Abstract
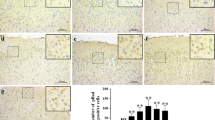
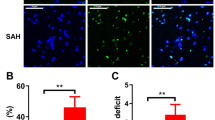
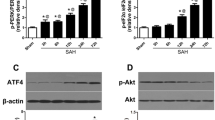
Nur77 is a potent pro-apoptotic member of the orphan nuclear receptor superfamily. Our previous study revealed Nur77-mediated apoptotic also involved in early brain injury (EBI) after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). Previous researches show that c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) positively regulates Nur77 nuclear export and apoptosis by phosphorylating Nur77. To determine whether activation of JNK is directly associated with Nur77 dependent apoptosis pathway. We hypothesized that SP600125, a chemical inhibitor of JNK, may effectively ameliorate EBI by inhibiting Nur77 phosphorylation and its transcriptional activity. Hence, in this study was designed to explore the neuroprotective effects of SP600125 in EBI after SAH. Adult male SD rats were randomly assigned to four groups: control; SAH + DMSO; SAH + SP10 and SAH + SP30, a dose of 10 and 30 mg/kg SP600125 was directly administered intraperitoneally 30 min before and 2 h after SAH induction. SP600125 markedly decreased expressions of p-JNK, p-Nur77, Bcl-2, cyto C, caspase-3 and inhibited apoptosis. Improvement of neurological deficit, alleviation of brain edema and amelioration of EBI were obtained after treatment of SP600125. Transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling-positive cells were reduced markedly in brain cortex by SP600125. Our studies indicate JNK plays important roles in Nur77 activation. These findings strongly support the hypothesis that SP600125 treatment can ameliorate EBI after experimentally induced SAH by inhibiting a Nur77-dependent apoptotic pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balasubramanian S, Jansen M, Valerius MT, Humphreys BD, Strom TB (2012) Orphan nuclear receptor Nur77 promotes acute kidney injury and renal epithelial apoptosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:674–686
Cahill J, Calvert JW, Zhang JH (2006) Mechanisms of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:1341–1353
Chang LF, Lin PC, Ho LI, Liu PY, Wu WC, Chiang IP, Chang HW, Lin SZ, Harn YC, Harn HJ, Chiou TW (2011) Overexpression of the orphan receptor Nur77 and its translocation induced by PCH4 may inhibit malignant glioma cell growth and induce cell apoptosis. J Surg Oncol 103:442–450
Chen D, Wei XT, Guan JH, Yuan JW, Peng YT, Song L, Liu YH (2012) Inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase prevents blood-brain barrier disruption and normalizes the expression of tight junction proteins clautin-5 and ZO-1 in a rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir 154:1469–1476
Chen Q, Gao Y, Kao X, Chen J, Xue W, Xiong Y, Wang Z (2012) SNP-induced apoptosis may be mediated with caspase inhibitor by JNK signaling pathways in rabbit articular chondrocytes. J Toxicol Sci 37:157–167
Cheng Z, Völkers M, Din S, Avitabile D, Khan M, Gude N, Mohsin S, Bo T, Truffa S, Alvarez R, Mason M, Fischer KM, Konstandin MH, Zhang XK, Heller Brown J, Sussman MA (2011) Mitochondrial translocation of Nur77 mediates cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Eur Heart J 32:2179–2188
Cheng G, Wei L, Zhi-Dan S, Shi-Guang Z, Xiang-Zhen L (2009) Atorvastatin ameliorates cerebral vasospasm and early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage and inhibits caspase-dependent apoptosis pathway. BMC Neurosci 10:7
Czosnyka M, Richards H, Pickard JD, Kirkpatrick PJ (2005) Effects of acute treatment with pravastatin on cerebral vasospasm, autoregulation, and delayed ischemic deficits after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a phase II randomized placebo-controlled trial. Stroke 36:1627–1632
Endo H, Nito C, Kamada H, Yu F, Chan PH (2006) Akt/GSK3beta survival signaling is involved in acute brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rat. Stroke 37:2140–2146
