Abstract
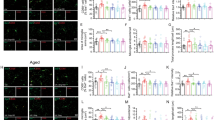
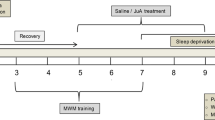
Sleep deprivation (SD) is widespread in society causing serious damage to cognitive function. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S), the third gas signal molecule, plays important regulatory role in learning and memory functions. Inhibition of excessive autophagy and upregulation of silent information regulator 1 (Sirt-1) have been reported to prevent cognitive dysfunction. Therefore, this present work was to address whether H2S attenuates the cognitive impairment induced by SD in Wistar rats and whether the underlying mechanisms involve in inhibition of excessive autophagy and upregulation of Sirt-1. After treatment with SD for 72 h, the cognitive function of Wistar rats was evaluated by Y-maze, new object recognition, object location, and Morris water maze tests. The results shown that SD-caused cognitive impairment was reversed by treatment with NaHS (a donor of H2S). NaHS also prevented SD-induced hippocampal excessive autophagy, as evidenced by the decrease in autophagosomes, the down-regulation of Beclin1, and the up-regulation of p62 in the hippocampus of SD-exposed Wistar rats. Furthermore, Sirtinol, an inhibitor of Sirt-1, reversed the inhibitory roles of NaHS in SD-induced cognitive impairment and excessive hippocampal autophagy in Wistar rats. Taken together, our results suggested that H2S improves the cognitive function of SD-exposed rats by inhibiting excessive hippocampal autophagy in a hippocampal Sirt-1-dependent way.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Koyanagi I, Akers KG, Vergara P, Srinivasan S, Sakurai T, Sakaguchi M (2019) Memory consolidation during sleep and adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Neural Regen Res 14:20–23
Chee MWL, Zhou J (2019) Functional connectivity and the sleep-deprived brain. Prog Brain Res 246:159–176
Feng L, Wu HW, Song GQ, Lu C, Li YH, Qu LN, Chen SG, Liu XM, Chang Q (2016) Chronical sleep interruption-induced cognitive decline assessed by a metabolomics method. Behav Brain Res 302:60–68
Bubu OM, Brannick M, Mortimer J, Umasabor-Bubu O, Sebastiao YV, Wen Y, Schwartz S, Borenstein AR, Wu Y, Morgan D, Anderson WM (2017) Sleep, cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep 40:1–18
Havekes R, Vecsey CG, Abel T (2012) The impact of sleep deprivation on neuronal and glial signaling pathways important for memory and synaptic plasticity. Cell Signal 24:1251–1260
Hu LF, Lu M, Hon Wong PT, Bian JS (2011) Hydrogen sulfide: neurophysiology and neuropathology. Antioxid Redox Signal 15:405–419
Qu K, Lee SW, Bian JS, Low CM, Wong PT (2008) Hydrogen sulfide: neurochemistry and neurobiology. Neurochem Int 52:155–165
Tan BH, Wong PT, Bian JS (2010) Hydrogen sulfide: a novel signaling molecule in the central nervous system. Neurochem Int 56:3–10
Kumar M, Modi M, Sandhir R (2017) Hydrogen sulfide attenuates homocysteine-induced cognitive deficits and neurochemical alterations by improving endogenous hydrogen sulfide levels. BioFactors 43:434–450
Kimura H (2013) Physiological role of hydrogen sulfide and polysulfide in the central nervous system. Neurochem Int 63:492–497
Liu C, Xu X, Gao J, Zhang T, Yang Z (2016) Hydrogen sulfide prevents synaptic plasticity from VD-induced damage via Akt/GSK-3beta pathway and notch signaling pathway in rats. Mol Neurobiol 53:4159–4172
Shefa U, Kim D, Kim MS, Jeong NY, Jung J (2018) Roles of gasotransmitters in synaptic plasticity and neuropsychiatric conditions. Neural Plast 2018:1824713
He JT, Li H, Yang L, Mao CY (2019) Role of hydrogen sulfide in cognitive deficits: evidences and mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol 849:146–153
Duan H, Li L, Shen S, Ma Y, Yin X, Liu Z, Yuan C, Wang Y, Zhang J (2020) Hydrogen sulfide reduces cognitive impairment in rats after subarachnoid hemorrhage by ameliorating neuroinflammation mediated by the TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway in microglia. Front Cell Neurosci 14:210
Vandini E, Ottani A, Zaffe D, Calevro A, Canalini F, Cavallini GM, Rossi R, Guarini S, Giuliani D (2019) Mechanisms of hydrogen sulfide against the progression of severe Alzheimer’s disease in transgenic mice at different ages. Pharmacology 103:50–60
Zhang LM, Jiang CX, Liu DW (2009) Hydrogen sulfide attenuates neuronal injury induced by vascular dementia via inhibiting apoptosis in rats. Neurochem Res 34:1984–1992
Zou W, Yuan J, Tang ZJ, Wei HJ, Zhu WW, Zhang P, Gu HF, Wang CY, Tang XQ (2017) Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates cognitive dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: involving suppression in hippocampal endoplasmic reticulum stress. Oncotarget 8:64203–64216
