Abstract
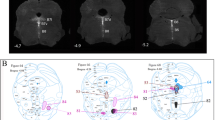
Serotonin-synthesizing raphé/parapyramidal neurons (5-HT neurons) may function as sympathetic premotor neurons regulating sympathetic outflow to the cutaneous vascular bed. In the present study a genetically engineered pseudorabies virus (PRV) expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) was injected into the rat tail. After survival for 3–4 days the medulla oblongata was examined using double-label immunohistochemistry, with an antibody against GFP for the virus and an antibody against phenylalanine hydroxylase 8 (PH8) for 5-HT synthesis. Sections were examined using light microscopy, and conventional and confocal fluorescence microscopy. There were two subpopulations of PRV+ve neurons in the raphé/parapyramidal region: a more dorsally and laterally located subgroup of medium-sized and large neurons, mainly non-serotonergic, and a more ventrally located subgroup of small mainly serotonin-synthesizing neurons, including those just dorsal to the pyramids, those in raphé pallidus, and those in close relationship to the ventral surface in the parapyramidal-subependymal zone.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blessing WW, Yu YH, Nalivaiko E (1999) Raphe pallidus and parapyramidal neurons regulate ear pinna vascular conductance in the rabbit. Neurosci Lett 270:33–36
Blessing WW, Nalivaiko E (2001) Raphe magnus/pallidus neurons regulate tail but not mesenteric arterial blood flow in rats. Neurosci 105:923–929
Rathner JA, McAllen RM (1999) Differential control of sympathetic drive to the rat tail artery and kidney by medullary premotor cell groups. Brain Res 834:196–199
Korsak A, Gilbey MP (2004) Rostral ventromedial medulla and the control of cutaneous vasoconstrictor activity following i.c.v. prostaglandin E(1). Neurosci 124:709–717
Ootsuka Y, Blessing WW, McAllen RM (2004) Inhibition of rostral medullary raphe neurons prevents cold-induced activity in sympathetic nerves to rat tail and rabbit ear arteries. Neurosci Lett 357:58–62
Ootsuka Y, Blessing WW (2003) 5-Hydroxytryptamine 1A receptors inhibit cold-induced sympathetically-mediated cutaneous vasoconstriction in rabbits. J Physiol 552.1:303–314
Blessing WW (2004) 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor activation reduces cutaneous vasoconstriction and fever associated with the acute inflammatory response in rabbits. Neurosci 123:1–4
Blessing WW, Seaman B (2003) 5-hydroxytryptamine(2A) receptors regulate sympathetic nerves constricting the cutaneous vascular bed in rabbits and rats. Neurosci 117:939–948
Ootsuka Y, Nalivaiko E, Blessing WW (2004) Spinal 5-HT2A receptors regulate cutaneous sympathetic vasomotor outflow in rabbits and rats; relevance for cutaneous vasoconstriction elicited by MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine, “Ecstasy”) and its reversal by clozapine. Brain Res (1014):34–44
Ootsuka Y, Blessing W (2005) Activation of slowly conducting medullary raphé-spinal neurons, including serotonergic neurons, increases cutaneous sympathetic vasomotor in rabbit. Am J Physiol 288: R909–918
Ross CA, Ruggiero DA, Reis DJ (1981) Projections to the spinal cord from neurons close to the ventral surface of the hindbrain in the rat. Neurosci Lett 21:143–148
Loewy AD (1981) Raphe pallidus and raphe obscurus projections to the intermediolateral cell column in the rat. Brain Res 222:129–133
Steinbusch HW (1981) Distribution of serotonin-immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat-cell bodies and terminals. Neurosci 4:557–561
Skagerberg G, Bjorklund A (1985) Topographic principles in the spinal projections of serotonergic and non-serotonergic brainstem neurons in the rat. Neurosci 15:445–480
Bowker RM, Abbott LC, Dilts RP (1988) Peptidergic neurons in the nucleus raphe magnus and the nucleus gigantocellularis: their distributions, interrelationships, and projections to the spinal cord. Prog Brain Res 77:95–127
Bowker RM, Abbott LC (1990) Quantitative re-evaluation of descending serotonergic and non-serotonergic projections from the medulla of the rodent: evidence for extensive co-existence of serotonin and peptides in the same spinally projecting neurons, but not from the nucleus raphe magnus. Brain Res 512:15–25
Jones BE, Holmes CJ, Rodriguez-Veiga E, Mainville L (1991) GABA-synthesizing neurons in the medulla: Their relationship to serotonin-containing and spinally projecting neurons in the rat. J Comp Neurol 313:349–367
Dahlström A, Fuxe K (1965) Evidence for the existence of monoamine neurons in the central nervous system. II. Experimentally induced changes in the intraneuronal amine levels of the bulbospinal neuron systems. Acta Physiol Scand 64:1–36
Jensen I, Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Pilowsky P, Minson JB, Chalmers J (1995) Serotonin inputs to rabbit sympathetic preganglionic neurons projecting to the superior cervical ganglion or adrenal medulla. J Comp Neurol 353:427–438
Bacon SJ, Zagon A, Smith AD (1990) Electron microscopic evidence of a monosynaptic pathway between cells in the caudal raphe nuclei and sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the rat spinal cord. Exp Brain Res 79:589–602
Smith JE, Jansen AS, Gilbey MP, Loewy AD (1998) CNS cell groups projecting to sympathetic outflow of tail artery: neural circuits involved in heat loss in the rat. Brain Res 786:153–164
