Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of the study is to evaluate the effect of surfactant-plasticizers on the physical stability of amorphous drug in polymer matrices formed by hot melt extrusion.
Method
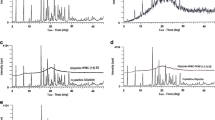
Solid dispersions of a poorly soluble drug were prepared using PVP-K30, Plasdone-S630, and HPMC-E5 as the polymeric carriers and surfactants as plasticizers. The solid dispersions were produced by hot melt extrusion at temperatures 10°C above and below the glass transition temperature (Tg) of the carrier polymers using a 16 mm-Haake Extruder. The surfactants tested in this study included Tween-80 and Docusate Sodium. The particle size of the extrudate was reduced to have mean of 100–200 micron. The physical stability of the solid dispersions produced was monitored at 30°C/60% for six-months and at 60°C/85% for two-months in open HDPE bottles. Modulated differential scanning calorimetry, polarized light microscopy, powder X-ray diffraction and dissolution testing was performed to assess the physical stability of solid dispersions upon stress testing.
Results
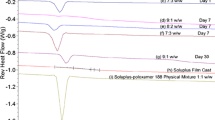
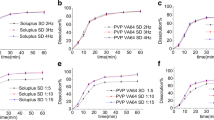
The dispersions containing HPMC-E5 were observed especially to be susceptible to physical instability under an accelerated stress conditions (60°C/85%RH) of the solid dispersion. About 6% conversion of amorphous drug to crystalline form was observed. Consequently, the system exhibits similar degree of re-crystallization upon addition of the surfactant. However, under 30°C/60%RH condition, the otherwise amorphous Drug-HPMC-E5 system has been destabilized by the addition of the surfactant. This effect is much more reduced in the extruded solid dispersions where polymeric carriers such as Plasdone S-603 and PVP-K30 (in addition to surfactants) are present. Furthermore, the drug release from the solid dispersions was unaffected at the stress conditions reported above.
Conclusions
Possible reasons for the enhanced stability of the dispersions are due to the surfactants ability to lower the viscosity of the melt, increase the API solubility and homogeneity in the carrier polymer. In contrast, while it is possible for the surfactants to destabilize the system by lowering the Tg and increasing the water uptake, the study confirms that this effect is minimal. By and large, the surfactants appear to be promising plasticizers to produce solid dispersions by hot melt extrusion, in so doing improving dissolution rate without compromising the physical stability of the systems.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. C. Etter, J. C. Macdonald, and J. Bernstein. Graph-set analysis of hydrogen-bond patterns in organic crystals. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B, Struct. Commun. 46:256–262 (1990).
M. C. Etter and S. M. Reutzel. Hydrogen-bond directed cocrystallization and molecular recognition properties of acyclic imides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 113:2586–2598 (1991).
B. Moulton and M. J. Zaworotko. From molecules to crystal engineering: supramolecular isomerism and polymorphism in network solids. Chem. Rev. 101:1629–1658 (2001).
B. Rodríguez-Spong, C. P. Price, A. Jayasankar, A. J. Matzger, and N. Rodríguez-Hornedo. General principles of pharmaceutical solid polymorphism: a supramolecular perspective. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 56:241–274 (2004).
D. Q. M. Craig. The mechanism of drug release from solid dispersions in water-soluble polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 231:131–144 (2002).
A. N. Ghebremeskel, C. Vemavarapu, and M. Lodaya. Use of surfactants as plasticizers in preparing solid dispersions of poorly soluble API: selection of polymer/surfactant combinations using solubility parameters and testing the processability. Accepted July 11, 2006 to Int. J. Pharm. (2006).
A. Dakkuri, H. G. Schreoeder, and P. P. Deluca. Sustaining release from inert wax matrices. II. Effect of surfactants on tripelennamin hydrochloride release. J. Pharm. Sci. 67:355–357 (1978).
N. Najib and M. S. Suleiman. Kinetics of drug release from ethylcellulose solid dispersions. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. Sci. 11:2169–2181 (1985).
S. Luhtala. Effect of sodium lauryl sulphate and polysorbate 80 on crystal growth and aqueous solubility of carbamazepine. Acta Pharm Nord. 4:85–90 (1992).
A. Nokhodchi, P. Khaseh, T. Ghafourian, and M. R. Siahi-Shadbad. The role of various surfactants and fillers in controlling the release rate of theophylline from HPMC matrices. STP Pharmacol. Sci. 9:555–560 (1999).
A. Nokhodchi, S. Norouzi-Sani, M. R. Siahi-Shadbad, F. Lotfipoor, and M. Saeedi. The effect of various surfactants on the release rate of propranolol hydrochloride from hydroxypropyl-methlcellulose (HPMC)-Eudragit matrices. Eur. J. Pharm. and Biopharm. 54:349–356 (2002).
L. R. Chen, J. A. Wesley, S. Bhattachar, B. Ruiz, K. Bahash, and S. R. Babu. Dissolution behavior of a poorly water soluble compound in the presence of Tween 80. Pharm. Res. 20:797–801 (2003).
Acknowledgments
A.N. Ghebremeskel greatly appreciates the assistance given by Dr. Zeri Teweldemedhin and Dr. Darshan Parikh.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghebremeskel, A.N., Vemavarapu, C. & Lodaya, M. Use of Surfactants as Plasticizers in Preparing Solid Dispersions of Poorly Soluble API: Stability Testing of Selected Solid Dispersions. Pharm Res 23, 1928–1936 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-9034-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-9034-1