Abstract
Purpose
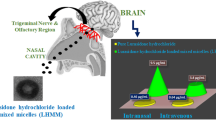
The investigation was aimed at developing micellar nanocarriers for nose-to-brain delivery of zolmitriptan with the objective to investigate the pathway involved in the drug transport.
Methods
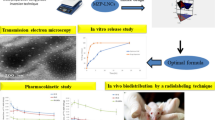
The micellar nanocarrier was successfully formulated and characterized for particle size and shape by multi-angle dynamic light scattering, small angle neutron scattering and cryo-transmission electron microscopy. Toxicity and biodistribution studies were carried out in rat. The distribution of the nasally administered labeled micellar nanocarrier in various regions of the rat brain was determined using the brain localization and autoradiography studies.
Results
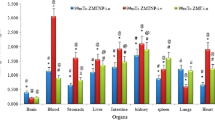
Micellar nanocarrier of zolmitriptan, with size of around 23 nm, was successfully formulated. The spherical nature of the nanocarrier was confirmed using DLS, SANS and cryo-TEM. Toxicity studies indicated the safety for administration in the nasal cavity. In vivo biodistribution studies indicated the superiority of the developed nanocarrier for brain targeting when compared with the intravenous and nasal solutions of the drug. Brain localization and autoradiography studies illustrated the distribution of the drug in various regions of the brain and revealed a possible nose-to-brain transport pathway for the labeled drug.
Conclusion
The investigation indicated the potential of the developed nanocarrier as an effective new-generation vehicle for brain targeting of zolmitriptan.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tepper SJ, Rapoport AM. The triptans: a summary. CNS Drugs. 1999;12:403–17.
Vyas TK, Babbar AK, Sharma RK, Misra A. Intranasal mucoadhesive microemulsions of zolmitriptan: preliminary studies on brain-targeting. J Drug Target. 2005;13:317–24.
Rao BM, Srinivasu MK, Sridhar G, Rajender Kumar P, Chandrasekhar KB, Islam A. A stability indicating LC method for zolmitriptan. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2005;39:503–9.
Rolan PE, Martin GR. Zolmitriptan: a new acute treatment for migraine. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 1998;7:633–52.
Patel SR, Zhong H, Sharma A, Kalia YN. Controlled non-invasive transdermal iontophoretic delivery of zolmitriptan hydrochloride in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008;72:304–9.
Bigal ME, Bordini CA, Antoniazzi AL, Speciali JG. The triptan formulations: a critical evaluation. Arq Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2003;61:313–20.
Goadsby PJ, Yates R. Zolmitriptan intranasal: a review of the pharmacokinetics and clinical efficacy. Headache. 2006;46:138–49.
Yates R, Nairn K, Dixon R, Seaber E. Preliminary studies of the pharmacokinetics and tolerability of zolmitriptan nasal spray in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 2002;42:1237–43.
Tepper SJ, Donnan GA, Dowson AJ, Bomhof MAM, Elkind A, Meloche J, et al. A long-term study to maximize migraine relief with zolmitriptan. Curr Med Res Opin. 1999;15:254–71.
Vyas TK, Babbar AK, Sharma RK, Singh S, Misra A. Intranasal mucoadhesive microemulsions of clonazepam: preliminary studies on brain targeting. J Pharm Sci. 2006;95:570–80.
Torchilin VP. Micellar nanocarriers: pharmaceutical perspectives. Pharm Res. 2007;24:1–16.
Simon M, Wittmar M, Kissel T, Linn T. Insulin containing nanocomplexes formed by self-assembly from biodegradable amine-modified poly (Vinyl Alcohol)-Graft-Poly (L-Lactide): bioavailability and nasal tolerability in rats. Pharm Res. 2005;22:1879–86.
Quadir M, Zia H, Needham TE. Toxicological implications of nasal formulations. Drug Deliv. 1999;6:227–42.
Schillen K, Brown W, Johnson RM. Micellar sphere-to-rod transition in an aqueous triblock copolymer system. A dynamic light scattering study of translational and rotational diffusion. Macromolecules. 1994;27:4825–32.
Almgren M, Edwards K, Karlsson G. Cryo transmission electron microscopy of liposomes and related structures. Colloids Surf A. 2000;174:3–21.
Nabar SJ, Jain R, Patravale VB. Preparation, quality control and stability of 99mTc-Zolmitriptan nanocarrier. Ind J Nucl Med. 2008;23:77.
