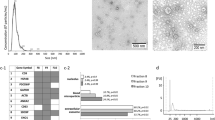
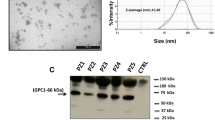
Abstract
Analysis of extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from plasma or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) has emerged as a promising biomarker platform for therapeutic monitoring in glioblastoma patients. However, the contents of the various subpopulations of EVs in these clinical specimens remain poorly defined. Here we characterize the relative abundance of miRNA species in EVs derived from the serum and cerebrospinal fluid of glioblastoma patients. EVs were isolated from glioblastoma cell lines as well as the plasma and CSF of glioblastoma patients. The microvesicle subpopulation was isolated by pelleting at 10,000×g for 30 min after cellular debris was cleared by a 2000×g (20 min) spin. The exosome subpopulation was isolated by pelleting the microvesicle supernatant at 120,000×g (120 min). qRT-PCR was performed to examine the distribution of miR-21, miR-103, miR-24, and miR-125. Global miRNA profiling was performed in select glioblastoma CSF samples. In plasma and cell line derived EVs, the relative abundance of miRNAs in exosome and microvesicles were highly variable. In some specimens, the majority of the miRNA species were found in exosomes while in other, they were found in microvesicles. In contrast, CSF exosomes were enriched for miRNAs relative to CSF microvesicles. In CSF, there is an average of one molecule of miRNA per 150–25,000 EVs. Most EVs derived from clinical biofluids are devoid of miRNA content. The relative distribution of miRNA species in plasma exosomes or microvesicles is unpredictable. In contrast, CSF exosomes are the major EV compartment that harbor miRNAs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Farah P, Ondracek A, Chen Y et al (2013) CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2006–2010. Neuro Oncol. 15(Suppl 2):ii1–ii56
Bartek J Jr, Ng K, Bartek J, Fischer W, Carter B et al (2012) Key concepts in glioblastoma therapy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83:753–760
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ et al (2009) Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol 10:459–466
Clarke JL, Chang SM (2012) Neuroimaging: diagnosis and response assessment in glioblastoma. Cancer J 18:26–31
Sorensen AG, Batchelor TT, Wen PY, Zhang WT, Jain RK (2008) Response criteria for glioma. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 5:634–644
Teodori L, Albertini MC, Uguccioni F, Falcieri E, Rocchi MB et al (2006) Static magnetic fields affect cell size, shape, orientation, and membrane surface of human glioblastoma cells, as demonstrated by electron, optic, and atomic force microscopy. Cytometry A 69:75–85
Chen CC, Motegi A, Hasegawa Y, Myung K, Kolodner R et al (2006) Genetic analysis of ionizing radiation-induced mutagenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals TransLesion Synthesis (TLS) independent of PCNA K164 SUMOylation and ubiquitination. DNA Repair (Amst) 5:1475–1488
Verma N, Cowperthwaite MC, Burnett MG, Markey MK (2013) Differentiating tumor recurrence from treatment necrosis: a review of neuro-oncologic imaging strategies. Neuro Oncol 15:515–534
Air EL, Leach JL, Warnick RE, McPherson CM (2009) Comparing the risks of frameless stereotactic biopsy in eloquent and noneloquent regions of the brain: a retrospective review of 284 cases. J Neurosurg 111:820–824
Chen CC, Hsu PW, Erich Wu TW, Lee ST, Chang CN et al (2009) Stereotactic brain biopsy: single center retrospective analysis of complications. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 111:835–839
Skog J, Wurdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer DH, Gainche L et al (2008) Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol 10:1470–1476
