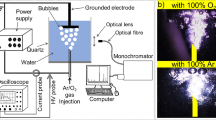
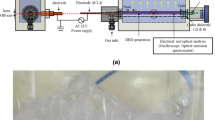
Abstract
Although the erosion of high-voltage electrodes was extensively studied in in-liquid electrical discharges, to the best of our knowledge, the erosion produced by discharges generated above water has been barely explored. This work studies the erosion of three pin electrode materials (hafnium, copper, stainless steel) in two gas atmospheres (oxygen, air). They are powered by repetitive high-voltage nanosecond pulses, producing pulsed streamer discharges above water. The electrode material does not affect the energy deposited per pulse. The surfaces of all three electrodes erode, releasing metal particles into the water. Stainless steel is the material with least erosion, in both gas atmospheres. Overall, copper in air shows the highest erosion. We also examine how the metals released into the water affect three long-lived reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS), H2O2, NO2− and NO3−, during four weeks post-discharge. After treatment with air plasma, NO2− and NO3− are measured in the treated water, but H2O2 is not detected. NO2− is almost completely converted into NO3− after two weeks. H2O2 is measured for samples prepared with an oxygen plasma. Neither the RONS nor the conductivity of plasma-treated water are significantly affected by the use of different electrode materials.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Locke BR, Lukeš P (2018) Special issue: plasma and liquids. Plasma Process Polym 15:1815062. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppap.201815062
Bruggeman PJ, Kushner MJ, Locke BR et al (2016) Plasma–liquid interactions: a review and roadmap. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 25:053002. https://doi.org/10.1088/0963-0252/25/5/053002
Puač N, Gherardi M, Shiratani M (2018) Plasma agriculture: a rapidly emerging field. Plasma Process Polym 15:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppap.201700174
Malik MA (2010) Water purification by plasmas: which reactors are most energy efficient? Plasma Chem Plasma Process 30:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-009-9202-2
Stratton GR, Bellona CL, Dai F et al (2015) Plasma-based water treatment: conception and application of a new general principle for reactor design. Chem Eng J 273:543–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.03.059
Kozakova Z, Klimova EJ, Obradovic BM et al (2018) Comparison of liquid and liquid-gas phase plasma reactors for discoloration of azo dyes: analysis of degradation products. Plasma Process Polym. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppap.201700178
Lukes P, Locke BR, Brisset JL (2012) Aqueous-phase chemistry of electrical discharge plasma in water and in gas-liquid environments. In: Parvulescu VI, Magureanu M, Lukes P (eds) Plasma chemistry and catalysis in gases and liquids, 1st edn. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co, KGaA, pp 243–308
Velikonja J, Bergougnou MA, Castle GSP et al (2001) Co-generation of ozone and hydrogen peroxide by dielectric barrier AC discharge in humid oxygen. Ozone Sci Eng 23:467–478. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919510108962031
Traylor MJ, Pavlovich MJ, Karim S et al (2011) Long-term antibacterial efficacy of air plasma-activated water. J Phys D Appl Phys 44:472001. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/44/47/472001
Boehm D, Heslin C, Cullen PJ, Bourke P (2016) Cytotoxic and mutagenic potential of solutions exposed to cold atmospheric plasma. Sci Rep 6:21464. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21464
Shen J, Tian Y, Li Y et al (2016) Bactericidal effects against S. aureus and physicochemical properties of plasma activated water stored at different temperatures. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28505
Foster JE (2017) Plasma-based water purification: challenges and prospects for the future. Phys Plasmas 24:0–16. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4977921
Dobrin D, Bradu C, Magureanu M et al (2013) Degradation of diclofenac in water using a pulsed corona discharge. Chem Eng J 234:389–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.08.114
Tampieri F, Giardina A, Bosi FJ et al (2018) Removal of persistent organic pollutants from water using a newly developed atmospheric plasma reactor. Plasma Process Polym. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppap.201700207
Mededovic Thagard S, Stratton GR, Dai F et al (2017) Plasma-based water treatment: development of a general mechanistic model to estimate the treatability of different types of contaminants. J Phys D Appl Phys 50:014003. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/50/1/014003
Oh JS, Szili EJ, Gaur N et al (2016) How to assess the plasma delivery of RONS into tissue fluid and tissue. J Phys D Appl Phys 49:304005. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/49/30/304005
Tanaka H, Mizuno M, Ishikawa K et al (2018) Molecular mechanisms of non-thermal plasma-induced effects in cancer cells. Biol Chem 400:87–91. https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2018-0199
