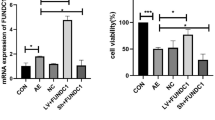
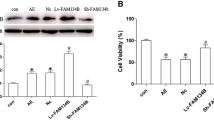
Abstract
Uncovering mechanisms underlying epileptogenesis aids in preventing further epilepsy progression and to lessen seizure severity and frequency. The purpose of this study is to explore the antiepileptogenic and neuroprotective mechanisms of EGR1 in neuron injuries encountered in epilepsy. Bioinformatics analysis was conducted to identify the key genes related to epilepsy. The mice were rendered epileptic using the kainic acid protocol, followed by measurement of seizure severity, high amplitude and frequency, pathological changes of hippocampal tissues and neuron apoptosis. Furthermore, an in vitro epilepsy model was constructed in the neurons isolated from newborn mice, which was then subjected to loss- and gain-of-function investigations, followed by neuron injury and apoptosis assessment. Interactions among EGR1, METTL3, and VIM were analyzed by a series of mechanistic experiments. In the mouse and cell models of epilepsy, VIM was robustly induced. However, its knockdown reduced hippocampal neuron injury and apoptosis. Meanwhile, VIM knockdown decreased inflammatory response and neuron apoptosis in vivo. Mechanistic investigations indicated that EGR1 transcriptionally activated METTL3, which in turn downregulated VIM expression through m6A modification. EGR1 activated METTL3 and reduced VIM expression, thereby impairing hippocampal neuron injury and apoptosis, preventing epilepsy progression. Taken together, this study demonstrates that EGR1 alleviates neuron injuries in epilepsy by inducing METTL3-mediated inhibition of VIM, which provides clues for the development of novel antiepileptic treatments.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that supports the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Thijs RD, Surges R, O’Brien TJ, Sander JW (2019) Epilepsy in adults. Lancet 393:689–701
Wang X, Zhang W, Ge P, Yu M, Meng H (2022) Parthanatos participates in glutamate-mediated HT22 cell injury and hippocampal neuronal death in kainic acid-induced status epilepticus rats. CNS Neurosci Ther 28:2032–2043
Mendez-Armenta M, Nava-Ruiz C, Juarez-Rebollar D, Rodriguez-Martinez E, Gomez PY (2014) Oxidative stress associated with neuronal apoptosis in experimental models of epilepsy. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2014:293689
Henshall DC, Simon RP (2005) Epilepsy and apoptosis pathways. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:1557–1572
Chen KZ, Liu SX, Li YW, He T, Zhao J, Wang T, Qiu XX, Wu HF (2023) Vimentin as a potential target for diverse nervous system diseases. Neural Regen Res 18:969–975
Mhatre R, Poyuran R, Arimappamagan A, Sinha S, Kulanthaivelu K, Kenchaiah R, Ajay A, Chowdary RM, Saini J, Bharath RD, Zanzmera P, Seetharam R, Sadashiva N, Jamuna R, Satishchandra P, Malla BR, Sk S, Anita M (2020) Dual/double pathology in neurocysticercosis causing drug resistant epilepsy-chance association or causal? Epilepsy Res 168:106472
Aronica E, van Vliet EA, Mayboroda OA, Troost D, da Silva FH, Gorter JA (2000) Upregulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR3 and mGluR5 in reactive astrocytes in a rat model of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Eur J Neurosci 12:2333–2344
Liu ZF, Yang J, Wei SP, Luo XG, Jiang QS, Chen T, Gong YQ (2020) Upregulated METTL3 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma enhances the motility of cancer cells. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 36:895–903
Pan Z, Zhang Q, Liu X, Zhou H, Jin T, Hao LY, Xie L, Zhang M, Yang XX, Sun ML, Xue ZY, Tao Y, Ye XC, Shen W, Cao JL (2021) Methyltransferase-like 3 contributes to inflammatory pain by targeting TET1 in YTHDF2-dependent manner. Pain 162:1960–1976
Zhang N, Ding C, Zuo Y, Peng Y, Zuo L (2022) N6-methyladenosine and neurological diseases. Mol Neurobiol 59:1925–1937
Zhao F, Xu Y, Gao S, Qin L, Austria Q, Siedlak SL, Pajdzik K, Dai Q, He C, Wang W, O’Donnell JM, Tang B, Zhu X (2021) METTL3-dependent RNA m(6)a dysregulation contributes to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease through aberrant cell cycle events. Mol Neurodegener 16:70