Thorne RG, Emory CR, Ala TA, Frey WH. Quantitative analysis of the olfactory pathway for drug delivery to the brain. Brain Res. 1995;692:278–82.
Thomas GH, Hartman JA, Seiden LS. Rapid method for the regional dissection of the rat brain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1980;13:453–6.
Paxinos G, Watson C. The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. San Diego: Academic; 1998.
Oh KT, Bronich TK, Kabanov AV. Micellar formulations for drug delivery based on mixtures of hydrophobic and hydrophilic Pluronic® block copolymers. J Control Release. 2004;94:411–22.
Ivanova R, Lindman B, Alexandridis P. Effect of pharmaceutically acceptable glycols on the stability of the liquid crystalline gels formed by Poloxamer 407 in water. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2002;252:226–35.
Gao Y, Li LB, Zhai G. Preparation and characterization of Pluronic/TPGS mixed micelles for solubilization of camptothecin. Colloids Surf B. 2008;64:194–9.
Xie Y, Wei L, Cao S, Jiang X, Yin M, Tang W. Preparation of bupleurum nasal spray and evaluation on its safety and efficacy. Chem Pharm Bull. 2006;54:48–53.
Hammad MA, Müller BW. Solubility and stability of clonazepam in mixed micelles. Int J Pharm. 1998;169:55–64.
Bryant G, Thomas JC. Improved particle size distribution measurements using multiangle dynamic light scattering. Langmuir. 1995;11:2480–5.
Mackeben S, Muller M, Muller-Goymann CC. The influence of water on phase transitions of a drug-loaded reverse micellar solution into lamellar liquid crystals. Colloid Surf A. 2001;183–185:699–713.
Herzon FS. Nasal ciliary structural pathology. Laryngoscope. 1983;93:63–7.
Rautianen M, Muutinen J, Kiukaaniemi H, Collan Y. Ultrastructural changes in human cilia caused by the common cold and recovery of ciliated epithelium. In vivo results in animals. Drug Invest. 1994;8:127–33.
Meaney CM, O’Driscoll CM. A comparison of the permeation enhancement potential of simple bile salt and mixed bile salt:fatty acid micellar systems using the CaCo-2 cell culture model. Int J Pharm. 2000;207:21–30.
Illum L. Transport of drugs from the nasal cavity to central nervous system. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2000;11:1–18.
Thorne RG, Pronk GJ, Padmanabhan V, Frey WH. Delivery of insulin-like growth factor-I to the rat brain and spinal cord along olfactory and trigeminal pathways following intranasal administration. Neuroscience. 2004;127:481–96.
Kanayama Y, Enomoto S, Irie T, Amano R. Axonal transport of rubidium and thallium in the olfactory nerve of mice. Nucl Med Biol. 2005;32:505–12.
Haberly LB, Price JL. Association and commissural fiber systems of the olfactory cortex of the rat: I. Systems originating in the piriform cortex and adjacent areas. J Comp Neurol. 1978;178:711–40.
Fechter LD, Johnson DL, Lynch RA. The relationship of particle size to olfactory nerve uptake of a non-soluble form of manganese into brain. Neurotoxicology. 2002;23:177–83.
Sakane T, Akizuki M, Yoshida M, Yamashita S, Nadai T, Hashida M, et al. Transport of cephalexin to the cerebrospinal fluid directly from the nasal cavity. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1991;43:449–51.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Archarchem Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd. and Chokhani Pharmaceutical Ltd. for the gift sample of zolmitriptan; Gattefosse, Mumbai, India and BASF India Ltd. for the gift sample of excipients; and Aptar Pharma India Pvt. Ltd., Mumbai, India for the kind gift of Equadel™ Pump. The authors are grateful to Lalit Borde and Dr. Krishanu Ray from Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai, India; Prof. Katarina Edwards, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden; and Prof. Ishi Talmon, Haifa, Israel for conducting the cryo-TEM analysis. The authors are thankful to Dr. P. A. Hassan, Dr. V. K. Aswal for DLS and SANS analysis, and Dr. Tanuja Shet for authoradiography Studies. Ratnesh Jain is thankful to the Board of Research in Nuclear Sciences (Sanction No. 2006/35/11/BRNS), Department of Atomic Energy, Gov’t of India, for providing the funding to execute the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, R., Nabar, S., Dandekar, P. et al. Micellar Nanocarriers: Potential Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Zolmitriptan as Novel Migraine Therapy. Pharm Res 27, 655–664 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-009-0041-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-009-0041-x