Abstract
Purpose
Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) has been shown to establish local control in patients with resected brain metastases, yet its efficacy may be limited, particularly for resected lesions with large post-operative resection cavities. We describe the efficacy of postoperative fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (FSRT) for local control in patients who have undergone resection for brain metastases.
Methods
In this retrospective cohort study, we analyzed patients who received FSRT for resected brain metastases in 3 or 5 fractions. Time to local recurrence was the primary endpoint in this study.
Results
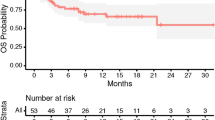
Sixty-seven patients (n = 29 female, n = 38 male) met study criteria for review. The median age of the cohort was 62 years (range 18–79 years). Median preoperative tumor volume was 11.1 cm3 (range 0.4–77.0 cm3). The rate of local control was 91.0% at 6 months, 85.1% at 12 months, and 85.1% at 18 months. Estimates of freedom from local recurrence at 6 and 12 months were 90.9% and 84.3%, respectively. Higher biologically equivalent doses (BED10) were found to be predictive of longer freedom from local recurrence on univariate and multivariable analysis. Larger cavity volumes were found to correspond to longer time to local recurrence on univariate and multivariable analysis.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that postoperative FSRT may be an effective method for providing local control to the surgical bed in patients with resected brain metastases, particularly for larger tumors not amenable to conventional, single-fraction SRS. Additional prospective studies are needed to confirm these findings.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- WBRT:
-
Whole-brain radiotherapy
- SRS:
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery
- FSRT:
-
Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- KPS:
-
Karnofsky performance score
- GPA:
-
Graded prognostic assessment
- IRB:
-
Institutional review board
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- T1C+:
-
T1-weighted post-contrast
- BED10 :
-
Biologically effective dose
- EQD2:
-
equivalent dose in 2 Gy
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- IORT:
-
Intraoperative radiotherapy
References
Nayak L, Lee EQ, Wen PY (2012) Epidemiology of brain metastases. Curr Oncol Rep 14:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-011-0203-y
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW, Flanders AE, Gaspar LE, Schell MC, Werner-Wasik M, Demas W, Ryu J, Bahary JP, Souhami L, Rotman M, Mehta MP, Curran WJ Jr (2004) Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet (London, England) 363:1665–1672. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(04)16250-8
Choi CY, Chang SD, Gibbs IC, Adler JR, Harsh GRT, Lieberson RE, Soltys SG, (2012) Stereotactic radiosurgery of the postoperative resection cavity for brain metastases: prospective evaluation of target margin on tumor control. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 84:336–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.12.009
Luther N, Kondziolka D, Kano H, Mousavi SH, Engh JA, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2013) Predicting tumor control after resection bed radiosurgery of brain metastases. Neurosurgery 73:1001–1006. https://doi.org/10.1227/neu.0000000000000148
Badiyan SN, Regine WF, Mehta M (2016) Stereotactic radiosurgery for treatment of brain metastases. J Oncol Pract 12:703–712. https://doi.org/10.1200/JOP.2016.012922
Brown PD, Ballman KV, Cerhan JH, Anderson SK, Carrero XW, Whitton AC, Greenspoon J, Parney IF, Laack NNI, Ashman JB, Bahary JP, Hadjipanayis CG, Urbanic JJ, Barker FG 2nd, Farace E, Khuntia D, Giannini C, Buckner JC, Galanis E, Roberge D (2017) Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery compared with whole brain radiotherapy for resected metastatic brain disease (NCCTG N107C/CEC.3): a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18:1049–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(17)30441-2
Mahajan A, Ahmed S, McAleer MF, Weinberg JS, Li J, Brown P, Settle S, Prabhu SS, Lang FF, Levine N, McGovern S, Sulman E, McCutcheon IE, Azeem S, Cahill D, Tatsui C, Heimberger AB, Ferguson S, Ghia A, Demonte F, Raza S, Guha-Thakurta N, Yang J, Sawaya R, Hess KR, Rao G (2017) Post-operative stereotactic radiosurgery versus observation for completely resected brain metastases: a single-centre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18:1040–1048. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30414-X
Korytko T, Radivoyevitch T, Colussi V, Wessels BW, Pillai K, Maciunas RJ, Einstein DB (2006) 12 Gy gamma knife radiosurgical volume is a predictor for radiation necrosis in non-AVM intracranial tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:419–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.07.980
