Abstract
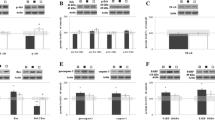
We analyzed the protective effect of 17β-estradiol (17β-ED) injection against delayed neuronal death in the hippocampus tissue of the brain in Mongolian gerbils after transient ischemia/recirculation treatment, especially in relation with bcl-2 gene expression and enzymatic activity changes of caspase-3 and tissue transglutaminase (tTGase). Daily intraperitoneal injection of 17β-ED to the animal after the ischemia stimulated the expression of an apoptosis suppressor gene, bcl-2, in the hippocampal tissue for a week. The gradually increasing apoptotic enzyme activity of caspase-3 and increased number of TUNEL positive fragmented neuronal nuclei caused by ischemic attack in the gerbil brain were clearly suppressed by 17β-ED administration. The reduced activity and enzyme protein of tTGase, a neurodegenerative marker of apoptosis in the hippocampus after ischemia, were also restored to nearly normal levels by 17β-ED injection. These results suggest that daily 17β-ED administration to the gerbil after transient ischemic insult with progressing neuronal deteriorative changes in hippocampus tissue can effectively prevent apoptotic changes through a molecular cascade involving gene expression regulation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kirino T (1982) Delayed neuronal death in the gerbil hippocampus following ischemia. Brain Res 239:57–69
Pulsinelli WC, Brierly JB, Plum F (1982) Temporal profile of neuronal damage in a model of transient forebrain ischemia. Ann Neurol 11:491–498
Nitatori T, Sato N, Waguri S, Kurasawa Y, Arai M, Shibatani K, Kominami E, Uchimura Y (1995) Delayed neuronal death in the CA1 pyramidal cell layer in the gerbil hippocampus following transient ischemia is apoptosis. J Neurosci 15:1001–1011
Chen J, Graham SH, Nakajima M, Zhu RL, Jin KL, Stetler RA, Simon RP (1997) Apoptosis receptor genes bcl-2 and bcl-x-long are expressed in the rat brain following global ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17:1–10
Namura S, Zhu J, Fink K, Enders M, Srinivasan A, Tomaselli KJ, Yuan J, Moskovitz MA (1998) Activation and cleavage of caspase-3 in apoptosis induced by experimental cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci 18:3659–3668
Emerson CS,Headrick JP, Vink R (1993) Estrogen improves biochemical and neurologic outcome following traumatic brain injury in male rats, but not in females. Brain Res 608:95–100
Goodman Y, Gruce AJ, Cheng B, Mattson MP (1996) Estrogen attenuate and corticosterone exacerbates excitotoxicity, oxidative injury, and amyloid β-peptide toxicity in hippocampal neurons. J Neurocjem 66:1836–1844
Sudo S, Wen T-C, Desaki J, Matsuda S, Tanaka J, Arai T, Maeda N, Sakanaka M (1997) βEstradiol protects hippocampal CA1 neurons against transient forebrain ischemia in gerbil. Neurosci Res 29:345–354
Dubal DB, Shughrue PJ, Wilson ME, Merchenthaler I, Wise PM (1999) Estradiol modulates bcl-2 in cerebral ischemia: a potential role for estrogen receptors. J Neurosci 19:6385–6393
Harukuni I, Hurn PD, Crain BJ (2001) Deleterious effect of β-estradiol in a rat model of transient forebrain ischemia. Brain Res 900:137–142
Chan PH (1994) Oxygen radicals in focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Pathol 4:59–65
Culmsee C, Vedder H, Ravati A, Otto D, Ahlemeyer B, Krieg JC, Krieglstein J (1999) Neuroprotection by estrogens in a mouse model of focal cerebral ischemia and in cultured neurons: evidence for a receptor-independent antioxidative mechanism. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 19:1263–1269
Chen J, Xu W, Jiang H (2001) 17β-estradiol protects neurons from ischemic damage and attenuates accumulation of extracellular excitatory amino acids. Anesth Analg 92:1520–1523
Dubal DB, Zhu H, Yu J, Rau SW, Shughrue PJ, Merchenthaler I, Kindy MS, Wise PM (2001) Estradiol receptor alpha, not beta, is a critical link in estradiol-mediated protection against brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:1952–1957
Oliverio S, Amendola A, Sano FD, Farrace MG, Fesus L, Nemes Z, Piredda L, Spinedi A, Piacentini M (1997) Tissue transglutaminase-dependent posttranslational modification of the retinoblastoma gene product in promonocytic cells undergoing apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 17:6040–6048
Melino G, Piacentini M (1998) ‘ Tissue’ transglutaminase in cell death: a downstream or a multifunctional upstream effector? FEBS Lett 430:59–63
Thomazy VA, Davies PJ (1999) Expression of tissue transglutaminase in the developing chicken limb is associated both with apoptosis and endochondral ossification. Cell Death Differ 6:146–154
Stone GC, Hammerschlag R (1981) Differential effects of cobalt on the initiation of fast axonal transport. Cell Mol Neurobiol 1:3–17
