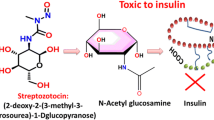
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is an age-related, multifactorial progressive neurodegenerative disorder manifested by cognitive impairment and neuronal death in the brain areas like hippocampus, yet the precise neuropathology of AD is still unclear. Continuous failure of various clinical trial studies demands the utmost need to explore more therapeutic targets against AD. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and neuronal insulin resistance due to serine phosphorylation of Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 at 307 exhibits correlation with AD. Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP-4i) have also indicated therapeutic effects in AD by increasing the level of Glucagon-like peptide-1 in the brain after crossing Blood Brain Barrier. The present study is hypothesized to examine Linagliptin, a DPP-4i in intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced neurodegeneration, and neuroinflammation and hippocampal insulin resistance in rat model of AD. Following infusion on 1st and 3rd day, animals were treated orally with Linagliptin (0.513 mg/kg, 3 mg/kg, and 5 mg/kg) and donepezil (5 mg/kg) as a standard for 8 weeks. Neurobehavioral, biochemical and histopathological analysis was done at the end of treatment. Dose-dependently Linagliptin significantly reversed behavioral alterations done through locomotor activity (LA) and morris water maze (MWM) test. Moreover, Linagliptin augmented hippocampal GLP-1 and Akt-ser473 level and mitigated soluble Aβ (1–42), IRS-1 (s307), GSK-3β, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, AchE and oxidative/nitrosative stress level. Histopathological analysis also exhibited neuroprotective and anti-amylodogenic effect in Hematoxylin and eosin and Congo red staining respectively. The findings of our study concludes remarkable dose-dependent therapeutic potential of Linagliptin against neuronal insulin resistance via IRS-1 and AD-related complication. Thus, demonstrates unique molecular mechanism that underlie AD.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- ICV:
-
Intracerebroventricular
- STZ:
-
Streptozotocin
- Aβ:
-
Amyloid-beta
- T3DM:
-
Type 3 Diabetes Mellitus
- IRS-1:
-
Insulin Receptor Substrate-1
- ISP:
-
Insulin Signaling Pathway
- DPP-4:
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4
- GLP-1:
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1
- GSK-3β:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta
- p-tau:
-
Phosphorylated tau
- LA:
-
Locomotor activity
- MWM:
-
Morris water maze
- TNF-a:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-a
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- BBB:
-
Blood Brain Barrier
- AchE:
-
Acetylcholinesterase
References
Akhtar M, Imam SS, Ahmad MA, Najmi AK, Mujeeb M, Aqil M (2014) Neuroprotective study of Nigella sativa-loaded oral provesicular lipid formulation: in vitro and ex vivo study. Drug Deliv 21:487–494
Asadbegi M, Yaghmaei P, Salehi I, Komaki A, Ebrahim-Habibi A (2017) Investigation of thymol effect on learning and memory impairment induced by intrahippocampal injection of amyloid beta peptide in high fat diet-fed rats. Metab Brain Dis 32:827–839
Ayutyanont N, Chen K, Fleisher AS, Langbaum J, Reschke C, Parks SA, Lee W, Liu X, Protas H, Bandy D (2013) Whole brain atrophy and sample size estimate via iterative principal component analysis for twelve-month Alzheimer’s disease trials. Neurosci Biomed Eng 1:40–47
Ayyub M, Najmi AK, Akhtar M (2017) Protective effect of irbesartan an angiotensin (AT1) receptor antagonist in unpredictable chronic mild stress induced depression in mice. Drug Res 67:59–64
Badawi GA, Abd El Fattah MA, Zaki HF, El Sayed MI (2017) Sitagliptin and liraglutide reversed nigrostriatal degeneration of rodent brain in rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease. Inflammopharmacol 25:369–382
Blázquez E, Velázquez E, Hurtado-Carneiro V, Ruiz-Albusac JM (2014) Insulin in the brain: its pathophysiological implications for States related with central insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Front Endocrinol 5:161
Block ML, Zecca L, Hong JS (2007) Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci 8(1):57–69
Bomfim TR, Forny-Germano L, Sathler LB, Brito-Moreira J, Houzel JC, Decker H, Silverman MA, Kazi H, Melo HM, McClean PL, Holscher C, Arnold SE, Talbot K, Klein WL, Munoz DP, Ferreira ST, Felice FGD (2012) An anti-diabetes agent protects the mouse brain from defective insulin signaling caused by Alzheimer’s disease–associated Aβ oligomers. J Clin Invest 122:1339–1353