Akers JC, Ramakrishnan V, Kim R, Skog J, Nakano I et al (2013) MiR-21 in the extracellular vesicles (EVs) of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): a platform for glioblastoma biomarker development. PLoS One 8:e78115
Chen WW, Balaj L, Liau LM, Samuels ML, Kotsopoulos SK et al (2013) BEAMing and droplet digital PCR analysis of mutant IDH1 mRNA in glioma patient serum and cerebrospinal fluid extracellular vesicles. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2:e109
Zhang W, Zhang J, Yan W, You G, Bao Z et al (2013) Whole-genome microRNA expression profiling identifies a 5-microRNA signature as a prognostic biomarker in Chinese patients with primary glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer 119:814–824
Zhang W, Zhang J, Hoadley K, Kushwaha D, Ramakrishnan V et al (2012) miR-181d: a predictive glioblastoma biomarker that downregulates MGMT expression. Neuro-Oncology 14:712–719
Kushwaha D, Ramakrishnan V, Ng K, Steed T, Nguyen T et al (2014) A genome-wide miRNA screen revealed miR-603 as a MGMT-regulating miRNA in glioblastomas. Oncotarget 5:4026–4039
Shifrin DA Jr, Demory Beckler M, Coffey RJ, Tyska MJ (2013) Extracellular vesicles: communication, coercion, and conditioning. Mol Biol Cell 24:1253–1259
Street J, Barran P, Mackay CL, Weidt S, Balmforth C et al (2012) Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human cerebrospinal fluid. J Trans Med 10:5
Noerholm M, Balaj L, Limperg T, Salehi A, Zhu LD et al (2012) RNA expression patterns in serum microvesicles from patients with glioblastoma multiforme and controls. BMC Cancer 12:22
Blank A, Dekker CA (1981) Ribonucleases of human serum, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, and leukocytes. Activity staining following electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Biochemistry 20:2261–2267
Shao H, Chung J, Balaj L, Charest A, Bigner DD et al (2012) Protein typing of circulating microvesicles allows real-time monitoring of glioblastoma therapy. Nat Med 18:1835–1840
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C (2008) MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 110:13–21
Akers J, Gonda D, Kim R, Carter B, Chen C (2013) Biogenesis of extracellular vesicles (EV): exosomes, microvesicles, retrovirus-like vesicles, and apoptotic bodies. J Neuro-Oncology 113:1–11
Bass DM, Baylor M, Chen C, Upadhyayula U (1995) Dansylcadaverine and cytochalasin D enhance rotavirus infection of murine L cells. Virology 212:429–437
Camussi G, Deregibus MC, Bruno S, Grange C, Fonsato V et al (2011) Exosome/microvesicle-mediated epigenetic reprogramming of cells. Am J Cancer Res 1:98–110
Johnstone RM (2006) Exosomes biological significance: a concise review. Blood Cells Mol Dis 36:315–321
Booth AM, Fang Y, Fallon JK, Yang JM, Hildreth JE et al (2006) Exosomes and HIV Gag bud from endosome-like domains of the T cell plasma membrane. J Cell Biol 172:923–935
Gould SJ, Raposo G (2013) As we wait: coping with an imperfect nomenclature for extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles 2
Joshi K, Banasavadi-Siddegowda Y, Mo X, Kim SH, Mao P et al (2013) MELK-dependent FOXM1 Phosphorylation is Essential for Proliferation of Glioma Stem Cells. Stem Cells. 31(6):1051–1063
Ng K, Nitta M, Hu L, Kesari S, Kung A et al (2009) A small interference RNA screen revealed proteasome inhibition as strategy for glioblastoma therapy. Clin Neurosurg 56:107–118
Thery C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, Clayton A (2006) Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol 3:3–22
Jayachandran M, Miller VM, Heit JA, Owen WG (2012) Methodology for isolation, identification and characterization of microvesicles in peripheral blood. J Immunol Methods 375:207–214
Sokolova V, Ludwig AK, Hornung S, Rotan O, Horn PA et al (2011) Characterisation of exosomes derived from human cells by nanoparticle tracking analysis and scanning electron microscopy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 87:146–150
