Abstract
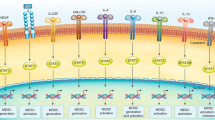
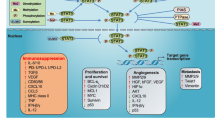
The role of tumor-induced immune modulation in cancer progression is currently a focus of investigation. The signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is an established molecular hub of immunosuppression, and its signaling pathways are classically overactivated within malignancies. This article will review STAT3 operational mechanisms within the immune system and the tumor microenvironment, with a focus on therapeutic strategies that may impact outcomes for patients with cancer.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kortylewski M, Yu H (2007) Stat3 as a potential target for cancer immunotherapy. J Immunother 30(2):131–139. doi:10.1097/01.cji.0000211327.76266.65.00002371-200702000-00001
Kim JE, Patel M, Ruzevick J, Jackson CM, Lim M (2014) STAT3 activation in glioblastoma: biochemical and therapeutic implications. Cancers (Basel) 6(1):376–395. doi:10.3390/cancers6010376
Rebe C, Vegran F, Berger H, Ghiringhelli F (2013) STAT3 activation: a key factor in tumor immunoescape. JAKSTAT 2(1):e23010. doi:10.4161/jkst.23010.2012JAKS0054R
Chen F, Xu Y, Luo Y, Zheng D, Song Y, Yu K, Li H, Zhang L, Zhong W, Ji Y (2010) Down-regulation of Stat3 decreases invasion activity and induces apoptosis of human glioma cells. J Mol Neurosci 40(3):353–359. doi:10.1007/s12031-009-9323-3
Wei Z, Jiang X, Qiao H, Zhai B, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Wu Y, Jiang H, Sun X (2013) STAT3 interacts with Skp2/p27/p21 pathway to regulate the motility and invasion of gastric cancer cells. Cell Signal 25(4):931–938. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.01.011
Niu G, Wright KL, Huang M, Song L, Haura E, Turkson J, Zhang S, Wang T, Sinibaldi D, Coppola D, Heller R, Ellis LM, Karras J, Bromberg J, Pardoll D, Jove R, Yu H (2002) Constitutive Stat3 activity up-regulates VEGF expression and tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene 21(13):2000–2008
Yu H, Jove R (2004) The STATs of cancer–new molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer 4(2):97–105
Grandis JR, Drenning SD, Chakraborty A, Zhou MY, Zeng Q, Pitt AS, Tweardy DJ (1998) Requirement of Stat3 but not Stat1 activation for epidermal growth factor receptor- mediated cell growth In vitro. J Clin Invest 102(7):1385–1392. doi:10.1172/JCI3785
Catlett-Falcone R, Landowski TH, Oshiro MM, Turkson J, Levitzki A, Savino R, Ciliberto G, Moscinski L, Fernandez-Luna JL, Nunez G, Dalton WS, Jove R (1999) Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling confers resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma cells. Immunity 10(1):105–115. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80011-4
Ding BB, Yu JJ, Yu RY, Mendez LM, Shaknovich R, Zhang Y, Cattoretti G, Ye BH (2008) Constitutively activated STAT3 promotes cell proliferation and survival in the activated B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 111(3):1515–1523. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-04-087734
Doucette TA, Kong LY, Yang Y, Ferguson SD, Yang J, Wei J, Qiao W, Fuller GN, Bhat KP, Aldape K, Priebe W, Bogler O, Heimberger AB, Rao G (2012) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 promotes angiogenesis and drives malignant progression in glioma. Neuro Oncol 14(9):1136–1145. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nos139/nos139
Sherry MM, Reeves A, Wu JK, Cochran BH (2009) STAT3 is required for proliferation and maintenance of multipotency in glioblastoma stem cells. Stem Cells 27(10):2383–2392. doi:10.1002/stem.185
Bandaru A, Devalraju KP, Paidipally P, Dhiman R, Venkatasubramanian S, Barnes PF, Vankayalapati R, Valluri V (2014) Phosphorylated STAT3 and PD-1 regulate IL-17 production and IL-23 receptor expression in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Eur J Immunol 44(7):2013–2024. doi:10.1002/eji.201343680
Jiang X, Zhou J, Giobbie-Hurder A, Wargo J, Hodi FS (2013) The activation of MAPK in melanoma cells resistant to BRAF inhibition promotes PD-L1 expression that is reversible by MEK and PI3 K inhibition. Clin Cancer Res 19(3):598–609. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2731
de Groot J, Liang J, Kong LY, Wei J, Piao Y, Fuller G, Qiao W, Heimberger AB (2012) Modulating antiangiogenic resistance by inhibiting the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathway in glioblastoma. Oncotarget 3(9):1036–1048
Lin GS, Yang LJ, