Abstract
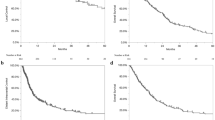
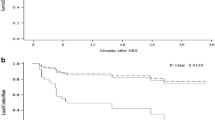
We investigated effects of breast cancer subtype on overall survival (OS), local and distant control, and time from initial diagnosis to brain metastases (BM). We also investigated advances in graded prognostic assessment (GPA) scores. A cohort of 72 patients treated for BM from breast cancer with Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery at our institution from 2000 to 2014 had subtyping available and were used for this study. Median follow up for OS was 12 months and for control was 6 months. OS for luminal, HER2, and triple negative subtypes were 26, 20, and 22 months. OS when stratified by Sperduto et al. (J Clin Oncol 30(4):419–425, 2012) and Subbiah et al. (J Clin Oncol 33(20):2239–2245, 2015) GPAs were similar (p = 0.087 and p = 0.063). KPS and treatment modality were significant for OS (p = 0.002; p = 0.034). On univariate analysis, triple negative subtype and >3 BM were trending and significant for decreased OS (p = 0.084; p = 0.047). On multivariable analysis HER2, triple negative, and >3 BM were significant for OS (p = 0.022; p = 0.040; p = 0.009). Subtype was significant for response on a per lesion basis (p = 0.007). Subtype was trending towards significance when analyzing time from initial diagnosis to BM treatment (p = 0.064). Breast cancer subtype is an important prognostic factor when stratifying breast cancer patients with BM. The addition of number of BM to the GPA is a useful addition and should be further investigated. Subtype has an effect on lesion response, and also on rate of development BM after initial diagnosis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Howlander N, Noone AM, Krpacho M et al (2015) SEER cancer statistics review. SEER web site
Eichler AF, Kuter I, Ryan P et al (2008) Survival in patients with brain metastases from breast cancer. Cancer 112(11):2359–2376
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D et al (2012) Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 30(4):419–425
Subbiah IM, Lei X, Weinberg JS et al (2015) Validation and development of a modified breast graded prognostic assessment as a tool for survival in patients with breast cancer and brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 33(20):2239–2245
Hofer S, Pestalozzi BC (2013) Treatment of breast cancer brain metastases. Eur J Pharmacol 717(1–3):84–87
Freedman RA, Anders CK (2012) Treatment of Breast Cancer in Brain Metastases. Curr Breast Cancer Rep 4(1):1–9
Tsukada Y, Fouad A, Pickren JW (1983) Central nervous system metastasis from breast carcinoma. Autopsy study. Cancer 52:1249–1254
Gori S, Rimondini S, De Angelis V (2007) Central nevous system metastases in HER-2 postive metastatic breast cancer patients treated with trastuzumab: incidence, survival, and risk factors. Oncologist 12:766–773
Tomasello G, Bedard P, De Azambuja E (2010) Brain metastases in HER2-positive breast cancer: the evolving role of lapatinib. Crit REv Oncol/Hematol 75:110–121
Kennecke H, Yerushalmi R, Woods R et al (2010) Metastatic behavior of breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol 28(20):3271–3277
Clayton AJ, Danson S, Jolly S et al (2004) Incidence of cerebral metastases in patients treated with trastuzumab for metastatic breast cancer. Br J Cancer 91:639–643
Niwinska A, Murawksa M, Pogoda K (2010) Breast cancer brain metastases: differences in survial depending of biological subtype, RPA RTOG prognostic class and systemic treatment after whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT). Ann Oncol 21(5):942–948
Nam BH, Kim SY, Han HS et al (2008) Breast cancer subtypes and survival in patients with brain metastases. Breast Cancer Res 10(1):R20
Gaspar LE, Scott C, Rotman M et al (1997) Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37:745–751
Sperduto PWKN, Roberge D et al (2011) The effect of tumor subtype on survival and the Graded Prognostic Assessment (GPA) for patients with breast cancer and brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:2111
Shaw E, Charles Scott, Souhami L et al (1999) single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90-05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47(2):291–298
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA et al (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. J Nat Cancer Inst 92(3):205–216
Jani A, Rozenblat T, Yaeh A et al (2015) the energy index does not affect local control of brain metastases treated by gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 77(1):119–125
Nayak L, Lee EQ, Wen PY (2012) Epidemiology of brain metastases. Curr Oncol Rep 14(1):48–54
Wang TJC, Saad S, Qureshi YH et al (2015) Does lung cancer mutation status and targeted therapy predict outcomes and local control in the setting of brain metastases treated with radiation? Nero-Oncology 17(7):1022–1028
Nguyen PL, Taghian AG, Katz MS et al (2008) Breast cancer subtype approximated by estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER-2 is associated with local and distant recurrence after breast-conserving therapy. J Clin Oncol 26(14):2373–2378
Parker JS, Mullins M, Cheang MCU et al (2009) Supervised risk predictor of breast cancer based on intrinsic subtypes. J Clin Oncol 27(8):1160–1167
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grubb, C.S., Jani, A., Wu, CC. et al. Breast cancer subtype as a predictor for outcomes and control in the setting of brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 127, 103–110 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-2014-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-2014-8