Nakamura K, Matsumura K, Hubschle T et al. (2004) Identification of sympathetic premotor neurons in medullary raphe regions mediating fever and other thermoregulatory functions. J Neurosci 24:5370–5380
Nakamura K, Li YQ, Kaneko T, Katoh H, Negishi M (2001) Prostaglandin EP3 receptor protein in serotonin and catecholamine cell groups: a double immunofluorescence study in the rat brain. Neurosci 103:763–775
Yoshida K, Nakamura K, Matsumura K et al. (2003) Neurons of the rat preoptic area and the raphe pallidus nucleus innervating the brown adipose tissue express the prostaglandin E receptor subtype EP3. Eur J Neurosci 18:1848–1860
Boldogkoi Z, Reichart A, Toth IE et al. (2002) Construction of recombinant pseudorabies viruses optimized for labeling and neurochemical characterization of neural circuitry. Brain Res 109:105–118
Halliday GM, Li YW, Joh TH et al. (1988) Distribution of monoamine-synthesizing neurons in the human medulla oblongata. J Comp Neurol 273:301–317
Jones SL, Light AR (1992) Serotoninergic medullary raphespinal projection to the lumbar spinal cord in the rat: A retrograde immunohistochemical study. J Comp Neurol 322:599–610
Masson RL Jr, Sparkes ML, Ritz LA (1991) Descending projections to the rat sacrocaudal spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 307:120–130
Olszewski J, Baxter D (1982) Cytoarchitecture of the human brain stem. 2 S. Karger A.G, Basel
Filiano JJ, Choi JC, Kinney HC (1990) Candidate cell populations for respiratory chemosensitive fields in the human infant medulla. J Comp Neurol 293:448–465
Kitzman PH, Bishop GA (1994) The origin of serotoninergic afferents to the cat’s cerebellar nuclei. J Comp Neurol 340:541–550
Bamshad M, Song CK, Bartness TJ (1999) CNS origins of the sympathetic nervous system outflow to brown adipose tissue. Am J Physiol 276:R1569–R1578
Oldfield BJ, Giles ME, Watson A, Anderson C, Colvill LM, McKinley MJ (2002) The neurochemical characterisation of hypothalamic pathways projecting polysynaptically to brown adipose tissue in the rat. Neurosci 110:515–526
Cano G, Passerin AM, Schiltz JC, Card JP, Morrison SF, Sved AF (2003) Anatomical substrates for the central control of sympathetic outflow to interscapular adipose tissue during cold exposure. J Comp Neurol 460:303–326
Nakamura K, Matsumura K, Kaneko T, Kobayashi S, Katoh H, Negishi M (2002) The rostral raphe pallidus nucleus mediates pyrogenic transmission from the preoptic area. J Neurosci 22:4600–4610
Morrison SF, Sved AF, Passerin AM (1999) GABA-mediated inhibition of raphe pallidus neurons regulates sympathetic outflow to brown adipose tissue. Am J Physiol 276:R290–R297
Morrison SF (2004) Activation of 5-HT1A receptors in raphe pallidus inhibits leptin-evoked increases in brown adipose tissue thermogenesis. Am J Physiol 286:R832–R837
Palkovits M, Horvath S (1994) Galanin immunoreactive neurons in the medulla oblongata of rats. Acta Biol Hung 45:399–417
Johansson O, Hokfelt T, Pernow B et al. (1981) Immunohistochemical support for three putative transmitters in one neuron: coexistence of 5-hydroxytryptamine, substance P- and thyrotropin releasing hormone-like immunoreactivity in medullary neurons projecting to the spinal cord. Neurosci 6:1857–1881
Blessing WW, Howe PR, Joh TH, Oliver JR, Willoughby JO (1986) Distribution of tyrosine hydroxylase and neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactive neurons in rabbit medulla oblongata, with attention to colocalization studies, presumptive adrenaline-synthesizing perikarya, and vagal preganglionic cells. J Comp Neurol 248:285–300
Melander T, Hökfelt T, Rokaeus A et al. (1986) Coexistence of galanin-like immunoreactivity with catecholamines, 5-hydroxytryptamine, GABA and neuropeptides in the rat CNS. J Neurosci 6:3640–3654
Blessing WW (1990) Distribution of glutamate decarboxylase-containing neurons in rabbit medulla oblongata with attention to intramedullary and spinal projections. Neurosci 37:171–185
Stornetta RL, Guyenet PG (1999) Distribution of glutamic acid decarboxylase mRNA-containing neurons in rat medulla projecting to thoracic spinal cord in relation to monoaminergic brainstem neurons. J Comp Neurol 407:367–80
Stornetta RL, McQuiston TJ, Guyenet PG (2004) GABAergic and glycinergic presympathetic neurons of rat medulla oblongata identified by retrograde transport of pseudorabies virus and in situ hybridization. J Comp Neurol 479:257–270
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr Jenny Hiscock (Flinders University), for the excellent help in confocal microscopy, and Dr Grant Hennig (Flinders University) for the coordinate mapping program and Ms Robyn Flook for technical help. We received financial support from the Hungarian Research Funds (OTKA) T-34231 and T-37532 and from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special issue dedicated to Miklós Palkovits.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tóth, I.E., Tóth, D.E., Boldogkoi, Z. et al. Serotonin-Synthesizing Neurons in the Rostral Medullary Raphé/Parapyramidal Region Transneuronally Labelled After Injection of Pseudorabies Virus into the Rat Tail. Neurochem Res 31, 277–286 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-9018-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-9018-2