Foster JE, Mujovic S, Groele J (2018) Towards high throughput plasma based water purifiers: design considerations and the pathway towards practical application. J Phys D Appl Phys 51:293001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aac816
Lukeš P, Člupek M, Babický V et al (2006) Erosion of needle electrodes in pulsed corona discharge in water. Czech J Phys 56:916–924. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10582-006-0304-2
Mededović S, Locke BR (2006) Platinum catalysed decomposition of hydrogen peroxide in aqueous-phase pulsed corona electrical discharge. Appl Catal B Environ 67:149–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2006.05.001
Holzer F, Locke BR (2008) Influence of high voltage needle electrode material on hydrogen peroxide formation and electrode erosion in a hybrid gas-liquid series electrical discharge reactor. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 28:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-007-9107-x
Kirkpatrick MJ, Locke BR (2006) Research notes: effects of platinum electrode on hydrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen peroxide formation in aqueous phase pulsed corona electrical discharge. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:2138–2142. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie0511480
Lukes P, Clupek M, Babicky V et al (2011) The catalytic role of tungsten electrode material in the plasmachemical activity of a pulsed corona discharge in water. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 20:034011. https://doi.org/10.1088/0963-0252/20/3/034011
Liu Y, Li Z, Luo Q et al (2016) Comparison and evaluation of electrode erosion under high-pulsed current discharges in air and water mediums. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 44:1169–1177. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPS.2016.2578343
Goryachev VL, Ufimtsev AA, Khodakovskii AM (1997) Mechanism of electrode erosion in pulsed discharges in water with a pulse energy of ~ 1. J. Tech Phys Lett 23:386–387. https://doi.org/10.1134/1.1261862
Parkansky N, Vegerhof A, Alterkop BA et al (2012) Submerged arc breakdown of methylene blue in aqueous solutions. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 32:933–947. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-012-9385-9
Kolikov VA, Kurochkin VE, Panina LK, Rutberg AFG (2005) Pulse electric discharges and prolonged microbial resistance of water. Dokl Biol Sci 403:279–281
Blokhin VI, Vysikailo FI, Dmitriev KI, Efremov NM (1999) Systems with different electrode materials for treatment of water by a pulsed electric discharge. High Temp 37:998–999
Mededovic S, Locke BR (2007) The role of platinum as the high voltage electrode in the enhancement of Fenton’s reaction in liquid phase electrical discharge. Appl Catal B Environ 72:342–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2006.11.014
Rutberg PG, Gorjachev V, Gorjachev VL, Kolikov VA et al (2010) Main results of investigations of pulsed electric discharges in water carried out at IEE RAS. High Temp Mater Process 14:175–184
Efremov NM, Yu Adamiak B, Blochin VI et al (2000) Experimental investigation of the action of pulsed electrical discharges in liquids on biological objects. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 28:224–229. https://doi.org/10.1109/27.842908
Cao Y, Qu G, Li T et al (2018) Review on reactive species in water treatment using electrical discharge plasma: formation, measurement, mechanisms and mass transfer. Plasma Sci Technol 20:103001. https://doi.org/10.1088/2058-6272/aacff4
Dai F, Fan X, Stratton GR et al (2016) Experimental and density functional theoretical study of the effects of Fenton’s reaction on the degradation of bisphenol A in a high voltage plasma reactor. J Hazard Mater 308:419–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.01.068
Walling C (1975) Fenton’s reagent revisited. Acc Chem Res 8:125–131. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar50088a003
Vukusic T, Shi M, Herceg Z et al (2016) Liquid-phase electrical discharge plasmas with a silver electrode for inactivation of a pure culture of Escherichia coli in water. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 38:407–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2016.07.007
Rutberg FG, Dubina MV, Kolikov VA et al (2008) Effect of silver oxide nanoparticles on tumor growth in vivo. Dokl Biochem Biophys 421:191–193. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672908040078
Chen Q, Li J, Li Y (2015) A review of plasma-liquid interactions for nanomaterial synthesis. J Phys D Appl Phys 48:424005. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/48/42/424005
Besser BJM, Leib KJ (2007) Toxicity of metals in water and sediment to aquatic biota. In: U.S. Department of the interior (ed) environmental effects of historical mining, Animas River Watershed, Colorado
de Benetoli LOB, Cadorin BBM, da Postiglione CS et al (2011) Effect of temperature on methylene blue decolorization in aqueous medium in electrical discharge plasma reactor. J Braz Chem Soc 22:1669–1678. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-50532011000900008
Pokryvailo A, Yankelevich Y, Wolf M et al (2004) A high-power pulsed corona source for pollution control applications. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 32:2045–2054. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPS.2004.835952
