Abstract
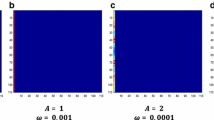
The formation of spiral waves in excitable media is a fascinating example of the beauty of nonlinear dynamics in spatiotemporal systems. Apart from the beauty of the patterns, the subject also has many practical application. For example, the emergence of spiral waves in cardiac tissue can lead to arrhythmias. Cortical spiral waves are also involved in epileptic seizures. Motivated by this, we here study the effects of magnetic induction on the formation of spiral waves in excitable media. An external sinusoidal magnetic induction with different amplitudes and angular frequencies is applied in order to study whether spiral waves could be eliminated. We use a network of coupled neurons as a model for the excitable medium. The four-variable magnetic Hindmarsh–Rose model is used for the local dynamics of each isolated neuron. The distribution of the cell membrane potential over time, affected by magnetic induction, is determined and the results are depicted as snapshots of the 2D network. Our research reveals that the continuance of rotating spiral seeds is impaired by high-amplitude magnetic induction. Moreover, we show that low-frequency induction is not capable of breaking the reorganizing rhythm of the spiral seeds, while much higher frequencies can be too fast to overcome this special rhythm.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldenfeld, N., Kadanoff, L.P.: Simple lessons from complexity. Science 284, 87–89 (1999)
Gell-Mann, M.: Simplicity and complexity in the description of nature. Eng. Sci. 51, 2–9 (1988)
Perc, M.: Stability of subsystem solutions in agent-based models. Eur. J. Phys. 39, 014001 (2017)
Holovatch, Y., Kenna, R., Thurner, S.: Complex systems: physics beyond physics. Eur. J. Phys. 38(2), 023002 (2017)
Guo, S., Xu, Y., Wang, C., Jin, W., Hobiny, A., Ma, J.: Collective response, synapse coupling and field coupling in neuronal network. Chaos Solitons Fractals 105, 120–127 (2017)
Wu, F., Wang, Y., Ma, J., Jin, W., Hobiny, A.: Multi-channels coupling-induced pattern transition in a tri-layer neuronal network. Physica A 493, 54–68 (2018)
Yilmaz, E., Ozer, M., Baysal, V., Perc, M.: Autapse-induced multiple coherence resonance in single neurons and neuronal networks. Sci. Rep. 6, 30914 (2016)
Li, X., Rakkiyappan, R., Sakthivel, N.: Non-fragile synchronization control for markovian jumping complex dynamical networks with probabilistic time-varying coupling delays. Asian J. Control 17, 1678–1695 (2015)
Li, X., Fu, X.: Synchronization of chaotic delayed neural networks with impulsive and stochastic perturbations. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 16, 885–894 (2011)
Ma, J., Tang, J.: A review for dynamics in neuron and neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 89, 1569–1578 (2017)
Gosak, M., Markovič, R., Dolenšek, J., Rupnik, M.S., Marhl, M., Stožer, A., Perc, M.: Network science of biological systems at different scales: a review. Phys. Life Rev. 24, 118–135 (2018)
Gosak, M., Markovič, R., Dolenšek, J., Rupnik, M.S., Marhl, M., Stožer, A., Perc, M.: Loosening the shackles of scientific disciplines with network science: reply to comments on network science of biological systems at different scales: a review. Phys. Life Rev. 24, 162–167 (2018)
Milton, J., Jung, P.: Epilepsy as a Dynamic Disease. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Xu, Y., Jia, Y., Ma, J., Hayat, T., Alsaedi, A.: Collective responses in electrical activities of neurons under field coupling. Sci. Rep. 8, 1349 (2018)
Wang, C., Ma, J.: A review and guidance for pattern selection in spatiotemporal system. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 32, 1830003 (2018)
Mvogo, A., Takembo, C.N., Fouda, H.P.E., Kofané, T.C.: Pattern formation in diffusive excitable systems under magnetic flow effects. Phys. Lett. A 381, 2264–2271 (2017)
Takembo, C.N., Mvogo, A., Ekobena Fouda, H.P., Kofané, T.C.: Modulated wave formation in myocardial cells under electromagnetic radiation. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 32, 1850165 (2018)
Xiang, W., Huangpu, Y.: Second-order terminal sliding mode controller for a class of chaotic systems with unmatched uncertainties. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 15, 3241–3247 (2010)
Sinha, S., Sridhar, S.: Patterns in Excitable Media: Genesis, Dynamics, and Control. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2014)
Zhang, J., Tang, J., Ma, J., Luo, J.M., Yang, X.Q.: The dynamics of spiral tip adjacent to inhomogeneity in cardiac tissue. Physica A 491, 340–346 (2018)
Banerjee, M., Ghorai, S., Mukherjee, N.: Approximated spiral and target patterns in Bazykins prey-predator model: Multiscale perturbation analysis. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 27, 1750038 (2017)
Woo, S.-J., Lee, J., Lee, K.J.: Spiral waves in a coupled network of sine-circle maps. Phys. Rev. E 68, 016208 (2003)
Hu, B., Ma, J., Tang, J.: Selection of multiarmed spiral waves in a regular network of neurons. PLoS ONE 8, e69251 (2013)
