Abstract
Purpose
Patients with high rates of developing new brain metastases have an increased likelihood of dying of neurologic death. It is unclear, however, whether this risk is affected by treatment choice following failure of primary stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS).
Methods
From July 2000 to March 2017, 440 patients with brain metastasis were treated with SRS and progressed to have a distant brain failure (DBF). Eighty-seven patients were treated within the immunotherapy era. Brain metastasis velocity (BMV) was calculated for each patient. In general, the institutional philosophy for use of salvage SRS vs whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) was to postpone the use of WBRT for as long as possible and to treat with salvage SRS when feasible. No further treatment was reserved for patients with poor life expectancy and who were not expected to benefit from salvage treatment.
Results
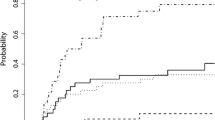
Two hundred and eighty-five patients were treated with repeat SRS, 91 patients were treated with salvage WBRT, and 64 patients received no salvage radiation therapy. One-year cumulative incidence of neurologic death after salvage SRS vs WBRT was 15% vs 23% for the low- (p = 0.06), 30% vs 37% for the intermediate- (p < 0.01), and 31% vs 48% (p < 0.01) for the high-BMV group. Salvage WBRT was associated with increased incidence of neurologic death on multivariate analysis (HR 1.64, 95% CI 1.13–2.39, p = 0.01) when compared to repeat SRS. One-year cumulative incidence of neurologic death for patients treated within the immunotherapy era was 9%, 38%, and 38% for low-, intermediate-, and high-BMV groups, respectively (p = 0.01).
Conclusion
Intermediate and high risk BMV groups are predictive of neurologic death. The association between BMV and neurologic death remains strong for patients treated within the immunotherapy era.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ellis TL, Neal MT, Chan MD (2012) The role of surgery, radiosurgery and whole brain radiation therapy in the management of patients with metastatic brain tumors. Int J Surg Oncol 2012:952345
Devoid H-M, McTyre ER, Page BR et al (2016) Recent advances in radiosurgical management of brain metastases. Front Biosci 8:203–214
Lanier CM, Hughes R, Ahmed T et al (2019) Immunotherapy is associated with improved survival and decreased neurologic death after SRS for brain metastases from lung and melanoma primaries. Neurooncol Pract. https://doi.org/10.1093/nop/npz004
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U et al (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952–26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29:134–141
Neal MT, Chan MD, Lucas JT Jr et al (2014) Predictors of survival, neurologic death, local failure, and distant failure after gamma knife radiosurgery for melanoma brain metastases. World Neurosurg 82:1250–1255
Jensen CA, Chan MD, McCoy TP et al (2011) Cavity-directed radiosurgery as adjuvant therapy after resection of a brain metastasis. J Neurosurg 114:1585–1591
Ayala-Peacock DN, Peiffer AM, Lucas JT et al (2014) A nomogram for predicting distant brain failure in patients treated with gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery without whole brain radiotherapy. Neuro Oncol 16:1283–1288
Shenker RF, McTyre ER, Taksler GB et al (2019) Analysis of the drivers of cost of management when patients with brain metastases are treated with upfront radiosurgery. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 176:10–14
Churilla TM, Ballman KV, Brown PD et al (2017) Stereotactic radiosurgery with or without whole-brain radiation therapy for limited brain metastases: a secondary analysis of the north central cancer treatment group N0574 (Alliance) randomized controlled trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 99:1173–1178
Soffietti R, Kocher M, Abacioglu UM et al (2013) A European organisation for research and treatment of cancer phase III trial of adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation in patients with one to three brain metastases from solid tumors after surgical resection or radiosurgery: quality-of-life results. J Clin Oncol 31:65–72
McTyre E, Ayala-Peacock D, Contessa J et al (2018) Multi-institutional competing risks analysis of distant brain failure and salvage patterns after upfront radiosurgery without whole brain radiotherapy for brain metastasis. Ann Oncol 29:497–503
Farris M, McTyre ER, Cramer CK et al (2017) Brain metastasis velocity: a novel prognostic metric predictive of overall survival and freedom from whole-brain radiation therapy after distant brain failure following upfront radiosurgery alone. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 98:131–141
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D et al (2012) Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 30:419–425
Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L et al (2000) Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90-05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:291–298
Dohm AE, Hughes R, Wheless W et al (2018) Surgical resection and postoperative radiosurgery versus staged radiosurgery for large brain metastases. J Neurooncol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-03008-8
McTyre ER, Johnson AG, Ruiz J et al (2017) Predictors of neurologic and nonneurologic death in patients with brain metastasis initially treated with upfront stereotactic radiosurgery without whole-brain radiation therapy. Neuro Oncol 19:558–566
McTyre ER, Soike MH, Farris M et al (2019) Multi-institutional validation of brain metastasis velocity, a recently defined predictor of outcomes following stereotactic radiosurgery. Radiother Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2019.08.011
Yamamoto M, Aiyama H, Koiso T et al (2019) Validity of a recently proposed prognostic grading index, brain metastasis velocity, for patients with brain metastasis undergoing multiple radiosurgical procedures. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 103:631–637
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW et al (1990) A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N Engl J Med 322:494–500
Brown PD, Gondi V (2018) Irrational fear of whole-brain radiotherapy: are we doing our patients a disservice? Cancer 124:3468–3473
Tawbi HA, Forsyth PA, Algazi A et al (2018) Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab in melanoma metastatic to the brain. N Engl J Med 379:722–730
Johnson AG, Ruiz J, Hughes R et al (2015) Impact of systemic targeted agents on the clinical outcomes of patients with brain metastases. Oncotarget 6:18945–18955
Funding
This work was not supported by any funding sources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization Michael C. LeCompte, Ryan T. Hughes, Michael D. Chan; Data Curation Michael C. LeCompte, Ryan T. Hughes, Claire M. Lanier, Chase Glenn; Formal Analysis Michael C. LeCompte, Ryan T. Hughes; Funding Acquisition NA; Investigation: Michael C. LeCompte, Ryan T. Hughes; Methodology Michael C. LeCompte, Ryan T. Hughes, Michael Farris, Adrianna Masters, Michael H. Soike; Christina K. Cramer, Ge Wang, Michael D. Chan; Project Administration Michael C. LeCompte; Resources Jimmy Ruiz, Christopher T. Whitlow, Adrian W. Laxton, Stephen B. Tatter; Software Ryan T. Hughes; Supervision Michael D. Chan; Validation Michael C. LeCompte, Ryan T. Hughes; Visualization Michael C. LeCompte, Ryan T. Hughes, Michael D. Chan; Writing—Original Draft Preparation Michael C. LeCompte, Ryan T. Hughes, Michael D. Chan; Writing—Review & Editing Michael C. LeCompte, Ryan T. Hughes, Adrianna Masters, Michael H. Soike, Claire M. Lanier, Christina K. Cramer, Kounosuke Watabe, Michael D. Chan.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Data was collected retrospectively, in accordance with the IRB.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LeCompte, M.C., Hughes, R.T., Farris, M. et al. Impact of brain metastasis velocity on neurologic death for brain metastasis patients experiencing distant brain failure after initial stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 146, 285–292 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03368-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03368-9