Abstract
Purpose
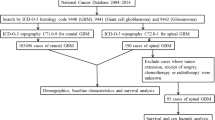
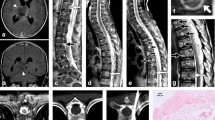
Intracranial glioblastomas with simultaneous spinal lesions prior to chemoradiation therapy or craniotomy, defined as initial spinal metastasis, are not well understood. Herein, we investigated intracranial glioblastoma and demonstrated the importance of spinal screening using gadolinium enhanced spinal magnetic resonance imaging (Gd-MRI).
Methods
Consecutive adult patients with intracranial glioblastoma were treated between 2010 and 2014 and received spinal screening using Gd-MRI. Spinal screening was performed regardless of spine-related symptoms, and patients presenting with and without initial spinal metastasis (spinal and non-spinal groups, respectively) were compared based on patient demographics, tumor characteristics, radiological and molecular features, and overall survival (OS).
Results
During the study period, 116 glioblastoma cases were treated and 87 of these (76%) underwent spinal screening. Among these patients, 11 (13%) were included in the spinal group, and 76 (87%) were included in the non-spinal group. All patients of the spinal group were free of symptoms related to spinal lesions. Compared with the non-spinal group, intracranial lesions of the spinal group presented higher incidences of intracranial dissemination and were located at subventricular zones (P = 0.0012 and 0.020, respectively). MIB-1 labeling index, molecular alterations such as IDH1 mutation, TERT promoter mutation, and immunoreactivity of ATRX and MGMT did not differ between two groups. OS was significantly shorter in the spinal group than in the non-spinal group (P = 0.0054).
Conclusions
This study revealed a relatively high incidence of spinal metastasis. A subset of glioblastoma patients benefited from spinal screening, through which early detection of asymptomatic spinal metastasis was achieved.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wick W, Stupp R, Beule AC, Bromberg J, Wick A, Ernemann U, Platten M, Marosi C, Mason WP, van den Bent M, Weller M, Rorden C, Karnath HO (2008) A novel tool to analyze MRI recurrence patterns in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol 10(6):1019–1024. https://doi.org/10.1215/15228517-2008-058
Shibahara I, Sonoda Y, Saito R, Kanamori M, Yamashita Y, Kumabe T, Watanabe M, Suzuki H, Watanabe T, Ishioka C, Tominaga T (2013) The expression status of CD133 is associated with the pattern and timing of primary glioblastoma recurrence. Neuro Oncol 15(9):1151–1159. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/not066
Lawton CD, Nagasawa DT, Yang I, Fessler RG, Smith ZA (2012) Leptomeningeal spinal metastases from glioblastoma multiforme: treatment and management of an uncommon manifestation of disease. J Neurosurg Spine 17(5):438–448. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.7.SPINE12212
Saito R, Kumabe T, Jokura H, Shirane R, Yoshimoto T (2003) Symptomatic spinal dissemination of malignant astrocytoma. J Neurooncol 61(3):227–235
Lin L, Innerfield CE, Cuccurullo SJ (2014) Symptomatic spinal leptomeningeal metastasis from intracranial glioblastoma multiforme. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 93(9):838–839. https://doi.org/10.1097/PHM.0b013e3182a51b90
Alatakis S, Malham GM, Thien C (2001) Spinal leptomeningeal metastasis from cerebral glioblastoma multiforme presenting with radicular pain: case report and literature review. Surg Neurol 56(1):33–37 (discussion 37–38)
Onda K, Tanaka R, Takahashi H, Takeda N, Ikuta F (1989) Cerebral glioblastoma with cerebrospinal fluid dissemination: a clinicopathological study of 14 cases examined by complete autopsy. Neurosurgery 25(4):533–540
Fujimura M, Kumabe T, Jokura H, Shirane R, Yoshimoto T, Tominaga T (2004) Intractable vomiting as an early clinical symptom of cerebrospinal fluid seeding to the fourth ventricle in patients with high-grade astrocytoma. J Neurooncol 66(1–2):209–216