Lv D, Gimple RC, Zhong C, Wu Q, Yang K, Prager BC, Godugu B, Qiu Z, Zhao L, Zhang G, Dixit D, Lee D, Shen JZ, Li X, Xie Q, Wang X, Agnihotri S, Rich JN (2022) PDGF signaling inhibits mitophagy in glioblastoma stem cells through N(6)-methyladenosine. Dev Cell 57:1466–1481e1466
Szyndler J, Maciejak P, Wislowska-Stanek A, Lehner M, Plaznik A (2013) Changes in the Egr1 and Arc expression in brain structures of pentylenetetrazole-kindled rats. Pharmacol Rep 65:368–378
Friocourt G, Parnavelas JG (2011) Identification of Arx targets unveils new candidates for controlling cortical interneuron migration and differentiation. Front Cell Neurosci 5:28
Levkovitz Y, Baraban JM (2001) A dominant negative inhibitor of the Egr family of transcription regulatory factors suppresses cerebellar granule cell apoptosis by blocking c-Jun activation. J Neurosci 21:5893–5901
Chi ZL, Adini A, Birsner AE, Bazinet L, Akula JD, D’Amato RJ (2019) PR1P ameliorates neurodegeneration through activation of VEGF signaling pathway and remodeling of the extracellular environment. Neuropharmacology 148:96–106
Wang X, Tian X, Yang Y, Lu X, Li Y, Ma Y, Zhang Y, Zheng F, Lu S, Xu D, Xu X, Wang W, Wang X (2017) POSH participates in epileptogenesis by increasing the surface expression of the NMDA receptor: a promising therapeutic target for epilepsy. Expert Opin Ther Targets 21:1083–1094
Dibue M, Kamp MA, Neumaier F, Steiger HJ, Hanggi D, Hescheler J, Schneider T (2014) Cardiac phenomena during kainic-acid induced epilepsy and lamotrigine antiepileptic therapy. Epilepsy Res 108:666–674
Mathon B, Navarro V, Lecas S, Roussel D, Charpier S, Carpentier A (2023) Safety profile of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier opening in non-epileptic mice and in a mouse model of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Ultrasound Med Biol 49:1327–1336
Ma DL, Qu JQ, Goh EL, Tang FR (2015) Reorganization of basolateral amygdala-subiculum circuitry in mouse epilepsy model. Front Neuroanat 9:167
Pottoo FH, Bhowmik M, Vohora D (2014) Raloxifene protects against seizures and neurodegeneration in a mouse model mimicking epilepsy in postmenopausal woman. Eur J Pharm Sci 65:167–173
Pan W, Song X, Hu Q, Zhang Y (2021) miR-485 inhibits histone deacetylase HDAC5, HIF1alpha and PFKFB3 expression to alleviate epilepsy in cellular and rodent models. Aging 13:14416–14432
Wang D, Li Z, Zhang Y, Wang G, Wei M, Hu Y, Ma S, Jiang Y, Che N, Wang X, Yao J, Yin J (2016) Targeting of microRNA-199a-5p protects against pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus and seizure damage via SIRT1-p53 cascade. Epilepsia 57:706–716
Ying C, Ying L, Yanxia L, Le W, Lili C (2020) High mobility group box 1 antibody represses autophagy and alleviates hippocampus damage in pilocarpine-induced mouse epilepsy model. Acta Histochem 122:151485
Zhu P, Wang Y, Wu J, Huang G, Liu B, Ye B, Du Y, Gao G, Tian Y, He L, Fan Z (2016) LncBRM initiates YAP1 signalling activation to drive self-renewal of liver cancer stem cells. Nat Commun 7:13608
Zhang N, Hua X, Tu H, Li J, Zhang Z, Max C (2021) Isorhapontigenin (ISO) inhibits EMT through FOXO3A/METTL14/VIMENTIN pathway in bladder cancer cells. Cancer Lett 520:400–408
Zhang W, Tong H, Zhang Z, Shao S, Liu D, Li S, Yan Y (2018) Transcription factor EGR1 promotes differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by regulating MyoG gene expression. J Cell Physiol 233:350–362
Otte WM, Bielefeld P, Dijkhuizen RM, Braun KP (2012) Focal neocortical epilepsy affects hippocampal volume, shape, and structural integrity: a longitudinal MRI and immunohistochemistry study in a rat model. Epilepsia 53:1264–1273
Stringer JL (1996) Repeated seizures increase GFAP and vimentin in the hippocampus. Brain Res 717:147–153
Chen G, Wang L, Wu J, Jin Y, Wang X, Jin Y (2014) Intractable epilepsy due to angiocentric glioma: a case report and minireview. Exp Ther Med 7:61–65
Larsson A, Wilhelmsson U, Pekna M, Pekny M (2004) Increased cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of old GFAP(−/−)Vim(−/−) mice. Neurochem Res 29:2069–2073
Huang SH, Chi F, Peng L, Bo T, Zhang B, Liu LQ, Wu X, Mor-Vaknin N, Markovitz DM, Cao H, Zhou YH (2016) Vimentin, a novel NF-kappaB regulator, is required for meningitic Escherichia coli K1-Induced pathogen invasion and PMN transmigration across the blood–brain barrier. PLoS ONE 11:e0162641
