Abstract
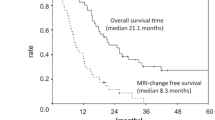
Panobinostat is an oral HDAC inhibitor with radiosensitizing activity. We investigated the safety, tolerability and preliminary efficacy of panobinostat combined with fractionated stereotactic re-irradiation therapy (FSRT) for recurrent high grade gliomas. Patients with recurrent high grade gliomas were enrolled in a 3 + 3 dose escalation study to determine dose limiting toxicities (DLTs), maximum tolerated dose (MTD), safety, tolerability, and preliminary efficacy. FSRT was prescribed to 30–35 Gy delivered in 10 fractions. Panobinostat was administrated concurrently with radiotherapy. Of 12 evaluable patients, 8 had recurrent GBM, and 4 had recurrent anaplastic astrocytoma. There were three grade 3 or higher toxicities in each the 10 and 30 mg cohorts. In the 30 mg cohort, there was one DLT; grade 4 neutropenia. One patient developed late grade 3 radionecrosis. The median follow up was 18.8 months. The PFS6 was 67, 33, and 83 % for 10, 20, and 30 mg cohorts, respectively. The median OS was 7.8, 6.1 and 16.1 months for the 10, 20 and 30 mg cohorts, respectively. Panobinostat administrated with FSRT is well tolerated at 30 mg. A phase II trial is warranted to assess the efficacy of panobinostat plus FSRT for recurrent glioma.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Farah P, Ondracek A, Chen Y, Wolinsky Y et al. (2013) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2006–2010, Neuro-Oncol, 15 Suppl 2: ii1–56
Lee SW, Fraass BA, Marsh LH, Herbort K, Gebarski SS, Martel MK et al (1999) Patterns of failure following high-dose 3-D conformal radiotherapy for high-grade astrocytomas: a quantitative dosimetric study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 43:79–88
Helseth R, Helseth E, Johannesen TB, Langberg CW, Lote K, Rønning P et al (2010) Overall survival, prognostic factors, and repeated surgery in a consecutive series of 516 patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Acta Neurol Scand 122:159–167
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines) Central Nervous System Cancers (2014)
Fogh SE, Andrews DW, Glass J, Curran W, Glass C, Champ C et al (2010) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiation therapy: an effective therapy for recurrent high-grade gliomas. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 28:3048–3053
Friedman HS, Prados MD, Wen PY, Mikkelsen T, Schiff D, Abrey LE et al (2009) Bevacizumab alone and in combination with irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 27:4733–4740
Taal W, Oosterkamp HM, Walenkamp AME, Dubbink HJ, Beerepoot LV, Hanse MCJ, et al. (2014) Single-agent bevacizumab or lomustine versus a combination of bevacizumab plus lomustine in patients with recurrent glioblastoma (BELOB trial): a randomised controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol
Li J, Li G, Xu W (2013) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: an attractive strategy for cancer therapy. Curr Med Chem 20:1858–1886
Glozak MA, Sengupta N, Zhang X, Seto E (2005) Acetylation and deacetylation of non-histone proteins. Gene 363:15–23
Bar-Sela G, Jacobs KM, Gius D (2007) Histone deacetylase inhibitor and demethylating agent chromatin compaction and the radiation response by cancer cells. Cancer J Sudbury Mass 13:65–69
Chinnaiyan P, Vallabhaneni G, Armstrong E, Huang S-M, Harari PM (2005) Modulation of radiation response by histone deacetylase inhibition. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 62:223–229
Karagiannis TC, El-Osta A (2006) Modulation of cellular radiation responses by histone deacetylase inhibitors. Oncogene 25:3885–3893
Alvarez AA, Field M, Bushnev S, Longo MS, Sugaya K (2015) The effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors on glioblastoma-derived stem cells. J Mol Neurosci MN 55:7–20
Drappatz J, Lee EQ, Hammond S, Grimm SA, Norden AD, Beroukhim R et al (2012) Phase I study of panobinostat in combination with bevacizumab for recurrent high-grade glioma. J Neurooncol 107:133–138
Karagiannis TC, El-Osta A (2006) The paradox of histone deacetylase inhibitor-mediated modulation of cellular responses to radiation. Cell Cycle Georget Tex. 5:288–295
Camphausen K, Scott T, Sproull M, Tofilon PJ (2004) Enhancement of xenograft tumor radiosensitivity by the histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275 and correlation with histone hyperacetylation. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 10:6066–6071
Chinnaiyan P, Allen GW, Harari PM (2006) Radiation and new molecular agents, part II: targeting HDAC, HSP90, IGF-1R, PI3K, and Ras. Semin Radiat Oncol 16:59–64
Entin-Meer M, Yang X, VandenBerg SR, Lamborn KR, Nudelman A, Rephaeli A et al (2007) In vivo efficacy of a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor in combination with radiation for the treatment of gliomas. Neuro-Oncol 9:82–88
Lee EQ, Reardon DA, Schiff D, Drappatz J, Muzikansky A, Grimm SA et al (2015) Phase II study of panobinostat in combination with bevacizumab for recurrent glioblastoma and anaplastic glioma. Neuro-Oncol 17:862–867
Kreisl TN, Kim L, Moore K, Duic P, Royce C, Stroud I et al (2009) Phase II trial of single-agent bevacizumab followed by bevacizumab plus irinotecan at tumor progression in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 27:740–745
Funding
Novartis provided panobinostat and partial funding for the trial.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, W., Palmer, J.D., Werner-Wasik, M. et al. Phase I trial of panobinostat and fractionated stereotactic re-irradiation therapy for recurrent high grade gliomas. J Neurooncol 127, 535–539 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2059-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2059-3