Matsudaira P (1987) Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinyl difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem 262:10035–10038
Matsui T, Fujimura S, Nishida S, Titani K (1993) Human plasma α2-macroglobulin and von Wilbrand factor posses covalently linked ABO Rh blood group antigens in subjects with corresponding ABO phenotype. Blood 82:663–668
Lorand L, Campbell-Wilkes LK, Cooperstein L (1972) A filter paper assay for transamidating enzymes using radioactive amine substrates. Anal Biochem 72:17–23
Ando M, Kunii S, Tatematsu T, Nagata Y (1993) Rapid and transient alterations in transglutaminase activity in rat superior ganglion following denervation or axotomy. Neurosci Res 17:47–52
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–252
Pattmann B, Henderson CE (1998) Neuronal cell death. Neuron 20:633–647
Chan HP (2004) Mitochondria and neuronal death/survival signaling pathways in cerebral ischemia. Neurochem Res 29:1943–1949
Kitagawa K, Matsumoto M, Tsujimoto Y, Ohtsuki T, Kuwabata K, Matsushita K, Yang G, Tanabe H, Martinou J-C, Hori M, Yanagihara T (1998) Amelioration of hippocampal neuronal damage after global ischemia by neuronal overexpression of bcl-2 in transgenic mice. Stroke 29:2616–2621
Garcia I, Martinou I, Tsujimoto Y, Martinou JC (1992) Prevention of programmed cell death of sympathetic neurons by bcl-2 proto-oncogene. Science 258:302–304
Allsopp TE, Wyatt S, Paterson HF, Davies AM (1993) The proto-oncogene bcl-2 can selectively rescue neurotrophic factor-dependent neurons from apoptosis. Cell 73:295–307
Farlie PG, Dringen R, Rees SM, Kannourakis G, Bernard O (1995) Bcl-2 transgene expression can protect neurons against developmental and induced cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:4397–4401
Krajewski S, Mai JK, Krajewska M, Sikorska M, Mossakowski MJ, Reed JC (1995) Upregulation of Bax protein levels in neurons following cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci 15:6364–6376
Pike CJ (1999) Estrogen modulates neuronal Bcl-xL expression and β-amyloid induced apoptosis: relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 72:1552–1563
Jover T, Tanaka H, Calderone A, Oguro K, Bennett MVL, Etgen AM, Zukin RS (2002) estrogen protects agonist global ischemia-induced neuronal death and prevents activation of apoptotic signaling cascades in the hippocampal CA1. J Neurosci 22:2115–2124
Wise MP (2000) Estradiol: A protective factor in the adult brain. J Pediatr Endocr Met 13:1425–1429
Zhao H, Yenaei AM, Cheng D, Sapolsky MR, Steinberg KG (2003) Bcl-2 over-expression protects against neuron loss within the ischemic margin following experimental stroke and inhibits cytochrome C translocation and caspase-3 activity. J Neurochem 85:1026–1036
Greenberg CS, Birckbichler PJ, Rice RH (1992) Transglutaminase: multifunctional cross-linking enzymes that stabilize tissues. FASEB J 3071–3077
Fujita K, Ando M, Yamauchi M, Nagata Y, Honda M (1995) Alteration of transglutaminase activity in rat and human spinal cord after neuronal degeneration. Neurochem Res 20:1195–2001
Folk JE (1980) Transglutaminase. Ann Rev Biochem 49:517–531
Fesus L, Thomazy V, Falus A (1988) Reaching for function of tissue transglutaminase; its possible involvement in biochemical pathway of programmed cell death. Adv Exp Biol 231:119–139
Johnson VWG, Cox MT, Lockhart PJ, Zinnerman DM, Miller LM, Powers ER (1997) Transglutaminase activity is increased in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Brain Res 751:323–(329)
Fujita K, Shibayama K, Yamauchi M, Kato T, Takahashi H, Iritani K, Yoshimoto N, Nagata Y (1998) Alteration of enzymic activities implicating in neuronal degeneration in the spinal cord of motor neuron degeneration mouse during postnatal development. Neurochem Res 23:561–566
Fesus L (1998) Transglutaminase-catalyzed protein cross-linking in the molecular program of apoptosis and its relationship to neuronal process. Cell Mol Neurobiol 18:683–694
Melino G, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, Piredda L, Candi E, Gentile V, Davies PJ, Piacentini M (1994) Tissue transglutaminase and apoptosis: sense and antisense transfection studies with human neuroblastoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 14:6584–6596
Green DR (1999) Harm’s way: Polyglutamine repeats and the activation of an apoptotic pathway. Neuron 22:416–417
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujita, K., Kato, T., Shibayama, K. et al. Protective Effect Against 17β-Estradiol on Neuronal Apoptosis in Hippocampus Tissue Following Transient Ischemia/Recirculation in Mongolian Gerbils via Down-Regulation of Tissue Transglutaminase Activity. Neurochem Res 31, 1059–1068 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-006-9114-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-006-9114-y