Bosco D, Fava A, Plastino M, Montalcini T, Pujia A (2011) Possible implications of insulin resistance and glucose metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. J Cell Mol Med 15:1807–1821
Caruso M, Ma D, Msallaty Z, Lewis M, Seyoum B, Al-Janabi W, Diamond M, Abou-Samra AB, Højlund K, Tagett R (2014) Increased interaction with insulin receptor substrate-1, a novel abnormality in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 63:1933–1947
Chen S, Liu AR, An FM, Yao WB, Gao XD (2012) Amelioration of neurodegenerative changes in cellular and rat models of diabetes-related Alzheimer’s disease by exendin-4. Age (Omaha) 34:1211–1224
Chow VW, Mattson MP, Wong PC, Gleichmann M (2010) An overview of APPprocessing enzymes and products. Neuromol Med 12(1):1–12
Cioanca O, Hritcu L, Mihasan M, Hancianu M (2013) Cognitive-enhancing and antioxidant activities of inhaled coriander volatile oil in amyloid β (1–42) rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Physiol Behav 120:193–202
Cui H, Kong Y, Zhang H (2012) Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and aging. J Signal Transduct 1–13
Darsalia V, Ortsater H, Olverling A (2013) The DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin counteracts stroke in the normal and diabetic mouse brain: a comparison with glimepiride. Diabetes 62:1289–1296
Darsalia V, Larsson M, Lietzau G, Nathanson D, Nystrom T, Klein T, Patrone C (2016) Gliptins-mediated neuroprotection against stroke requires chronic pre-treatment and is glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor independent. Diabetes Obes Metabol 18(5):537–541
Darsalia V, Olverling A, Larsson M, Mansouri S, Nathanson D, Nystrom T, Klein T, Sjoholm A, Patrone C (2014) Linagliptin enhances neural stem cell proliferation after stroke in type 2 diabetic mice. Regul Pept 190–1:25–31
El-Agnaf OM, Mahil DS, Patel BP, Austen BM (2000) Oligomerization and toxicity of beta-amyloid-42 implicated in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 273:1003–1007
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Fargo K (2014) Alzheimer’s association report: 2014 Alzheimers disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement 10:e47–e92
Hamilton A, Holscher C (2009) Receptors for the incretin glucagon-like peptide-1 are expressed on neurons in the central nervous system. NeuroReport 20:1161–1166
Hernandez E, Barreda GD, Fuster-Matanzo A, Lucas JJ, Avila J (2010) GSK3: a possible link between beta amyloid peptide and tau protein. Exp Neurol 223:322–325
Holscher C (2010) Incretin analogues that have been developed to treat type 2 diabetes hold promise as a novel treatment strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov 5:109–117
Hou DR, Wang Y, Zhou I, Chen K, Tian Y, Song Z, Bao J, Yang QD (2008) Altered angiotensin-converting enzyme and its effect on the brain in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Chin Med J (Engl) 121:2320–2323
Husain I, Akhtar M, Abdin MZ, Islamuddin M, Shaharyar M, Najmi AK (2018) Rosuvastatin ameliorates cognitive impairment in rats fed with high-salt and cholesterol diet via inhibiting acetylcholinesterase activity and amyloid beta peptide aggregation. Hum Exp Toxicol 37(4):399–411
Husain I, Akhtar M, Madaan T, Vohora D, Islamuddin M, Abdin MZ, Najmi AK (2018) Tannins enriched fraction of Emblica officinalis fruits alleviates highsalt and cholesterol diet-induced cognitive impairment in rats via Nrf2–ARE pathway. Front Pharmacol 9:23
Husain I, Akhtar M, Vohora D, Abdin MZ, Islamuddin M, Akhtar MJ, Najmi AK (2017) Rosuvastatin attenuates high-salt and cholesterol diet induced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment via preventing nuclear factor kappaB pathway. Neurochem Res 42:2404–2416
Jarrett JT, Lansbury PT (1993) Seeding “one_dimensional crystallization” of amyloid: a pathogenic mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease and scrapie? Cell 73:1055–1058
Javed H, Vaibhav K, Ahmed ME, Khan A, Tabassum R, Islam F, Safhi MM, Islam F (2015) Effect of hesperidin on neurobehavioral, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and lipid alteration in intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced cognitive impairment in mice. J Neurol Sci 348(1–2):51–59