Garcia JH, Wagner S, Liu KF, Hu XJ (1995) Neurological deficit and extent of neuronal necrosis attributable to middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats Statistical validation. Stroke 26:627–634
Gules I, Satoh M, Clower BR, Nanda A, Zhang JH (2002) Comparison of three rat models of cerebral vasospasm. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 283:2551–2559
Guo Z, Sun X, He Z, Jiang Y, Zhang X (2010) Role of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in apoptosis of hippocampal neurons in rats during early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurol Sci 31:143–149
Han Y-H, Cao X, Lin B, Kin F, Kolluri SK, Reed JC et al (2006) Regulation of Nur77 nuclear export by c-Jun N-terminal kinase and Akt. Oncogene 25:2974–2986
Hasegawa Y, Suzuki H, Sozen T, Altay O, Zhang JH (2011) Apoptotic mechanisms for neuronal cells in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl 110:43–48
He Z, Ostrowski RP, Sun X, Ma Q, Huang B, Zhan Y, Zhang JH (2012) CHOP silencing reduces acute brain injury in the rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 43:484–490
Ingelmo II, Fàbregas JN, Rama-Maceiras P, Hernández-Palazón J, Rubio RR, Carmona AJ et al (2010) Subarachnoid hemorrhage: epidemiology, social impact and a multidisciplinary approach. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim 57:S4–15
Kolluri SK, Cao X, Bruey-Sedano N, Lin B, Lin F, Han Y et al (2003) Mitogenic effect of orphan receptor TR3 and its regulation by MEKK1 in lung cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol 23:8651–8667
Kusaka G, Ishikawa M, Nanda A, Granger DN, Zhang JH (2004) Signaling pathways for early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24:916–925
Le Roux AA, Wallace MC (2010) Outcome and cost of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurg Clin N Am 21:235–246
Li H, Kolluri SK, Gu J, Dawson MI, Cao X, Hobbs PD et al (2000) Cytochrome c release and apoptosis induced by mitochondrial targeting of nuclear orphan receptor TR3. Science 289:1159–1164
Lin B, Kolluri SK, Lin F, Liu W, Han YH, Cao X, Dawson MI, Reed JC, Zhang XK (2004) Conversion of Bcl-2 from protector to killer by interaction with nuclear orphan receptor Nur77/TR3. Cell 116:527–540
Milbrandt J (1998) Nerve growth factor induces a gene homologous to the glucocorticoid receptor gene. Neuron 1:183–188
Moll UM, Marchenko N, Zhang XK (2006) p53 and Nur77/TR3 -transcription factors that directly target mitochondria for cell death induction. Oncogene 25:4725–4743
Ostrowski RP, Colohan AR, Zhang JH (2006) Molecular mechanisms of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurol Res 28:399–414
Prunell GF, Mathiesen T, Svendgaard NA (2002) A new experimental model in rats for study of the pathophysiology of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neuroreport 13:2553–2556
Sabri M, Lass E, Macdonald RL (2013) Early brain injury: a common mechanism in subarachnoid hemorrhage and global cerebral ischemia. Stroke Res Treat 2013:394036
Yang H, Zhan Q, Wan YJ (2011) Enrichment of Nur77 mediated by retinoic acid receptor β leads to apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells induced by fenretinide and histone deacetylase inhibitors. Hepatology 53:865–874
Zhuang Z, Zhou ML, You WC, Zhu L, Ma CY, Sun XJ, Shi JX (2012) Hydrogen-rich saline alleviates early brain injury via reducing oxidative stress and brain edema following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rabbits. BMC Neurosci 13:47
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, Y., Zhang, W., Zhou, X. et al. Inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal Kinase Ameliorates Early Brain Injury After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Through Inhibition of a Nur77 Dependent Apoptosis Pathway. Neurochem Res 39, 1603–1611 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1355-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1355-6