Kornev I, Preis S (2016) Aqueous benzene oxidation in low-temperature plasma of pulsed corona discharge. J Adv Oxid Technol 19:284–289. https://doi.org/10.1515/jaots-2016-0212
Panorel I, Preis S, Kornev I et al (2013) Oxidation of aqueous pharmaceuticals by pulsed corona discharge. Environ Technol 34:923–930. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2012.722691
Yoon S, Jeon H, Yi C et al (2018) Mutual interaction between plasma characteristics and liquid properties in AC-driven pin-to-liquid discharge. Sci Rep 8:12037. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30540-4
Kolikov VA, Kurochkin VE, Panina LK et al (2007) Prolonged microbial resistance of water treated by a pulsed electrical discharge. Tech Phys 52:263–270. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063784207020193
Nemchinsky VA, Severance WS (2006) What we know and what we do not know about plasma arc cutting. J Phys D Appl Phys. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/39/22/R01
Rusterholtz D (2012) Nanosecond repetitively pulsed discharges in atmospheric pressure air. École Centrale Paris
Takahashi A, Hashimoto K, Kumazawa S, Nakayama T (1999) Determination of hydrogen peroxide by high-performance liquid chromatography with a cation-exchange resin gel column and electrochemical detector. Anal Sci 15:481–483. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.15.481
Fridman A, Gutsol A, Cho YI (2007) Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma. Adv Heat Transf 40:1–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2717(07)40001-6
Park JY, Lee YN (1988) Solubility and decomposition kinetics of nitrous acid in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem 92:6294–6302. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100333a025
Karlsson R, Tortensson L-G (1974) Controlled-potential iodometric titration of nitrite. Application to the determination of nitrite in meat products. Talanta 21:945–950
Lukes P, Clupek M, Babicky V et al (2005) Generation of ozone by pulsed corona discharge over water surface in hybrid gas-liquid electrical discharge reactor. J Phys D Appl Phys 38:409–416. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/38/3/010
Lieberman MA, Lichtenberg AJ (2005) Principles of plasma discharges and materials processing. Wiley, London
Massarczyk R, Chu P, Dugger C et al (2017) Paschen’s law studies in cold gases. J Instrum 12:P06019. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-0221/12/06/P06019
Lukes P, Clupek M, Babicky V (2011) Discharge filamentary patterns produced by pulsed corona discharge at the interface between a water surface and air. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 39:2644–2645. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPS.2011.2158611
Kingzett CT (1880) Report on the atmospheric oxidation of phosphorus and some reactions of ozone and hydric peroxide. J Chem Soc Trans 37:792–807. https://doi.org/10.1039/CT8803700792
Lew RB (1975) Interference of nitrite in the iodometric determination of sulfite. J Am Soc Sugar Beet Technol 18:252–256
Kolthoff JM (1921) Jodometrische Studien. Zeitschrift für Anal Chemie 60:338–353
Porter D, Poplin MD, Holzer F et al (2009) Formation of hydrogen peroxide, hydrogen, and oxygen in gliding arc electrical discharge reactors with water spray. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 45:623–629. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2009.2013560
Liu ZC, Liu DX, Chen C et al (2018) Post-discharge evolution of reactive species in the water activated by a surface air plasma: a modeling study. J Phys D Appl Phys. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aab635
Laurita R, Barbieri D, Gherardi M et al (2015) Chemical analysis of reactive species and antimicrobial activity of water treated by nanosecond pulsed DBD air plasma. Clin Plasma Med 3:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpme.2015.10.001
Hauschild MZ, Rosenbaum RK, Olsen SI (2017) Life cycle assessment: theory and practice. Springer, Cham, Switzerland
Schmidt LJ, Gaikowski MP, Gingerich WH (2006) Environmental assessment of hydrogen peroxide for aquaculture use. U.S. Geological Survey, Biological Resources Division, Wisconsin, USA
Šunka P (2001) Pulse electrical discharges in water and their applications. Phys Plasmas 8:2587–2594. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1356742
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Gerald Hatch Faculty Fellowship and the McGill Engineering Doctoral Award. The authors thank Andrew Golsztajn for technical assistance and Benjamin Münch for helping to design and build the reactor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corella Puertas, E., Dzafic, A. & Coulombe, S. Investigation of the Electrode Erosion in Pin-to-Liquid Discharges and Its Influence on Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species in Plasma-Activated Water. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 40, 145–167 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-019-10036-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-019-10036-3