Yuan DS, Huang YQ, Fu YJ, Xie J, Huang YL, Zhou SS, Sun PY, Tang XQ (2020) Hydrogen sulfide alleviates cognitive deficiency and hepatic dysfunction in a mouse model of acute liver failure. Exp Ther Med 20:671–677
Li X, Zhuang YY, Wu L, Xie M, Gu HF, Wang B, Tang XQ (2020) Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates cognitive dysfunction in formaldehyde-exposed rats: involvement in the upregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Neuropsychobiology 79:119–130
Mizushima N, Komatsu M (2011) Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell 147:728–741
Ghavami S, Shojaei S, Yeganeh B, Ande SR, Jangamreddy JR, Mehrpour M, Christoffersson J, Chaabane W, Moghadam AR, Kashani HH, Hashemi M, Owji AA, Los MJ (2014) Autophagy and apoptosis dysfunction in neurodegenerative disorders. Prog Neurobiol 112:24–49
Yang SQ, Jiang L, Lan F, Wei HJ, Xie M, Zou W, Zhang P, Wang CY, Xie YR, Tang XQ (2019) Inhibited endogenous H2S generation and excessive autophagy in hippocampus contribute to sleep deprivation-induced cognitive impairment. Front Psychol 10:53
Cao Y, Li Q, Liu L, Wu H, Huang F, Wang C, Lan Y, Zheng F, Xing F, Zhou Q, Li Q, Shi H, Zhang B, Wang Z, Wu X (2019) Modafinil protects hippocampal neurons by suppressing excessive autophagy and apoptosis in mice with sleep deprivation. Br J Pharmacol 176:1282–1297
Shui M, Liu X, Zhu Y, Wang Y (2016) Exogenous hydrogen sulfide attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting autophagy in mice. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 94:1187–1192
Jiang WW, Huang BS, Han Y, Deng LH, Wu LX (2017) Sodium hydrosulfide attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing overactivated autophagy in rats. FEBS Open Bio 7:1686–1695
Michan S, Sinclair D (2007) Sirtuins in mammals: insights into their biological function. Biochem J 404:1–13
Cao Y, Yan Z, Zhou T, Wang G (2017) SIRT1 regulates cognitive performance and ability of learning and memory in diabetic and nondiabetic models. J Diabetes Res 2017:7121827
Lu Y, Tan L, Wang X (2019) Circular HDAC9/microRNA-138/Sirtuin-1 pathway mediates synaptic and amyloid precursor protein processing deficits in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Bull 35:877–888
Michan S, Li Y, Chou MM, Parrella E, Ge H, Long JM, Allard JS, Lewis K, Miller M, Xu W, Mervis RF, Chen J, Guerin KI, Smith LE, McBurney MW, Sinclair DA, Baudry M, de Cabo R, Longo VD (2010) SIRT1 is essential for normal cognitive function and synaptic plasticity. J Neurosci 30:9695–9707
Gomes BAQ, Silva JPB, Romeiro CFR, Dos Santos SM, Rodrigues CA, Goncalves PR, Sakai JT, Mendes PFS, Varela ELP, Monteiro MC (2018) Neuroprotective mechanisms of resveratrol in Alzheimer’s disease: role of SIRT1. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018:8152373
Jiang Y, Botchway BOA, Hu Z, Fang M (2019) Overexpression of SIRT1 inhibits corticosterone-induced autophagy. Neuroscience 411:11–22
Zuo JX, Li M, Jiang L, Lan F, Tang YY, Kang X, Zou W, Wang CY, Zhang P, Tang XQ (2020) Hydrogen sulfide prevents sleep deprivation-induced hippocampal damage by upregulation of Sirt1 in the hippocampus. Front Neurosci 14:169
Wen X, Qi D, Sun Y, Huang X, Zhang F, Wu J, Fu Y, Ma K, Du Y, Dong H, Liu Y, Liu H, Song Y (2014) H(2)S attenuates cognitive deficits through Akt1/JNK3 signaling pathway in ischemic stroke. Behav Brain Res 269:6–14
Tang YY, Wang AP, Wei HJ, Li MH, Zou W, Li X, Wang CY, Zhang P, Tang XQ (2018) Role of silent information regulator 1 in the protective effect of hydrogen sulfide on homocysteine-induced cognitive dysfunction: involving reduction of hippocampal ER stress. Behav Brain Res 342:35–42
Qian C, Jin J, Chen J, Li J, Yu X, Mo H, Chen G (2017) SIRT1 activation by resveratrol reduces brain edema and neuronal apoptosis in an experimental rat subarachnoid hemorrhage model. Mol Med Rep 16:9627–9635
Suchecki D, Duarte Palma B, Tufik S (2000) Sleep rebound in animals deprived of paradoxical sleep by the modified multiple platform method. Brain Res 875:14–22
Suchecki D, Tufik S (2000) Social stability attenuates the stress in the modified multiple platform method for paradoxical sleep deprivation in the rat. Physiol Behav 68:309–316
Li XN, Chen L, Luo B, Li X, Wang CY, Zou W, Zhang P, You Y, Tang XQ (2017) Hydrogen sulfide attenuates chronic restrain stress-induced cognitive impairment by upreglulation of Sirt1 in hippocampus. Oncotarget 8:100396–100410
