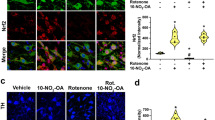
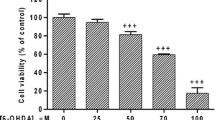
Abstract
FTY720 (fingolimod) is the first oral drug approved for treating relapsing-remitting forms of multiple sclerosis. It is also protective in other neurological models including ischemia, Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington disease and Rett syndrome. However, whether it might protect in a 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) mouse model associated with the dopaminergic pathology of Parkinson’s disease (PD), has not been explored. Therefore, in the present study, we investigated the effects of FTY720 on 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity in cell cultures and mice. Here we show that FTY720 protected against 6-OHDA cytotoxicity and apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. We also show that prior administration of FTY720 to 6-OHDA lesioned mice ameliorated both motor deficits and nigral dopaminergic neurotoxicity, while also reducing 6-OHDA-associated inflammation. The protective effects of FTY720 were associated with activation of AKT and ERK1/2 pro-survival pathways and an increase in brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression in vitro and in vivo. These findings suggest that FTY720 holds promise as a PD therapeutic acting, at least in part, through AKT/ERK1/2/P-CREB-associated BDNF expression.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brinkmann V (2009) FTY720 (fingolimod) in multiple sclerosis: therapeutic effects in the immune and the central nervous system. Brit J Pharmacol 158:1173–1182.
Strader CR, Pearce CJ, Oberlies NH (2011) Fingolimod (FTY720): a recently approved multiple sclerosis drug based on a fungal secondary metabolite. J Nat Prod 74:900–907
Brunkhorst R, Vutukuri R, Pfeilschifter W (2014) Fingolimod for the treatment of neurological diseases-state of play and future perspectives. Front Cell Neurosci 8:283
Deogracias R, Yazdani M, Dekkers MP, Guy J, Ionescu MC, Vogt KE, Barde YA (2012) Fingolimod, a sphingosine-1 phosphate receptor modulator, increases BDNF levels and improves symptoms of a mouse model of Rett syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:14230–14235
Di Pardo A, Amico E, Favellato M, Castrataro R, Fucile S, Squitieri F, Maglione V (2014) FTY720 (fingolimod) is a neuroprotective and disease-modifying agent in cellular and mouse models of Huntington disease. Hum Mol Genet 23:2251–2265
Sivasubramanian M, Kanagaraj N, Dheen ST, Tay SS (2015) Sphingosine kinase 2 and sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes mitochondrial function in dopaminergic neurons of mouse model of Parkinson’s disease and in MPP+ -treated MN9D cells in vitro. Neuroscience 290:636–648
Vargas-Medrano J, Krishnamachari S, Villanueva E, Godfrey WH, Lou H, Chinnasamy R, Arterburn, JB, Perez RG (2014) Novel FTY720-based compounds stimulate neurotrophin expression and phosphatase activity in dopaminergic cells. ACS Med Chem Lett 5:782–786.
Vidal-Martínez G, Vargas-Medrano J, Gil-Tommee C, Medina D, Garza NT, Yang B, Segura-Ulate I, Dominguez SJ, Perez RG (2016) FTY720/fingolimod reduces synucleinopathy and improves gut motility in A53T mice: contribution of pro-brain-derived neurotrophic factor (pro-BDNF) and mature BDNF. J Biol Chem 291:20811–20821
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH image to imagej: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675
Lou H, Jing X, Wei X, Shi H, Ren D, Zhang X (2014) Naringenin protects against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity via activation of the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Neuropharmacology 79:380–388
Signore AP, Weng Z, Hastings T, Van Laar AD, Liang Q, Lee YJ, Chen J (2006) Erythropoietin protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced dopaminergic cell death. J Neurochem 96:428–443
Zhu KY, Fu Q, Leung KW, Wong ZC, Choi RC, Tsim KW (2011) The establishment of a sensitive method in determining different neurotransmitters simultaneously in rat brains by using liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 879:737–742
Fukumoto K, Mizoguchi H, Takeuchi H, Horiuchi H, Kawanokuchi J, Jin S, Mizuno T, Suzumura A (2014) Fingolimod increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and ameliorates amyloid beta-induced memory impairment. Behav Brain Res 268:88–93
Hemmati F, Dargahi L, Nasoohi S, Omidbakhsh R, Mohamed Z, Chik Z, Naidu M, Ahmadiani A (2013) Neurorestorative effect of FTY720 in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease: comparison with memantine. Behav Brain Res 252:415–421
Wei Y, Yemisci M, Kim HH, Yung LM, Shin HK, Hwang SK, Guo S, Qin T, Alsharif N, Brinkmann V, Liao JK, Lo EH, Waeber C (2011) Fingolimod provides long-term protection in rodent models of cerebral ischemia. Ann Neurol 69:119–129
Scalzo P, Kummer A, Bretas TL, Cardoso F, Teixeira AL (2010) Serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor correlate with motor impairment in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 257:540–545
Razgado-Hernandez LF, Espadas-Alvarez AJ, Reyna-Velazquez P, Sierra-Sanchez A, Anaya-Martinez V, Jimenez-Estrada I, Bannon MJ, Martinez-Fong D, Aceves-Ruiz J (2015) The transfection of BDNF to dopamine neurons potentiates the effect of dopamine d3 receptor agonist recovering the striatal innervation, dendritic spines and motor behavior in an aged rat model of Parkinson’s disease. PloS One 10:e0117391
Sano H, Murata M, Nambu A (2015) Zonisamide reduces nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurodegeneration in a mouse genetic model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 134:371–381
Cipriani R, Chara JC, Rodriguez-Antiguedad A, Matute C (2015) FTY720 attenuates excitotoxicity and neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflamm 12:86
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81274124, No. 81200982) and Shandong Province Science and Technology Program (No. 2014GSF118038, No.2016GSF201061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, M., Han, M., Wei, X. et al. FTY720 Attenuates 6-OHDA-Associated Dopaminergic Degeneration in Cellular and Mouse Parkinsonian Models. Neurochem Res 42, 686–696 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2125-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2125-4