeostasis. Plant Physiol 161:918. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.202853
Zhang R, Zhang X, Wang J et al (1995) The effect of auxin on cytokinin levels and metabolism in transgenic tobacco tissue expressing an ipt gene. Planta 196:84–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193221
Zhang XD, Letham DS, Zhang R, Higgins TJV (1996) Expression of the isopentenyl transferase gene is regulated by auxin in transgenic tobacco tissues. Transg Res 5:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01979922
Zhang X, Chen Y, Lin X et al (2013) Adenine phosphoribosyl transferase 1 is a key enzyme catalyzing cytokinin conversion from nucleobases to nucleotides in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 6:1661–1672. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/sst071
Zhang K, Novak O, Wei Z et al (2014) Arabidopsis ABCG14 protein controls the acropetal translocation of root-synthesized cytokinins. Nat Commun 5:3274. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4274
Zhang K, Wang R, Zi H et al (2018) AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR3 regulates floral meristem determinacy by repressing cytokinin biosynthesis and signaling. Plant Cell 30:324–346. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00705
Zhao J, Yu N, Ju M et al (2019) ABC transporter OsABCG18 controls the shootward transport of cytokinins and grain yield in rice. J Exp Bot (In press). https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz382
Zhou M, Ghnaya T, Dailly H et al (2019) The cytokinin trans-zeatine riboside increased resistance to heavy metals in the halophyte plant species Kosteletzkya pentacarpos in the absence but not in the presence of NaCl. Chemosphere 233:954–965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.023
Zürcher E, Tavor-Deslex D, Lituiev D et al (2013) A robust and sensitive synthetic sensor to monitor the transcriptional output of the cytokinin signaling network in planta. Plant Physiol 161:1066–1075. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.211763
Zürcher E, Liu J, di Donato M et al (2016) Plant development regulated by cytokinin sinks. Science 353:1027–1030. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf7254
Funding
This work was supported by the National Council of Science and Technology (FS-1515 and 257436 to VML-V).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Márquez-López, R.E., Quintana-Escobar, A.O. & Loyola-Vargas, V.M. Cytokinins, the Cinderella of plant growth regulators. Phytochem Rev 18, 1387–1408 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-019-09656-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-019-09656-6