Xue P, Chen L, Lu X, Zhang J, Bao G, Xu G, Sun Y, Guo X, Jiang J, Gu H, Cui Z (2017) Vimentin promotes astrocyte activation after chronic constriction injury. J Mol Neurosci 63:91–99
Wanna-Udom S, Terashima M, Lyu H, Ishimura A, Takino T, Sakari M, Tsukahara T, Suzuki T (2020) The m6A methyltransferase METTL3 contributes to transforming growth factor-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lung cancer cells through the regulation of JUNB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 524:150–155
Liu J, Zhang N, Zeng J, Wang T, Shen Y, Ma C, Yang M (2022) N(6)-methyladenosine-modified lncRNA ARHGAP5-AS1 stabilises CSDE1 and coordinates oncogenic RNA regulons in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Transl Med 12:e1107
Han X, Guo J, Fan Z (2021) Interactions between m6A modification and miRNAs in malignant tumors. Cell Death Dis 12:598
Zhang N, Zuo Y, Peng Y, Zuo L (2021) Function of N6-methyladenosine modification in tumors. J Oncol 2021:6461552
Liu X, Sun Q, Cao Z, Liu W, Zhang H, Xue Z, Zhao J, Feng Y, Zhao F, Wang J, Wang X (2022) Identification of RNA N6-methyladenosine regulation in epilepsy: significance of the cell death mode, glycometabolism, and drug reactivity. Front Genet 13:1042543
Si W, Li Y, Ye S, Li Z, Liu Y, Kuang W, Chen D, Zhu M (2020) Methyltransferase 3 mediated miRNA m6A methylation promotes stress granule formation in the early stage of acute ischemic stroke. Front Mol Neurosci 13:103
Ming Y, Deng Z, Tian X, Jia Y, Ning M, Cheng S (2022) m6A methyltransferase METTL3 reduces hippocampal neuron apoptosis in a mouse model of autism through the MALAT1/SFRP2/Wnt/beta-catenin axis. Psychiatry Investig 19:771–787
Helbig I, Matigian NA, Vadlamudi L, Lawrence KM, Bayly MA, Bain SM, Diyagama D, Scheffer IE, Mulley JC, Holloway AJ, Dibbens LM, Berkovic SF, Hayward NK (2008) Gene expression analysis in absence epilepsy using a monozygotic twin design. Epilepsia 49:1546–1554
Longueville S, Nakamura Y, Brami-Cherrier K, Coura R, Herve D, Girault JA (2021) Long-lasting tagging of neurons activated by seizures or cocaine administration in Egr1-CreER(T2) transgenic mice. Eur J Neurosci 53:1450–1472
Lopez-Lopez D, Gomez-Nieto R, Herrero-Turrion MJ, Garcia-Cairasco N, Sanchez-Benito D, Ludena MD, Lopez DE (2017) Overexpression of the immediate-early genes Egr1, Egr2, and Egr3 in two strains of rodents susceptible to audiogenic seizures. Epilepsy Behav 71:226–237
Bi GR, Zhang HM, Bai LJ, Zhou HJ, Hai H, Zhang H, Fang XB (2006) Effect of adrenomedullin on neuron apoptosis, infarction volume and expression of Egr-1 mRNA after focal ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Neurosci Bull 22:323–330
Zhu W, Long JL, Yin YT, Guo HN, Jiang EP, Li YL, He QL, Zeng C, Sun YQ (2019) MicroRNA-34a suppresses the invasion and migration of colorectal cancer cells by enhancing EGR1 and inhibiting vimentin. Exp Ther Med 18:2459–2466
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by The Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2021A1515220116), Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou (Grant No. 202201010071, 2023A03J0960) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82001370).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZD, FM and SZ wrote the paper and conceived and designed the experiments; HZ and TZ analyzed the data; ZD and FM collected and provided the sample for this study. All authors have read and approved the final submitted manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
The current study was performed with the approval of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee(IACUC), Sun Yat-Sen University and performed according to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the US National Institutes of Health (SYSU-IACUC-2020-B0178).
Consent for Publication
Consent for publication was obtained from the participants.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Z., Min, F., Zhang, S. et al. EGR1-Driven METTL3 Activation Curtails VIM-Mediated Neuron Injury in Epilepsy. Neurochem Res 48, 3349–3362 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-023-03950-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-023-03950-8