Blonigen BJ, Steinmetz RD, Levin L, Lamba MA, Warnick RE, Breneman JC (2010) Irradiated volume as a predictor of brain radionecrosis after linear accelerator stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:996–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.06.006
Kwon AK, Dibiase SJ, Wang B, Hughes SL, Milcarek B, Zhu Y (2009) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for the treatment of brain metastases. Cancer 115:890–898. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.24082
Minniti G, D'Angelillo RM, Scaringi C, Trodella LE, Clarke E, Matteucci P, Osti MF, Ramella S, Enrici RM, Trodella L (2014) Fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with brain metastases. J Neuro-oncol 117:295–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1388-3
Matsuyama T, Kogo K, Oya N (2013) Clinical outcomes of biological effective dose-based fractionated stereotactic radiation therapy for metastatic brain tumors from non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85:984–990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.09.008
Lischalk JW, Oermann E, Collins SP, Nair MN, Nayar VV, Bhasin R, Voyadzis JM, Rudra S, Unger K, Collins BT (2015) Five-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for single inoperable high-risk non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) brain metastases. Radiat Oncol (London, England) 10:216. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-015-0525-2
Ishihara T, Yamada K, Harada A, Isogai K, Tonosaki Y, Demizu Y, Miyawaki D, Yoshida K, Ejima Y, Sasaki R (2016) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases from lung cancer: Evaluation of indications and predictors of local control. Strahlentherapie und Onkologie: Organ der Deutschen Rontgengesellschaft [et al] 192:386–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-016-0963-2
Ahmed KA, Sarangkasiri S, Chinnaiyan P, Sahebjam S, Yu HH, Etame AB, Rao NG (2016) Outcomes following hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in the management of brain metastases. Am J Clin Oncol 39:379–383. https://doi.org/10.1097/coc.0000000000000076
Jeong WJ, Park JH, Lee EJ, Kim JH, Kim CJ, Cho YH (2015) Efficacy and safety of fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for large brain metastases. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 58:217–224. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.3.217
Steinmann D, Maertens B, Janssen S, Werner M, Fruhauf J, Nakamura M, Christiansen H, Bremer M (2012) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (hfSRT) after tumour resection of a single brain metastasis: report of a single-centre individualized treatment approach. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138:1523–1529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1227-x
Dore M, Martin S, Delpon G, Clement K, Campion L, Thillays F (2017) Stereotactic radiotherapy following surgery for brain metastasis: predictive factors for local control and radionecrosis. Cancer Radiother 21:4–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canrad.2016.06.010
Keller A, Dore M, Cebula H, Thillays F, Proust F, Darie I, Martin SA, Delpon G, Lefebvre F, Noel G, Antoni D (2017) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiation therapy to the resection bed for intracranial metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 99:1179–1189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.08.014
Kumar AMS, Miller J, Hoffer SA, Mansur DB, Coffey M, Lo SS, Sloan AE, Machtay M (2018) Postoperative hypofractionated stereotactic brain radiation (HSRT) for resected brain metastases: improved local control with higher BED10. J Neuro-oncol 139:449–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-2885-6
Shibamoto Y, Miyakawa A, Otsuka S, Iwata H (2016) Radiobiology of hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy: what are the optimal fractionation schedules? J Radiat Research 57(Suppl 1):i76–i82. https://doi.org/10.1093/jrr/rrw015
Ahmed KA, Freilich JM, Abuodeh Y, Figura N, Patel N, Sarangkasiri S, Chinnaiyan P, Yu HH, Etame AB, Rao NG (2014) Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy to the post-operative cavity for radioresistant and radiosensitive brain metastases. J Neuro-oncol 118:179–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1417-2
Eaton BR, LaRiviere MJ, Kim S, Prabhu RS, Patel K, Kandula S, Oyesiku N, Olson J, Curran W, Shu HK, Crocker I (2015) Hypofractionated radiosurgery has a better safety profile than single fraction radiosurgery for large resected brain metastases. J Neuro-oncol 123:103–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1767-4
Lima LC, Sharim J, Levin-Epstein R, Tenn S, Teles AR, Kaprealian T, Pouratian N (2017) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy to large resection cavity of metastatic brain tumors. World Neurosurg 97:571–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.10.076
