Abstract
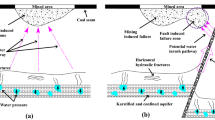
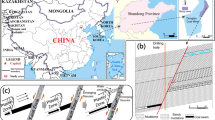
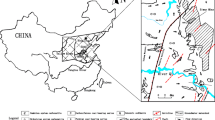
Groundwater outburst has an impartible relationship with geological structures such as water-conducting faults, which are widely distributed in north China. In order to study the seepage property and mechanism of water outburst from the faults above a confined aquifer in the coal mining, the simulation model of ground water inrush for fault was designed. The water outburst parameters, such as water inflow, permeability, seepage velocity, porosity and other variables under different material combination and water pressures, were obtained; the research results indicate as follows: (1) The changes of the water inflow can be divided into three stages, i.e., the water inflow slowly increases at the early stage, rapidly increases at the middle stage and keeps unchanged at the late stage. (2) The seepage process can be represented by the seepage combination types, which are composed of pore flow, fissure flow and pipe flow, and the seepage changes not only with time but also with different conditions. (3) Mining would lead to the reactivation of faults and further enhance the permeability of fault zone potentially. The tiny granules in fault would be eroded and moved to exterior as the time under the high water pressure and lead to the change of porosity parameters. In this case, the seepage velocity would increase ceaselessly, and then the seepage would convert into pipe flow and finally lead to water inrush accidents.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babiker M, Gudmundsson A (2004) The effects of dykes and faults on groundwater flow in an arid land: the Red Sea Hills, Sudan. J Hydrol 297:256–273
Bieniawski ZT (1982) Improved design of coal pillars for US mining conditions. In: Proceedings of the first international conference on stability in underground mining, Vancouver, Canada, pp 8–16
Caine JS, Evans JP, Foster CB (1995) Fault zone architecture and permeability structure. Geology 24:1025–1028
Li LJ (1996) Study of water in-rush mechanism, Ph.D. thesis, China University of Mining and Geology, Xuzhou, People’s Republic of China
Li GY, Zhou WF (2006) Impact of karst water on coal mining in North China. Eng Geol 49:449–457
Li LC, Yang TH, Liang ZZ et al (2011) Numerical investigation of groundwater outbursts near faults in underground coal mines. Int J Coal Geol 85:276–288
Wang ZY, Liu TQ (1989) Study of water in-rush mechanism of coal seam floor strata. Coalf Geol Surv 1:9–36 (in Chinese and abstract in English)
Wang LG, Miao XX (2006) Numerical simulation of coal floor fault activation influenced by mining. J Chin Univ Min Technol 16:385–388
Wang JA, Park HD (2003) Coal mining above a confined aquifer. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 40:537–555
Wu Q, Wang M, Wu X (2004) Investigations of groundwater bursting into coal mine seam floors from fault zones. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41:557–571
Wu Q, Zhou WF (2008) Prediction of groundwater inrush into coal mines from aquifers underlying the coal seams in China: vulnerability index method and its construction. Eng Geol 56:245–254
Zhang JC (2005) Investigations of water inrushes from aquifers under coal seams. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 42:350–360
Zhang JC, Peng SP (2005) Water inrush and environmental impact of shallow seam mining. Eng Geol 48:1068–1076
Zhang YS, Qu YX (2008) Some problems of karstic collapse posts in North China type coalfields. J Eng Geol 8:35–39 (in Chinese and abstract in English)
Zhang JC, Shen BH (2004) Coal mining under aquifers in China: a case study. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41:629–639
Zhang R, Jiang ZQ, Sun Q et al (2013) The relationship between the deformation mechanism and permeability on brittle rock. Nat Hazard 66:1179–1187
Zhu WC, Wei CH (2011) Numerical simulation on mining-induced water inrushes related to geologic structures using a damage-based hydro mechanical model. Eng Earth Sci 62:43–54
Zhu SY, Jiang ZQ, Cao DT et al (2013) Restriction function of lithology and its composite structure to deformation and failure of mining coal seam floor. Nat Hazard 68:483–495
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the following funding for the supporting of this study: the State Basic Research and Development Program of China (No. 2013CB036003), the PAPD (A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions) and the outstanding innovation PhD student scholarship of China University of Mining and Technology(2013–2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Jiang, Z., Zhou, H. et al. Groundwater outbursts from faults above a confined aquifer in the coal mining. Nat Hazards 71, 1861–1872 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0981-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0981-7