Kabel AM, Omar MS, Alhadhrami A, Alharthif SS, Alrobaianget MM (2018) Linagliptin potentiates the effect of L-dopa on the behavioural, biochemical and immunohistochemical changes in experimentally-induced Parkinsonism: role of toll-like receptor 4, TGF-β1, NF-κB and glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol Behav 188:108–118
Kastin AJ, Akerstrom V, Pan W (2002) Interactions of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) with the blood brain barrier. J Mol Neurosci 18:7–14
Katsurada K, Yada T (2016) Neural effects of gut- and brain-derived glucagon-like peptide-1 and its receptor agonist. J Diabetes Investig 7:64–69
Kaundal M, Akhtar M, Deshmukh R (2017) Lupeol isolated from Betula alnoides ameliorates amyloid beta induced neuronal damage via targeting various pathological events and alteration in neurotransmitter levels in rat’s brain. J Neurol Neurosci 8:1–8
Kaundal M, Deshmukh R, Akhtar M (2018) Protective effect of betulinic acid against Intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced cognitive impairment and neuronal damage in rats: possible neurotransmitters and neuroinflammatory mechanism. Pharmacol Rep 70:540–548
Kosaraju J, Gali CC, Khatwal RB, Dubala A, Chinni S, Holsinger RMD, Rao MVSSTS, Kumar MNS, Duraiswamy B (2013) Saxagliptin: a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor ameliorates streptozotocin induced Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology 72:291–300
Kosaraju J, Holsinger RMD, Guo L, Tam KY (2017) Linagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, mitigates cognitive deficits and pathology in the 3xTg-AD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 54:6074–6084
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Ma QL, Yang F, Rosario ER, Ubeda OJ, Beech W, Gant DJ, Chen PP, Hudspeth B, Chen C, Zhao Y, Vinters HV, Frautschy SA, Cole GM (2009) β-amyloid oligomers induce phosphorylation of tau and inactivation of insulin receptor substrate via c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling: suppression by fatty acids and curcumin. J Neurosci 29:9078–9089
Maqbool M, Mobashir M, Hoda N (2016) Pivotal role of glycogen synthase kinase-3: a therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Med Chem 107:63–81
Mishra SK, Singh S, Shukla S, Shukla R (2018) Intracerebroventricular streptozotocin impairs adult neurogenesis and cognitive functions via regulating neuroinflammation and insulin signaling in adult rats. Neurochem Int 113:56–68
Nassar NN, Al-Shorbagy MY, Arab HH, Abdallah DM (2015) Saxagliptin: a novel antiparkinsonian approach. Neuropharmacology 89:308–317
Neumiller JJ (2012) Pharmacology, Efficacy, and Safety of Linagliptin for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. The Annals of Pharmacother 46:358–367
Padurariu M, Ciobica A, Mavroudis I, Fotiou D, Baloyannis S (2012) Hippocampal neuronal lossin the CA1 and CA3 areas of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Psychiatr Danub 24:152–158
Pandey A, Bani S, Dutt P, Kumar Satti N, Avtar Suri K, Nabi Qazi G (2018) Multifunctional neuroprotective effect of Withanone, a compound from Withania somnifera roots in alleviating cognitive dysfunction. Cytokine 102:211–221
Puzzo D, Vitolo O, Trinchese F, Jacob JP, Palmeri A, Arancio A (2005) Amyloid-β peptide inhibits activation of the nitric oxide/cGMP/cAMP-responsive element binding protein pathway during hippocampal synaptic plasticity. J Neurosci 25:6887–6897
Rajasekar N, Nath C, Hanif K, Shukla R (2016) Intranasal insulin administration ameliorates streptozotocin (ICV)-induced insulin receptor dysfunction, neuroinflammation, amyloidogenesis, and memory impairment in rats. Mol Neurobiol 54(8):6507–6522
Rahman SO, Panda BP, Parvez S, Kaundal M, Hussain S, Akhtar M, Najmi AK (2019) Neuroprotective role of astaxanthin in hippocampal insulin resistance induced by Aβ peptides in animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Pharmacother 110:47–58
Rohnert P, Schmidt W, Emmerlich P, Goihl A, Wrenger S, Bank U, Nordhoff K, Tager M, Ansorge S, Reinhold D, Striggow F (2012) Dipeptidyl peptidase IV, aminopeptidase N and DPIV/APN-like proteases in cerebral ischemia. J Neuroinflamm 9:44
Sachdeva AK, Chopra K (2015) Lycopene abrogates Abeta (1–42) mediated neuroinflammatory cascade in an experimental model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Nutr Biochem 26:736–744
Shannon RP (2013) DPP-4 inhibition and neuroprotection: do mechanisms matter? Diabetes 62:1029–1031