Li, F., Ma, J.: Pattern selection in network of coupled multi-scroll attractors. PLoS ONE 11(4), e0154282 (2016)
Perc, M.: Effects of small-world connectivity on noise-induced temporal and spatial order in neural media. Chaos Solitons Fractals 31, 280–291 (2007)
Panfilov, A.V., Müller, S.C., Zykov, V.S., Keener, J.P.: Elimination of spiral waves in cardiac tissue by multiple electrical shocks. Phys. Rev. E 61, 4644–4647 (2000)
Pertsov, A.M., Davidenko, J.M., Salomonsz, R., Baxter, W.T., Jalife, J.: Spiral waves of excitation underlie reentrant activity in isolated cardiac muscle. Circ. Res. 72, 631–650 (1993)
Cherry, E.M., Fenton, F.H., Krogh-Madsen, T., Luther, S., Parlitz, U.: Introduction to focus issue complex cardiac dynamics (2017)
Cherry, E.M., Fenton, F.H.: Visualization of spiral and scroll waves in simulated and experimental cardiac tissue. New J. Phys. 10, 125016 (2008)
Christini, D.J., Glass, L.: Introduction: mapping and control of complex cardiac arrhythmias. Chaos 12, 732–739 (2002)
Gray, R.A., Pertsov, A.M., Jalife, J.: Spatial and temporal organization during cardiac fibrillation. Nature 392, 75 (1998)
Takagaki, K., Zhang, C., Wu, J.-Y., Ohl, F.W.: Flow detection of propagating waves with temporospatial correlation of activity. J. Neurosci. Methods 200, 207–218 (2011)
Schiff, S.J., Huang, X., Wu, J.-Y.: Dynamical evolution of spatiotemporal patterns in mammalian middle cortex. BMC Neurosci. 8, P61 (2007)
Li, Y., Oku, M., He, G., Aihara, K.: Elimination of spiral waves in a locally connected chaotic neural network by a dynamic phase space constraint. Neural Netw. 88, 9–21 (2017)
Ge, M., Jia, Y., Xu, Y., Yang, L.: Mode transition in electrical activities of neuron driven by high and low frequency stimulus in the presence of electromagnetic induction and radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 91, 515–523 (2018)
Li, J., Liu, S., Liu, W., Yu, Y., Wu, Y.: Suppression of firing activities in neuron and neurons of network induced by electromagnetic radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 83, 801–810 (2016)
Wu, F., Wang, C., Xu, Y., Ma, J.: Model of electrical activity in cardiac tissue under electromagnetic induction. Sci. Rep. 6, 28 (2016)
Lv, M., Ma, J.: Multiple modes of electrical activities in a new neuron model under electromagnetic radiation. Neurocomputing 205, 375–381 (2016)
Ma, J., Mi, L., Zhou, P., Xu, Y., Hayat, T.: Phase synchronization between two neurons induced by coupling of electromagnetic field. Appl. Math. Comput. 307, 321–328 (2017)
Perez-Olivas, H., Cordova-Fraga, T., Gómez-Aguilar, F., Rosas-Padilla, E., Lopez-Briones, S., Espinoza-García, A., Villagómez-Castro, J., Bernal-Alvarado, J., Sosa-Aquino, M.: Magnetic exposure system to stimulate human lymphocytes proliferation. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, Volume 1494, pp. 146–148. AIP (2012)
Rastogi, P., Lee, E., Hadimani, R.L., Jiles, D.C.: Transcranial magnetic stimulation-coil design with improved focality. AIP Adv. 7, 056705 (2017)
Hindmarsh, J., Rose, R.: A model of the nerve impulse using two first-order differential equations. Nature 296, 162 (1982)
Hodgkin, A.L., Huxley, A.F.: A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 117, 500–544 (1952)
Wu, J., Xu, Y., Ma, J.: Lévy noise improves the electrical activity in a neuron under electromagnetic radiation. PLoS ONE 12, e0174330 (2017)
Lv, M., Wang, C., Ren, G., Ma, J., Song, X.: Model of electrical activity in a neuron under magnetic flow effect. Nonlinear Dyn. 85, 1479–1490 (2016)
Chua, L.: Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 18, 507–519 (1971)
Li, X., Rakkiyappan, R., Velmurugan, G.: Dissipativity analysis of memristor-based complex-valued neural networks with time-varying delays. Inf. Sci. 294, 645–665 (2015)
Strukov, D.B., Snider, G.S., Stewart, D.R., Williams, R.S.: The missing memristor found. Nature 453, 80 (2008)
Rakkiyappan, R., Sivasamy, R., Li, X.: Synchronization of identical and nonidentical memristor-based chaotic systems via active backstepping control technique. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 34, 763–778 (2015)
Kandel, E.R., Schwartz, J.H., Jessell, T.M., Siegelbaum, S.A., Hudspeth, A.J., et al.: Principles of Neural Science, vol. 4. McGraw-Hill, New York (2000)
Shu, Y., Duque, A., Yu, Y., Haider, B., McCormick, D.A.: Properties of action-potential initiation in neocortical pyramidal cells: evidence from whole cell axon recordings. J. Neurophysiol. 97, 746–760 (2007)
Acknowledgements
Sajad Jafari was supported by the Iran National Science Foundation (Grant No. 96000815). Matjaž Perc was supported by the Slovenian Research Agency (Grants Nos. J1-7009 and P5-0027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rostami, Z., Jafari, S., Perc, M. et al. Elimination of spiral waves in excitable media by magnetic induction. Nonlinear Dyn 94, 679–692 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4385-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4385-9