Trang P, Wiggins JF, Daige CL, Cho C, Omotola M et al (2011) Systemic delivery of tumor suppressor microRNA mimics using a neutral lipid emulsion inhibits lung tumors in mice. Mol Ther 19:1116–1122
Teplyuk NM, Mollenhauer B, Gabriely G, Giese A, Kim E et al (2012) MicroRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid identify glioblastoma and metastatic brain cancers and reflect disease activity. Neuro-Oncology 14:689–700
Grigorenko EV, Ortenberg E, Hurley J, Bond A, Munnelly K (2011) miRNA profiling on high-throughput OpenArray system. Methods Mol Biol 676:101–110
Eldh M, Lotvall J, Malmhall C, Ekstrom K (2012) Importance of RNA isolation methods for analysis of exosomal RNA: evaluation of different methods. Mol Immunol 50:278–286
Schutzer SE, Liu T, Natelson BH, Angel TE, Schepmoes AA et al (2010) Establishing the proteome of normal human cerebrospinal fluid. PLoS One 5:e10980
Hu S, Loo JA, Wong DT (2006) Human body fluid proteome analysis. Proteomics 6:6326–6353
Mutungi G, Waters D, Ratliff J, Puglisi M, Clark RM et al (2010) Eggs distinctly modulate plasma carotenoid and lipoprotein subclasses in adult men following a carbohydrate-restricted diet. J Nutr Biochem 21:261–267
Lapointe A, Couillard C, Lemieux S (2006) Effects of dietary factors on oxidation of low-density lipoprotein particles. J Nutr Biochem 17:645–658
Witwer KW, Buzas EI, Bemis LT, Bora A, Lasser C et al (2013) Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J Extracell Vesicles. doi:10.3402/jev.v2i0.20360
Parvas M, Parada C, Bueno D (2008) A blood-CSF barrier function controls embryonic CSF protein composition and homeostasis during early CNS development. Dev Biol 321:51–63
Alegre E, Sanmamed MF, Rodriguez C, Carranza O, Martin-Algarra S et al (2014) Study of circulating microRNA-125b levels in serum exosomes in advanced melanoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med 138:828–832
Crescitelli R, Lasser C, Szabo TG, Kittel A, Eldh M et al (2013) Distinct RNA profiles in subpopulations of extracellular vesicles: apoptotic bodies, microvesicles and exosomes. J Extracell Vesicles. doi:10.3402/jev.v2i0.20677
Salido-Guadarrama I, Romero-Cordoba S, Peralta-Zaragoza O, Hidalgo-Miranda A, Rodriguez-Dorantes M (2014) MicroRNAs transported by exosomes in body fluids as mediators of intercellular communication in cancer. Onco Targets Ther 7:1327–1338
Pegtel DM, Cosmopoulos K, Thorley-Lawson DA, van Eijndhoven MA, Hopmans ES et al (2010) Functional delivery of viral miRNAs via exosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:6328–6333
Yuan A, Farber EL, Rapoport AL, Tejada D, Deniskin R et al (2009) Transfer of microRNAs by embryonic stem cell microvesicles. PLoS One 4:e4722
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ et al (2007) Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol 9:654–659
Acknowledgments
The work is supported by NIH UH2 TR000931-0, NIH PO1 2P30CA023100-28 (BSC and CCC) and International S&T Cooperation Program of China, 2014DFA31470 (CCC and YM). CCC is supported by the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation Clinical Scientist Development Award, Sontag Foundation Distinguished Scientist Award, Burroughs Wellcome Fund Career Awards for Medical Scientists, the Kimmel Scholar Award, a Grant from Accelerated Brain Cancer Cure, and the William Guy Forbeck Research Foundation.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Bob S. Carter and Clark C. Chen have shared responsibility as senior authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akers, J.C., Ramakrishnan, V., Kim, R. et al. miRNA contents of cerebrospinal fluid extracellular vesicles in glioblastoma patients. J Neurooncol 123, 205–216 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1784-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1784-3