Abstract
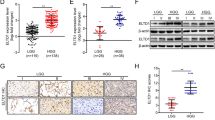
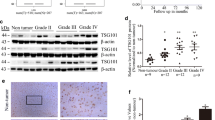
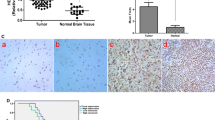
As an important member of the Annexins, AnnexinA5 has been attributed important functions in trophoblast membrane repair, anticoagulation and cellular signal transduction. Accumulated studies show that AnnexinA5 is closely associated with various types of carcinomas. However, the potential contribution of AnnexinA5 to glioma cancer progression remains unclear. In this study, we report that AnnexinA5 is significantly upregulated in both high-grade glioma samples and glioma cell lines. Moreover, overexpression of AnnexinA5 promotes cell migration and invasion in vitro and tumorigenicity of glioma cells in nude mice, while knockdown of AnnexinA5 manifests a repressive function during these cellular processes. Importantly, mechanistic studies further reveal that AnnexinA5 is an essential transcriptional target of Snail via activating the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway. Taken together, these findings suggest that AnnexinA5 or the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway may be promising therapeutic molecules to eradicate glioma metastases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chhabda S, Carney O, D’Arco F, Jacques TS, Mankad K (2016) The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of tumours of the Central Nervous System: what the paediatric neuroradiologist needs to know. Quant Imaging Med Surg 6:486–489. https://doi.org/10.21037/qims.2016.10.01
Komori T, Sasaki H, Yoshida K (2016) Revised WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system: summary of the revision and perspective. No shinkei geka Neurol Surg 44:625–635. https://doi.org/10.11477/mf.1436203347
Jansen M, Yip S, Louis DN (2010) Molecular pathology in adult gliomas: diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive markers. Lancet Neurol 9:717–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70105-8
Rock K, McArdle O, Forde P, Dunne M, Fitzpatrick D, O’Neill B, Faul C (2012) A clinical review of treatment outcomes in glioblastoma multiforme–the validation in a non-trial population of the results of a randomised Phase III clinical trial: has a more radical approach improved survival? Br J Radiol 85:e729-733. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr/83796755
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW, Kleihues P (2007) The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 114:97–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0243-4
Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG, Norden AD, Shu HK, Wen PY, Olson JJ (2010) Exciting new advances in neuro-oncology: the avenue to a cure for malignant glioma. CA 60:166–193. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.20069
Maher EA, Furnari FB, Bachoo RM, Rowitch DH, Louis DN, Cavenee WK, DePinho RA (2001) Malignant glioma: genetics and biology of a grave matter. Genes Dev 15:1311–1333. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.891601
Gerke V, Moss SE (2002) Annexins: from structure to function. Physiol Rev 82:331–371. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00030.2001
Xue G, Hao LQ, Ding FX, Mei Q, Huang JJ, Fu CG, Yan HL, Sun SH (2009) Expression of annexin a5 is associated with higher tumor stage and poor prognosis in colorectal adenocarcinomas. J Clin Gastroenterol 43:831–837. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0b013e31819cc731
Sun B, Bai Y, Zhang L, Gong L, Qi X, Li H, Wang F, Chi X, Jiang Y, Shao S (2016) Quantitative proteomic profiling the molecular signatures of annexin A5 in lung squamous carcinoma cells. PloS ONE 11:e0163622. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0163622
Lee EK, Cho H, Kim CW (2011) Proteomic analysis of cancer stem cells in human prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 412:279–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.07.083
Martin M, Leffler J, Blom AM (2012) Annexin A2 and A5 serve as new ligands for C1q on apoptotic cells. J Biol Chem 287:33733–33744. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.341339
Li X, Chen L, Liang XJ, Gao YF, Wang XJ, Xu Q, Yan Y, Gao FL (2012) Annexin A5 protein expression is associated with the histological differentiation of uterine cervical squamous cell carcinoma in patients with an increased serum concentration. Mol Med Rep 6:1249–1254. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2012.1078
Rajcevic U, Petersen K, Knol JC, Loos M, Bougnaud S, Klychnikov O, Li KW, Pham TV, Wang J, Miletic H, Peng Z, Bjerkvig R, Jimenez CR, Niclou SP (2009) iTRAQ-based proteomics profiling reveals increased metabolic activity and cellular cross-talk in angiogenic compared with invasive glioblastoma phenotype. Mol Cell Proteomics 8:2595–2612. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M900124-MCP200
Shi X, Zhan L, Xiao C, Lei Z, Yang H, Wang L, Zhao J, Zhang HT (2015) miR-1238 inhibits cell proliferation by targeting LHX2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 6:19043–19054. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.4232
Duan R, Han L, Wang Q, Wei J, Chen L, Zhang J, Kang C, Wang L (2015) HOXA13 is a potential GBM diagnostic marker and promotes glioma invasion by activating the Wnt and TGF-beta pathways. Oncotarget 6:27778–27793. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.4813
Li W, Zheng J, Deng J, You Y, Wu H, Li N, Lu J, Zhou Y (2014) Increased levels of the long intergenic non-protein coding RNA POU3F3 promote DNA methylation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Gastroenterology 146:1714–1726 e1715. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2014.03.002