Siddiqui N, Ali J, Parvez S, Zameer S, Najmi AK, Akhtar M (2021) Linagliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, ameliorates Aβ (1–42) peptides induced neurodegeneration and brain insulin resistance (BIR) via insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) in rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacol 195:1–14
Singh B, Sharma B, Jaggi AS, Singh N (2013) Attenuating effect of lisinopril and telmisartan in intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced experimental dementia of Alzheimer’s disease type: possible involvement of PPAR-gamma agonistic property. J Renin Syst 14(2):124–136
Soheili M, Tavirani MR, Salami M (2012) Clearance of amyloid beta plaques from brain of Alzheimeric rats by lavandula angustifolia. Neurosci Med 3(04):362
Song Y, Cui T, Xie N, Zhang X, Qian Z, Liu J (2014) Protocatechuic acid improves cognitive deficits and attenuates amyloid deposits, inflammatory response in aged A beta PP/PS1 double transgenic mice. Int Immunopharmacol 20(1):276–281
Stanciu GD, Luca A, Rusu RN, Bild V, Chiriac SIB, Solcan C, Bild W, Ababei DC (2020) Alzheimer’s disease Pharmacotherapy in Relation to Cholinergic System Involvement. Biomolecules 10:40
Talbot K (2014) Brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer’s disease and its potential treatment with GLP-1 analogs. Neurodegener Dis Manag 4:31–40
Thenmozhi AJ, Raja TRW, Janakiraman U, Manivasagam T (2015) Neuroprotective effect of hesperidin on aluminium chloride induced Alzheimer’s disease in Wistar rats. Neurochem Res 40:767–776
Wang D, Liu L, Li S, Wang C (2018) Effects of paeoniflorin on neurobehavior, oxidative stress, brain insulin signaling, and synaptic alterations in intracerebroventricular streptozotocin-induced cognitive impairment in mice. Physiol Behav 191:12–20
Wang D, Wang C, Liu L, Li S (2018) Protective effects of evodiamine in experimental paradigm of Alzheimer’s disease. Cogn Neurodyn 12(3):303–313
Wei L, Lv S, Huang Q, Wei J, Zhang S, Huang R, Lu Z, Lin X (2015) Pratensein attenuates Aβ-induced cognitive deficits in rats: enhancement of synaptic plasticity and cholinergic function. Fitoterapia 101:208–217
Wills ED (1966) Mechanisms of lipid peroxide formation in animal tissues. Biochem J 99:667–676
Zameer S, Kaundal M, Vohora D, Ali J, Najmi AK, Akhtar M (2019) Ameliorative effect of alendronate against intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced alteration in neurobehavioral, neuroinflammation and biochemical parameters with emphasis on Aβ and BACE-1. Neurotoxicol 70:122–134
Zhang X, Dong F, Ren J, Driscoll MJ, Culver B (2005) High dietary fat induces NADPH oxidase-associated oxidative stress and inflammation in rat cerebral cortex. Exp Neurol 191:318–325
Zhang YY, Fan YC, Wang M, Wang D, Li XH (2013) Atorvastatin attenuates the production of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in the hippocampus of an amyloid β1-42- induced rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Interv Aging 8:103
Zhang X, Tang S, Zhang Q, Shao W, Han X, Wang Y, Du Y (2016) Endoplasmic reticulum stress mediates JNK-dependent IRS-1 serine phosphorylation and results in Tau hyperphosphorylation in amyloid β oligomer-treated PC12 cells and primary neurons. Gene 587(2):183–193
Acknowledgements
The authors of this research express their gratitude to Prof. Suhel Parvez, Department of Medical Elementology and Toxicology, School of Chemical and Life Sciences (SCLS), Jamia Hamdard, New Delhi for extending his helping hands for the necessary facilities required during this research work.
Funding
Study was funded by Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. in collaboration with Pharmaceutical Medicine Program of Jamia Hamdard.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have reviewed the manuscript. There is no conflict of interest.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of Interest
Authors of our study declare no potential conflicts of interest in conducting research and publishing this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Siddiqui, N., Ali, J., Parvez, S. et al. Neuroprotective Role of DPP-4 Inhibitor Linagliptin Against Neurodegeneration, Neuronal Insulin Resistance and Neuroinflammation Induced by Intracerebroventricular Streptozotocin in Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem Res 48, 2714–2730 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-023-03924-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-023-03924-w