Lueptow LM (2017) Novel object recognition test for the investigation of learning and memory in mice. J Vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/55718
Wang S, Su G, Zhang Q, Zhao T, Liu Y, Zheng L, Zhao M (2018) Walnut ( Juglans regia) peptides reverse sleep deprivation-induced memory impairment in rat via alleviating oxidative Stress. J Agric Food Chem 66:10617–10627
Trost Bobic T, Secic A, Zavoreo I, Matijevic V, Filipovic B, Kolak Z, Basic Kes V, Ciliga D, Sajkovic D (2016) The impact of sleep deprivation on the brain. Acta Clin Croat 55:469–473
Pothuizen HH, Zhang WN, Jongen-Relo AL, Feldon J, Yee BK (2004) Dissociation of function between the dorsal and the ventral hippocampus in spatial learning abilities of the rat: a within-subject, within-task comparison of reference and working spatial memory. Eur J Neurosci 19:705–712
Shih YH, Tsai SF, Huang SH, Chiang YT, Hughes MW, Wu SY, Lee CW, Yang TT, Kuo YM (2016) Hypertension impairs hippocampus-related adult neurogenesis, CA1 neuron dendritic arborization and long-term memory. Neuroscience 322:346–357
Ott CV, Johnson CB, Macoveanu J, Miskowiak K (2019) Structural changes in the hippocampus as a biomarker for cognitive improvements in neuropsychiatric disorders: a systematic review. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 29:319–329
Alzoubi KH, Mayyas F, Abu Zamzam HI (2019) Omega-3 fatty acids protects against chronic sleep-deprivation induced memory impairment. Life Sci 227:1–7
Li H, Yu F, Sun X, Xu L, Miu J, Xiao P (2019) Dihydromyricetin ameliorates memory impairment induced by acute sleep deprivation. Eur J Pharmacol 853:220–228
Manchanda S, Singh H, Kaur T, Kaur G (2018) Low-grade neuroinflammation due to chronic sleep deprivation results in anxiety and learning and memory impairments. Mol Cell Biochem 449:63–72
Ocalan B, Cakir A, Koc C, Suyen GG, Kahveci N (2019) Uridine treatment prevents REM sleep deprivation-induced learning and memory impairment. Neurosci Res 148:42–48
Bredesen DE, Rao RV, Mehlen P (2006) Cell death in the nervous system. Nature 443:796–802
Xu Y, Tian Y, Tian Y, Li X, Zhao P (2016) Autophagy activation involved in hypoxic-ischemic brain injury induces cognitive and memory impairment in neonatal rats. J Neurochem 139:795–805
Hao Y, Li W, Wang H, Zhang J, Yu C, Tan S, Wang H, Xu X, Dong J, Yao B, Zhou H, Zhao L, Peng R (2018) Autophagy mediates the degradation of synaptic vesicles: a potential mechanism of synaptic plasticity injury induced by microwave exposure in rats. Physiol Behav 188:119–127
Li X, Wu Z, Zhang Y, Xu Y, Han G, Zhao P (2017) Activation of autophagy contributes to sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity in fetal rats. Front Mol Neurosci 10:432
Fusco S, Maulucci G, Pani G (2012) Sirt1: def-eating senescence? Cell Cycle 11:4135–4146
Shen J, Li Y, Qu C, Xu L, Sun H, Zhang J (2019) The enriched environment ameliorates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive-like behaviors and cognitive impairment by activating the SIRT1/miR-134 signaling pathway in hippocampus. J Affect Disord 248:81–90
Shen J, Xu L, Qu C, Sun H, Zhang J (2018) Resveratrol prevents cognitive deficits induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress: Sirt1/miR-134 signalling pathway regulates CREB/BDNF expression in hippocampus in vivo and in vitro. Behav Brain Res 349:1–7
Yan WJ, Wang DB, Ren DQ, Wang LK, Hu ZY, Ma YB, Huang JW, Ding SL (2019) AMPKalpha1 overexpression improves postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aged rats through AMPK-Sirt1 and autophagy signaling. J Cell Biochem:doi. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28443
Liu SY, Li D, Zeng HY, Kan LY, Zou W, Zhang P, Gu HF, Tang XQ (2017) Hydrogen sulfide inhibits chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive-like behavior by upregulation of Sirt-1: involvement in suppression of hippocampal endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 20:867–876
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81771178), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan province (2019JJ80101), and the Major Research Topics of the Health Commission of Hunan province (20201911).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest associated with this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, S., Tang, YY., Jiang, L. et al. H2S Attenuates Sleep Deprivation-Induced Cognitive Impairment by Reducing Excessive Autophagy via Hippocampal Sirt-1 in WISTAR RATS. Neurochem Res 46, 1941–1952 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03314-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03314-0