ABSTRACT
Purpose
Herein, we designed a nanoparticulate combined delivery system decorated on the surface with RGD peptide, and encapsulating paclitaxel (PTX) and combretastatin A4 (CA4) as the respective anticancer and antiangiogenesis agent in the nanoparticle.
Methods
PTX and CA4 were co-encapsulated into the biocompatible PLGA, followed by solvent evaporation to form solid nanoparticle. The cRGDfK peptide was then conjugated onto the nanoparticle surface with EDC/NHS chemistry.
Results
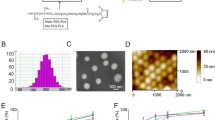
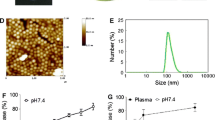
The developed nanoparticles (NPs) were found uniform in size and well dispersed in buffers. The cellular uptake of such NPs could be efficiently detected as early as 20 min after incubation. In 24-h incubation, the encapsulated PTX could induce caspase 3/7-dependent apoptosis at 50 nM, whereas the CA4-loaded NPs could disrupt tubulin structure at 2.5 μM. The targeted dual drug-loaded nanoparticle achieved significant tumor growth suppression in vivo compared to the control from day 8 (P < 0.05). Histological results revealed that the targeted dual drug nanoparticle led to dramatic tumor vasculature disruption, significant cancer cell apoptosis and cell proliferation inhibition in the mouse model.
Conclusion
These findings indicate that the targeted dual drug nanoparticulate delivery system encompassing both antiangiogenesis and anticancer effects can be a potential candidate in cancer therapy.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Coultas L, Chawengsaksophak K, Rossant J. Endothelial cells and VEGF in vascular development. Nature. 2005;438:937–45.
Shojaei F, Ferrara N. Antiangiogenesis to treat cancer and intraocular neovascular disorders. Lab Invest. 2007;87:227–30.
Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature. 2005;438:932–6.
Holmgren L, Oreilly MS, Folkman J. Dormancy of micrometastases—balanced proliferation and apoptosis in the presence of angiogenesis suppression. Nat Med. 1995;1:149–53.
Kerbel RS, Kamen BA. The anti-angiogenic basis of metronomic chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:423–36.
Dorrell MI, Aguilar E, Scheppke L, Barnett FH, Friedlander M. Combination angiostatic therapy completely inhibits ocular and tumor angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:967–72.
Uno T, Takeda K, Kojima Y, Yoshizawa H, Akiba H, Mittler RS, et al. Eradication of established tumors in mice by a combination antibody-based therapy. Nat Med. 2006;12:693–8.
Klement G, Baruchel S, Rak J, Man S, Clark K, Hicklin DJ, et al. Continuous low-dose therapy with vinblastine and VEGF receptor-2 antibody induces sustained tumor regression without overt toxicity. J Clin Invest. 2000;105:R15–24.
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, et al. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. New Engl J Med. 2004;350:2335–42.
Thorpe PE. Vascular targeting agents as cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:415–27.
Yeung SCJ, She MR, Yang HL, Pan JX, Sun LL, Chaplin D. Combination chemotherapy including combretastatin A4 phosphate and paclitaxel is effective against anaplastic thyroid cancer in a nude mouse xenograft model. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:2902–9.
Farokhzad OC, Cheng JJ, Teply BA, Sherifi I, Jon S, Kantoff PW, et al. Targeted nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates for cancer chemotherapy in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:6315–20.
Wang Z, Chui WK, Ho PC. Design of a multifunctional PLGA nanoparticulate drug delivery system: evaluation of its physicochemical properties and anticancer activity to malignant cancer cells. Pharm Res. 2009;26:1162–71.
Green JJ, Chiu E, Leshchiner ES, Shi J, Langer R, Anderson DG. Electrostatic ligand coatings of nanoparticles enable ligand-specific gene delivery to human primary cells. Nano Lett. 2007;7:874–9.
Devalapally H, Duan ZF, Seiden MV, Amiji MM. Paclitaxel and ceramide co-administration in biodegradable polymeric nanoparticulate delivery system to overcome drug resistance in ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer. 2007;121:1830–8.
Kumar P, Benedict R, Urzua F, Fischbach C, Mooney D, Polverini P. Combination treatment significantly enhances the efficacy of antitumor therapy by preferentially targeting angiogenesis. Lab Invest. 2005;85:756–67.
Minischetti M, Vacca A, Ribatti D, Iurlaro M, Ria R, Pellegrino A, et al. TNP-470 and recombinant human interferon-alpha 2a inhibit angiogenesis synergistically. Br J Haematol. 2000;109:829–37.
Abdollahi A, Griggs DW, Zieher H, Roth A, Lipson KE, Saffrich R, et al. Inhibition of alpha(v)beta(3) integrin survival signaling enhances antiangiogenic and antitumor effects of radiotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:6270–9.
Poeck H, Besch R, Maihoefer C, Renn M, Tormo D, Morskaya SS, et al. 5′-triphosphate-siRNA: turning gene silencing and Rig-I activation against melanoma. Nat Med. 2008;14:1256–63.
McCarron PA, Marouf WM, Quinn DJ, Fay F, Burden RE, Olwill SA, et al. Antibody targeting of camptothecin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles to tumor cells. Bioconjug Chem. 2008;19:1561–9.
Dhar S, Gu FX, Langer R, Farokhzad OC, Lippard SJ. Targeted delivery of cisplatin to prostate cancer cells by aptamer functionalized Pt(IV) prodrug-PLGA-PEG nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:17356–61.
McGown AT, Fox BW. Structural and biochemical-comparison of the anti-mitotic agents colchicine, Combretastatin-A4 AND amphethinile. Anticancer Drug Des. 1989;3:249–54.
Kanthou C, Tozer GM. The tumor vascular targeting agent combretastatin A-4-phosphate induces reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and early membrane blebbing in human endothelial cells. Blood. 2002;99:2060–9.
Winkler F, Kozin SV, Tong RT, Chae SS, Booth MF, Garkavtsev I, et al. Kinetics of vascular normalization by VEGFR2 blockade governs brain tumor response to radiation: role of oxygenation, angiopoietin-1, and matrix metal loproteinases. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:553–63.
Tozer GM, Kanthou C, Baguley BC. Disrupting tumour blood vessels. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:423–35.
Liu Z, Chen K, Davis C, Sherlock S, Cao QZ, Chen XY, et al. Drug delivery with carbon nanotubes for in vivo cancer treatment. Cancer Res. 2008;68:6652–60.
Henke E, Perk J, Vider J, de Candia P, Chin Y, Solit DB, et al. Peptide-conjugated antisense oligonucleotides for targeted inhibition of a transcriptional regulator in vivo. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26:91–100.
Stoeltzing O, Liu WB, Reinmuth N, Fan F, Parry GC, Parikh AA, et al. Inhibition of integrin alpha(5)beta(1) function with a small peptide (ATN-161) plus continuous 5-FU infusion reduces colorectal liver metastases and improves survival in mice. Int J Cancer. 2003;104:496–503.
Bozec A, Formento P, Lassalle S, Lippens C, Hofman P, Milano G. Dual inhibition of EGFR and VEGFR pathways in combination with irradiation: antitumour supra-additive effects on human head and neck cancer xenografts. B J Cancer. 2007;97:65–72.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Chui, WK. & Ho, P.C. Nanoparticulate Delivery System Targeted to Tumor Neovasculature for Combined Anticancer and Antiangiogenesis Therapy. Pharm Res 28, 585–596 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-010-0308-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-010-0308-2