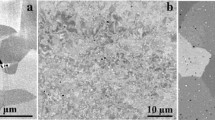
Abstract
The effect of water vapor on the initial stages of oxidation of the FeCrAl alloy Kanthal AF is reported. Polished samples were exposed isothermally at 900 °C for 1, 24, 72 and 168 h in a well-controlled environment consisting of dry O2 or O2 + 40% H2O. The samples were investigated using a combination of gravimetry and several surface-analytical techniques, including XRD, SEM, EDX, FIB, AES and TEM. The presence of water vapor significantly accelerates oxidation during the first 72 h. A two-layered oxide forms in both the dry and wet environments. The bottom layer consists of inward-growing α-Al2O3 while the outer layer initially consists of outward-growing γ-Al2O3. A straight and narrow Cr-enriched band is present at the top of the lower (α-Al2O3) oxide, corresponding to the original sample surface. In dry O2, the top (γ-Al2O3) layer is converted into a mixture of γ-Al2−x (Mg,Fe) x O3−(x/2), MgAl2O4 and α-Al2O3. This transformation does not occur in O2 + H2O. The initial acceleration of oxidation by H2O is attributed to the stabilization of the outward-growing γ-alumina layer by the hydroxylation of the γ-Al2O3 surface. A schematic mechanism of the early stages of oxidation of FeCrAl alloys is presented, emphasizing the influence of water vapor.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Berthome, E. N’Dah, Y. Wouters, and A. Galerie, Temperature dependence of metastable alumina formation during thermal oxidation of FeCrAl foils. Materials and Corrosion 56, 389–392 (2005).
J. R. Nicholls, M. J. Bennett, and R. Newton, A life prediction model for the chemical failure of FeCrAlRE alloys: preliminary assessment of model extension to lower temperatures. Materials at High Temperatures 20, 429–438 (2003).
H. Josefsson, F. Liu, J.-E. Svensson, M. Halvarsson, and L.-G. Johansson, Oxidation of FeCrAl alloys at 500–900°C in dry O2. Materials and Corrosion 56, 801–806 (2005).
M. Boualam, G. Beranger, and M. Lambertin, Oxidation of an alumina-forming alloy: Morphological and structural study. Microsc. Oxid. 2, Proc. Int. Conf., 2nd, 243–252 (1993).
P. Kofstad, High Temperature Corrosion (Elsevier Applied Science, 1988) 408–412.
F. H. Stott, G. C. Wood, and J. Stringer, The influence of alloying elements on the development and maintenance of protective scales. Oxidation of Metals 44, 113–145 (1995).
P. F. Tortorelli, K. L. More, E. D. Specht, B. A. Pint, and P. Zschack, Growth stress – microstructure relationships for alumina scales. Materials at High Temperatures 20, 303–309 (2003).
M. Schütze, Failure of oxide scales on advanced materials due to the presence of stresses. High Temperature Corrosion of Advanced Materials and Protective Coatings 39–49 (1992).
R. Newton, M. J. Bennett, J. P. Wilber, J. R. Nicholls, D. Naumenko, W. J. Quaddakkers, H. Al-Badairy, G. Tatlock, G. Strehl, G. Borchardt, A. Kolb-Telieps, B. Jönsson, A. Westerlund, V. Guttermann, M. Maier, and P. Beaven, The oxidation lifetime of commercial FeCrAl(RE) alloys. European Federation of Corrosion Publications 34, 15–36 (2001).
J. R. Nicholls, R. Newton, M. J. Bennett, H. E. Evans, H. Al-Badairy, G. J. Tatlock, D. Naumenko, W. J. Quaddakkers, G. Strehl, and G. Borchardt, Development of a life prediction model for the chemical failure of FeCrAl(RE) alloys in oxidizing environments. European Federation of Corrosion Publications 34, 83–106 (2001).
H. Al-Badairy, G. J. Tatlock, and M. J. Bennett, A comparison of breakaway oxidation in wedge-shaped and parallel sided coupons of Fe–Cr–Al alloys. Materials at High Temperatures 17, 101–107 (2000).
K. Onal, M. C. Maris-Sida, G. H. Meier, and F. S. Pettit, Water vapour effects on the cyclic oxidation resistance of alumina forming alloys. Materials at High Temperatures (2003).
H. Al-Badairy, and G. J. Tatlock, The influence of moisture content of the atmosphere on alumina scale formation and growth during high temperature oxidation of PM2000. Materials at High Temperatures 17, 133–137 (2000)
A. Kolb-Telieps, U. Miller, H. Al-Badairy, G. J. Tatlock, D. Naumenko, W. J. Quadakkers, G. Strehl, G. Borchardt, R. Newton, J. R. Nicholls, M. Maier, and D. Baxter, The Role of Bioxidant Corrodents on the Lifetime Behavior of FeCrAl(RE) Alloys. Lifetime modelling of high temperature corrosion processes, proceedings of an EFC workshop 34, 123–134 (2001).