Kanamori M, Kumabe T, Sonoda Y, Nishino Y, Watanabe M, Tominaga T (2009) Predictive factors for overall and progression-free survival, and dissemination in oligodendroglial tumors. J Neurooncol 93(2):219–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9762-7
Kato H, Fujimura M, Kumabe T, Ishioka C, Kanamaru R, Yoshimoto T (2004) PTEN gene mutation and high MIB-1 labeling index may contribute to dissemination in patients with glioblastoma. J Clin Neurosci 11(1):37–41
Saito R, Kumabe T, Jokura H, Yoshimoto T (2002) Fatal hemorrhage after radiochemotherapy for leptomeningeal dissemination of glioma: report of two cases. Surg Neurol 57(1):46–48
Saito R, Kumabe T, Kanamori M, Sonoda Y, Tominaga T (2017) Distant recurrences limit the survival of patients with thalamic high-grade gliomas after successful resection. Neurosurg Rev 40(3):469–477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-016-0804-x
Inoue T, Endo T, Nakamura T, Shibahara I, Endo H, Tominaga T (2018) Expression of CD133 as a putative prognostic biomarker to predict intracranial dissemination of primary spinal cord astrocytoma. World Neurosurg 110:e715–e726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.11.089
Denicolai E, Tabouret E, Colin C, Metellus P, Nanni I, Boucard C, Tchoghandjian A, Meyronet D, Baeza-Kallee N, Chinot O, Figarella-Branger D (2016) Molecular heterogeneity of glioblastomas: does location matter? Oncotarget 7(1):902–913. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6433
Lim DA, Cha S, Mayo MC, Chen MH, Keles E, VandenBerg S, Berger MS (2007) Relationship of glioblastoma multiforme to neural stem cell regions predicts invasive and multifocal tumor phenotype. Neuro Oncol 9(4):424–429. https://doi.org/10.1215/15228517-2007-023
Sonoda Y, Saito R, Kanamori M, Kumabe T, Uenohara H, Tominaga T (2014) The association of subventricular zone involvement at recurrence with survival after repeat surgery in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 54(4):302–309
Elliott JP, Keles GE, Waite M, Temkin N, Berger MS (1994) Ventricular entry during resection of malignant gliomas: effect on intracranial cerebrospinal fluid tumor dissemination. J Neurosurg 80(5):834–839. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1994.80.5.0834
Sonoda Y, Yokosawa M, Saito R, Kanamori M, Yamashita Y, Kumabe T, Watanabe M, Tominaga T (2010) O (6)-Methylguanine DNA methyltransferase determined by promoter hypermethylation and immunohistochemical expression is correlated with progression-free survival in patients with glioblastoma. Int J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-010-0065-6
Shibahara I, Sonoda Y, Suzuki H, Mayama A, Kanamori M, Saito R, Suzuki Y, Mashiyama S, Uenohara H, Watanabe M, Kumabe T, Tominaga T (2017) Glioblastoma in neurofibromatosis 1 patients without IDH1, BRAF V600E, and TERT promoter mutations. Brain Tumor Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10014-017-0302-z
Shibahara I, Sonoda Y, Kanamori M, Saito R, Yamashita Y, Kumabe T, Watanabe M, Suzuki H, Kato S, Ishioka C, Tominaga T (2012) IDH1/2 gene status defines the prognosis and molecular profiles in patients with grade III gliomas. Int J Clin Oncol 17(6):551–561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-011-0323-2
Sonoda Y, Kumabe T, Nakamura T, Saito R, Kanamori M, Yamashita Y, Suzuki H, Tominaga T (2009) Analysis of IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in Japanese glioma patients. Cancer Sci 100(10):1996–1998. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01270.x
Eckel-Passow JE, Lachance DH, Molinaro AM, Walsh KM, Decker PA, Sicotte H, Pekmezci M, Rice T, Kosel ML, Smirnov IV, Sarkar G, Caron AA, Kollmeyer TM, Praska CE, Chada AR, Halder C, Hansen HM, McCoy LS, Bracci PM, Marshall R, Zheng S, Reis GF, Pico AR, O’Neill BP, Buckner JC, Giannini C, Huse JT, Perry A, Tihan T, Berger MS, Chang SM, Prados MD, Wiemels J, Wiencke JK, Wrensch MR, Jenkins RB (2015) Glioma groups based on 1p/19q, IDH, and TERT promoter mutations in tumors. N Engl J Med 372(26):2499–2508. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1407279