Keller A, Dore M, Antoni D, Menoux I, Thillays F, Clavier JB, Delpon G, Jarnet D, Bourrier C, Lefebvre F, Chibbaro S, Darie I, Proust F, Noel G (2017) Risk of radionecrosis after hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy targeting the postoperative resection cavity of brain metastases. Cancer Radiother 21:377–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canrad.2017.01.017
Combs SE, Bilger A, Diehl C, Bretzinger E, Lorenz H, Oehlke O, Specht HM, Kirstein A, Grosu A-L (2018) Multicenter analysis of stereotactic radiotherapy of the resection cavity in patients with brain metastases. Cancer Med 7:2319–2327. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1477
Brown PD, Brown CA, Pollock BE, Gorman DA, Foote RL (2002) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with "radioresistant" brain metastases. Neurosurgery 51:656–665; discussion 665–657
Sawaya R, Hammoud M, Schoppa D, Hess KR, Wu SZ, Shi WM, Wildrick DM (1998) Neurosurgical outcomes in a modern series of 400 craniotomies for treatment of parenchymal tumors. Neurosurgery 42:1044–1055; discussion 1055–1046
Lin NU, Lee EQ, Aoyama H, Barani IJ, Barboriak DP, Baumert BG, Bendszus M, Brown PD, Camidge DR, Chang SM, Dancey J, de Vries EG, Gaspar LE, Harris GJ, Hodi FS, Kalkanis SN, Linskey ME, Macdonald DR, Margolin K, Mehta MP, Schiff D, Soffietti R, Suh JH, van den Bent MJ, Vogelbaum MA, Wen PY (2015) Response assessment criteria for brain metastases: proposal from the RANO group. Lancet Oncol 16:e270–e278. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(15)70057-4
Pawlik TM, Keyomarsi K (2004) Role of cell cycle in mediating sensitivity to radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:928–942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.03.005
Vargo JA, Sparks KM, Singh R, Jacobson GM, Hack JD, Cifarelli CP (2018) Feasibility of dose escalation using intraoperative radiotherapy following resection of large brain metastases compared to post-operative stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neuro-oncol 140:413–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-2968-4
Wernicke AG, Hirschfeld CB, Smith AW, Taube S, Yondorf MZ, Parashar B, Nedialkova L, Kulidzhanov F, Trichter S, Sabbas A, Ramakrishna R, Pannullo S, Schwartz TH (2017) Clinical outcomes of large brain metastases treated with neurosurgical resection and intraoperative cesium-131 brachytherapy: results of a prospective trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 98:1059–1068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.03.044
Mayo C, Martel MK, Marks LB, Flickinger J, Nam J, Kirkpatrick J (2010) Radiation dose-volume effects of opticnerves and chiasm. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76:S28–S35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.07.1753
Mayo C, Yorke E, Merchant TE (2010) Radiation associated brainstem injury. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76:S36–S41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.08.078
Ruzevick J, Kleinberg L, Rigamonti D (2014) Imaging changes following stereotactic radiosurgery for metastatic intracranial tumors: differentiating pseudoprogression from tumor progression and its effect on clinical practice. Neurosurg Rev 37:193–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-013-0504-8; discussion 201
Aoki M, Abe Y, Hatayama Y, Kondo H, Basaki K (2006) Clinical outcome of hypofractionated conventional conformation radiotherapy for patients with single and no more than three metastatic brain tumors, with noninvasive fixation of the skull without whole brain irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:414–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.03.017
Do L, Pezner R, Radany E, Liu A, Staud C, Badie B (2009) Resection followed by stereotactic radiosurgery to resection cavity for intracranial metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 73:486–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.04.070
Baliga S, Garg MK, Fox J, Kalnicki S, Lasala PA, Welch MR, Tome WA, Ohri N (2017) Fractionated stereotactic radiation therapy for brain metastases: a systematic review with tumour control probability modelling. Br J Radiol 90:20160666. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20160666
Murata R, Shibamoto Y, Sasai K, Oya N, Shibata T, Takagi T, Abe M (1996) Reoxygenation after single irradiation in rodent tumors of different types and sizes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 34:859–865
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee (University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Traylor, J.I., Habib, A., Patel, R. et al. Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for local control of resected brain metastases. J Neurooncol 144, 343–350 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03233-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03233-9