H. Buscail, S. Heinze, Ph. Dufour, and J. P. Larpin, Water-Vapor-Effect on the Oxidation of Fe-21.5wt.%Cr-5.6wt.Al at 1000°C. Oxidation of Metals 47, 445–465 (1997).
J. -R. Regina, J. N. DuPont, and A. R. Marder, The effect of Water Vapor on passive-Layer Stability and Corrosion Behavior of Fe–Al–Cr Base Alloys. Oxidation of Metals 61, 69–90 (2004).
I. Kvernes, M. Oliveira, and P. Kofstad, High temperature oxidation of Fe–13Cr–xAl alloys in air/water vapor mixtures. Corrosion Science 17, 237–52 (1977).
R. Janakiraman, G. H. Meier, and F. S. Pettit, The effect of water vapour on the oxidation of alloys that develop alumina scales for protection. Tri-Service Conference on Corrosion, Proceedings, Wrightsville Beach, N. C., 1997 2, 20/1–20/15 (1997).
R. Bachorczyk, and R. Fordham, Long-term, cyclic oxidation behaviour of alumina- and chromia- forming alloys. Diffusion and Defect Data–Solid State Data, Pt. A: Defect and Diffusion Forum 237–240, 1107–1114 (2005).
F. Liu, H. Josefsson, J.-E. Svensson, L.-G. Johansson, and M. Halvarsson, TEM investigation of the base oxide formed on FeCrAl at 900°C in dry O2 and O +2 40%H2O. Materials at High Temperatures 22(n3–4), 521–526 (2005).
H. Josefsson, F. Liu, J.-E. Svensson, M. Halvarsson, and L.-G. Johansson, The Formation of Oxide Scale on FeCrAl at 900°C in dry O2 and O +2 40% H2O. Electro Chemical Society, High Temperature Corrosion and Materials Chemistry V, 56–66 (2005).
H. J. Grabke, M. S. Siegers, and V. K. Tolpygo, Mechanisms of reactive element and impurity element effects in the oxidation of Fe–Cr–Al alloys. Int. Conf. on Metal supported automotive Catalytic Converters (Wuppertal, Germany, 1997).
I. M. Allam, D. P. Whittle, and J. Stringer Improvements in oxidation resistance by dispersed oxide addition: alumina-forming alloys. Oxidation of Metals 13, 381–401 (1979).
F. Liu, H. Josefsson, J.-E. Svensson, L.-G. Johansson, and M. Halvarsson, SEM investigation of reactive element particles on the surface of Kanthal AF oxidized at 900 °C. International Corrosion Congress in China 2005 (2005).
F. Liu, H. Josefsson, J.-E. Svensson, L.-G. Johansson, and M. Halvarsson, Early stages of the oxidation of the FeCrAl alloy Kanthal AF at 900 °C; a detailed microstructural investigation, to be published.
J. Mayer, H. J. Penkalla, A. Dimyati, M. Dani, M. Untoro, D. Naumenko, and W. J. Quaddakkers Time dependence of Mg-incorporation in alumina scales on FeCrAl alloys studied by FIB-prepared TEM cross sections. Materials at High Temperatures 20, 413–419 (2003).
A. Andoh, S. Taniguchi, and T. Shibata, TEM observation of phase transformations of alumina scales formed on Al-deposited Fe-Cr-Al foils. Materials Science Forum 369–372, 303–310 (2001)
H. El Kadiri, R. Molins, Y. Bienvenu and M. F. Horstemeyer, Abnormal high growth rates of metastable aluminas on FeCrAl alloys. Oxidation of Metals 64, 63–97 (2005).
H. Asteman, J.-E. Svensson, and L.-G. Johansson, Evidence for chromium evaporation influencing the oxidation of 304L: the effect of temperature and flow rate. Oxidation of Metals 57, 193–216 (2002).
Z. Lodziana, N.-Y. Topsoe, and J. K. Norskov, A negative surface energy for alumina. Nature Materials 3, 289–293 (2004).
L. K. Hudson, C. Misra, A. J. Perrotta, K. Wefers, and F. S. Williams, Aluminium Oxide. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry (2002).
Acknowledgements
The work was performed within the Swedish High Temperature Corrosion Centre (HTC). The authors wish to acknowledge the support from Kanthal AB, Sandvik Materials Technology AB and the National Graduate School in Materials Science at Chalmers. A grant from Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation for acquiring the FEG-SEM instrument is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Götlind, H., Liu, F., Svensson, JE. et al. The Effect of Water Vapor on the Initial Stages of Oxidation of the FeCrAl Alloy Kanthal AF at 900 °C. Oxid Met 67, 251–266 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-007-9055-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-007-9055-0