Pietschmann S, von Bueren AO, Henke G, Kerber MJ, Kortmann RD, Muller K (2014) An individual patient data meta-analysis on characteristics, treatments and outcomes of the glioblastoma/gliosarcoma patients with central nervous system metastases reported in literature until 2013. J Neurooncol 120(3):451–457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1596-x
Pezeshkpour GH, Henry JM, Armbrustmacher VW (1984) Spinal metastases. A rare mode of presentation of brain tumors. Cancer 54(2):353–356
Vertosick FT Jr, Selker RG (1990) Brain stem and spinal metastases of supratentorial glioblastoma multiforme: a clinical series. Neurosurgery 27(4):516–521 (discussion 521–512)
Ravindran K, Gaillard F, Lasocki A (2017) Distant spread of a supratentorial glioblastoma to the spinal cord. J Clin Neurosci 38:56–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2016.11.010
Shapiro MD (2006) MR imaging of the spine at 3T. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 14(1):97–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mric.2006.01.005
Rodegerdts EA, Boss A, Riemarzik K, Lichy M, Schick F, Claussen CD, Schlemmer HP (2006) 3D imaging of the whole spine at 3T compared to 1.5T: initial experiences. Acta Radiol 47(5):488–493
de Eulate-Beramendi SA, Pina-Batista KM, Rodrigo V, Torres-Rivas HE, Rial-Basalo JC (2016) Multicentric spinal cord and brain glioblastoma without previous craniotomy. Surg Neurol Int 7(Suppl 17):S492–S494. https://doi.org/10.4103/2152-7806.185785
Pohar S, Taylor W, Chandan VS, Shah H, Sagerman RH (2004) Primary presentation of glioblastoma multiforme with leptomeningeal metastasis in the absence of previous craniotomy: a case report. Am J Clin Oncol 27(6):640–641
Rivero-Garvia M, Boto GR, Perez-Zamarron A, Gutierrez-Gonzalez R, Ahmad IS, Martinez A (2008) Spinal cord and brain glioblastoma multiforme without previous craniotomy. J Neurosurg Spine 8(6):601. https://doi.org/10.3171/SPI/2008/8/6/601
Adeberg S, Konig L, Bostel T, Harrabi S, Welzel T, Debus J, Combs SE (2014) Glioblastoma recurrence patterns after radiation therapy with regard to the subventricular zone. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 90(4):886–893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.07.027
Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Bjork-Eriksson T, Alborn AM, Nordborg C, Peterson DA, Gage FH (1998) Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med 4(11):1313–1317. https://doi.org/10.1038/3305
Shahideh M, Fallah A, Munoz DG, Loch Macdonald R (2012) Systematic review of primary intracranial glioblastoma multiforme with symptomatic spinal metastases, with two illustrative patients. J Clin Neurosci 19(8):1080–1086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2011.09.024
Maslehaty H, Cordovi S, Hefti M (2011) Symptomatic spinal metastases of intracranial glioblastoma: clinical characteristics and pathomechanism relating to GFAP expression. J Neurooncol 101(2):329–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0257-y
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Enago (http://www.enago.jp) for the English language review. This work was supported in part by KAKENHI Grant Number 16K10749.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest concerning the materials or methods or the findings of this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shibahara, I., Saito, R., Osada, Y. et al. Incidence of initial spinal metastasis in glioblastoma patients and the importance of spinal screening using MRI. J Neurooncol 141, 337–345 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-03036-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-03036-4