Abstract
Background
Many studies have demonstrated in the last years that once medulloblastoma has recurred, the probability of regaining tumor control is poor despite salvage therapy. Although re-irradiation has an emerging role in other relapsed brain tumors, there is a lack of strong data on re-irradiation for medulloblastoma.
Methods
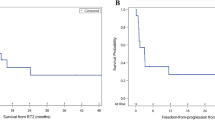
This is a retrospective cohort study of patients aged 18 years or under, treated at least by a second course of external beam for recurrence medulloblastoma at Garrahan Hospital between 2009 and 2020. Twenty-four patients met eligibility criteria for inclusion. All patients received upfront radiotherapy as part of the curative-intent first radiotherapy, either craniospinal irradiation (CSI) followed by posterior fossa boost in 20 patients or focal posterior fossa radiation in 4 infants. The second course of radiation consisted of CSI in 15 and focal in 9. The 3-year post first failure OS (50% vs. 0%; p = 0.0010) was significantly better for children who received re-CSI compared to children who received focal re-irradiation. Similarly, the 3-year post-re-RT PFS (31% vs. 0%; p = 0.0005) and OS (25% vs. 0%; p = 0.0003) was significantly improved for patients who received re-CSI compared to patients who received focal re-irradiation. No symptomatic intratumoral haemorrhagic events or symptomatic radionecrosis were observed. Survivors fell within mild to moderate intellectual disability range, with a median IQ at last assessment of 58 (range 43–69).
Conclusions
Re-irradiation with CSI is a safe and effective treatment for children with relapsed medulloblastoma; improves disease control and survival compared with focal re-irradiation. However this approach carries a high neurocognitive cost.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available within the article or its supplementary materials.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Koschmann C, Bloom K, Upadhyaya S, Geyer JR, Leary SE (2016) Survival after relapse of medulloblastoma. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 38(4):269–273. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPH.0000000000000547
Sabel M, Fleischhack G, Tippelt S, SIOP-E Brain Tumour Group et al (2016) Relapse patterns and outcome after relapse in standard risk medulloblastoma: a report from the HIT-SIOP-PNET4 study. J Neurooncol 129(3):515–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2202-1
Johnston DL, Keene D, Strother D et al (2018) Survival following tumor recurrence in children with medulloblastoma. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 40(3):e159–e163. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPH.0000000000001095
Adile AA, Kameda-Smith MM, Bakhshinyan D et al (2020) Salvage therapy for progressive, treatment-refractory or recurrent pediatric medulloblastoma: a systematic review protocol. Syst Rev. 9(1):47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-020-01307-8
Massimino M, Gandola L, Spreafico F et al (2009) No salvage using high-dose chemotherapy plus/minus re-irradiation for relapsing previously irradiated medulloblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 73(5):1358–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.06.1930
Peyrl A, Chocholous M, Kieran MW et al (2012) Antiangiogenic metronomic therapy for children with recurrent embryonal brain tumors. Pediatr Blood Cancer 59(3):511–517. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.24006
Tsang DS, Laperriere NJ (2019) Re-irradiation for paediatric tumours. Clin Oncol R Coll Radiol 31(3):191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clon.2018.10.003
Tsang DS, Oliveira C, Bouffet E et al (2019 Sep) Repeat irradiation for children with supratentorial high-grade glioma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 66(9):e27881. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.27881
Tsang DS, Murray L, Ramaswamy V et al (2019) Craniospinal irradiation as part of re-irradiation for children with recurrent intracranial ependymoma. Neuro Oncol 21(4):547–557. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noy191
Das Suman P, Kanhu, Mukherji A (2018) Recovery and tolerance of the organs at risk during re-irradiation. J Curr Oncol 1:23. https://doi.org/10.4103/jco.jco_2_17
Rao AD, Rashid AS, Chen Q et al (2017) Re-irradiation for Recurrent Pediatric Central Nervous System Malignancies: A Multi-institutional Review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 99(3):634–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.07.026
Wetmore C, Herington D, Lin T, Onar-Thomas A, Gajjar A, Merchant TE (2014) Re-irradiation of recurrent medulloblastoma: does clinical benefit outweigh risk for toxicity? Cancer. 120(23):3731–3737. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.28907
Tsang DS, Sarhan N, Ramaswamy V et al (2019 Oct) Re-irradiation for children with recurrent medulloblastoma in Toronto, Canada: a 20-year experience. J Neurooncol 145(1):107–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03272-2
Gupta T, Maitre M, Sastri GJ et al (2019 Sep) Outcomes of salvage re-irradiation in recurrent medulloblastoma correlate with age at initial diagnosis, primary risk-stratification, and molecular subgrouping. J Neurooncol 144(2):283–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03225-9
Baroni LV, Sampor C, Gonzalez A et al (2020) Bridging the treatment gap in infant medulloblastoma: molecularly informed outcomes of a globally feasible regimen. Neuro Oncol 22(12):1873–1881. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noaa122
Bakst RL, Dunkel IJ, Gilheeney S et al (2011) Re-irradiation for recurrent medulloblastoma. Cancer 117(21):4977–82. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.26148
Mineyeva OA, Bezriadnov DV, Kedrov AV, Lazutkin AA, Anokhin KV, Enikolopov GN (2019) Radiation induces distinct changes in defined subpopulations of neural stem and progenitor cells in the adult hippocampus. Front Neurosci 12:1013. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.01013
Padovani L, André N, Constine LS, Muracciole X (2012 Oct) Neurocognitive function after radiotherapy for paediatric brain tumors. Nat Rev Neurol 8(10):578–588. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2012.182
Pasquier E, Kavallaris M, Andre ́ N (2010) Metronomic chemotherapy: new rationale for new directions. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 7:455–465. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2010.82
Ruggiero A, Rizzo D, Attina G et al (2010) Phase I study of temozolomide combined with oral etoposide in children with recurrent or progressive medulloblastoma. Eur J Cancer 46:2943–2949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2010.05.016
Peyrl A, Chocholous M, Kieran MW et al (2012 Sep) Antiangiogenic metronomic therapy for children with recurrent embryonal brain tumors. Pediatr Blood Cancer 59(3):511–517. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.24006
Ramaswamy V, Remke M, Bouffet E et al (2013 Nov) Recurrence patterns across medulloblastoma subgroups: an integrated clinical and molecular analysis. Lancet Oncol 14(12):1200–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70449-2
Funding
No fundings.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: LB, CF, NF, AO, AG, NP, CS, FL; Methodology: LB, CF, AG; Investigation: LB, CF, NF, AG, AO, NP, CS, CR, FL Writing—Review & Editing: LB, CF, AO, DA; Project Administration: LB, DA; Supervision: DA.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baroni, L.V., Freytes, C., Fernández Ponce, N. et al. Craniospinal irradiation as part of re-irradiation for children with recurrent medulloblastoma. J Neurooncol 155, 53–61 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03842-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03842-3