Wang J, Zhang Y, Liu X, Ma J, Liu P, Hu C, Zhang G (2014) Annexin A5 inhibits diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell invasion and chemoresistance through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling. Oncol Rep 32:2557–2563. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2014.3547
Wu L, Yang L, Xiong Y, Guo H, Shen X, Cheng Z, Zhang Y, Gao Z, Zhu X (2014) Annexin A5 promotes invasion and chemoresistance to temozolomide in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Tumour Biol 35:12327–12337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2545-1
Singh AR, Joshi S, George E, Durden DL (2014) Anti-tumor effect of a novel PI3-kinase inhibitor, SF1126, in (12) V-Ha-Ras transgenic mouse glioma model. Cancer Cell Int 14:105. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-014-0105-9
Shingu T, Yamada K, Hara N, Moritake K, Osago H, Terashima M, Uemura T, Yamasaki T, Tsuchiya M (2003) Synergistic augmentation of antimicrotubule agent-induced cytotoxicity by a phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor in human malignant glioma cells. Cancer Res 63:4044–4047
Gaelzer MM, Coelho BP, de Quadros AH, Hoppe JB, Terra SR, Guerra MC, Usach V, Guma FC, Goncalves CA, Setton-Avruj P, Battastini AM, Salbego CG (2016) Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/AKT pathway inhibition by doxazosin promotes glioblastoma cells death, upregulation of p53 and triggers low neurotoxicity. PloS ONE 11:e0154612. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0154612
Moss SE, Morgan RO (2004) The annexins. Genome Biol 5:219. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2004-5-4-219
Laohavisit A, Davies JM (2011) Annexins. New Phytol 189:40–53. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03533.x
Mortimer JC, Laohavisit A, Macpherson N, Webb A, Brownlee C, Battey NH, Davies JM (2008) Annexins: multifunctional components of growth and adaptation. J Exp Bot 59:533–544. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erm344
Shin DW, Kwon YJ, Ye DJ, Baek HS, Lee JE, Chun YJ (2016) Auranofin suppresses plasminogen activator inhibitor-2 expression through annexin A5 induction in human prostate cancer cells. Biomol Ther. https://doi.org/10.4062/biomolther.2016.223
Hong M, Park N, Chun YJ (2014) Role of annexin a5 on mitochondria-dependent apoptosis induced by tetramethoxystilbene in human breast cancer cells. Biomol Ther 22:519–524. https://doi.org/10.4062/biomolther.2014.112
Park N, Chun YJ (2014) Auranofin promotes mitochondrial apoptosis by inducing annexin A5 expression and translocation in human prostate cancer cells. J Toxicol Environ Health A 77:1467–1476. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2014.955834
Tang Y, Lv P, Sun Z, Han L, Luo B, Zhou W (2015) 14-3-3zeta up-regulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in hepatocellular carcinoma via activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-small ka, CyrillicB signal transduction pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:15845–15853
Shan RF, Zhou YF, Peng AF, Jie ZG (2014) Inhibition of Aurora-B suppresses HepG2 cell invasion and migration via the PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signaling pathway in vitro. Exp Ther Med 8:1005–1009. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2014.1844
Rodriguez M, Luo W, Weng J, Zeng L, Yi Z, Siwko S, Liu M (2014) PSGR promotes prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and prostate cancer xenograft growth through NF-kappaB. Oncogenesis 3:e114. https://doi.org/10.1038/oncsis.2014.29
Felx M, Guyot MC, Isler M, Turcotte RE, Doyon J, Khatib AM, Leclerc S, Moreau A, Moldovan F (2006) Endothelin-1 (ET-1) promotes MMP-2 and MMP-9 induction involving the transcription factor NF-kappaB in human osteosarcoma. Clin Sci 110:645–654. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20050286
Ahmad A, Biersack B, Li Y, Kong D, Bao B, Schobert R, Padhye SB, Sarkar FH (2013) Targeted regulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR/NF-kappaB signaling by indole compounds and their derivatives: mechanistic details and biological implications for cancer therapy. Anti-cancer Agents Med Chem 13:1002–1013
Zhang LL, Mu GG, Ding QS, Li YX, Shi YB, Dai JF, Yu HG (2015) Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) represses colon cancer progression through inhibiting paxillin transcription via PI3K/AKT/NF-kappaB pathway. J Biol Chem 290:15018–15029. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.641407
Jiao Y, Li H, Liu Y, Guo A, Xu X, Qu X, Wang S, Zhao J, Li Y, Cao Y (2015) Resveratrol inhibits the invasion of glioblastoma-initiating cells via down-regulation of the PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Nutrients 7:4383–4402. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7064383
Funding
This work was supported by the National Scientific Foundation of China grants (No. 81560411).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Review Board at The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, and written informed consent was obtained from each participant. All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committees and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, C., Guo, H., Zhang, P. et al. AnnexinA5 promote glioma cell invasion and migration via the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway. J Neurooncol 138, 469–478 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-2818-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-2818-4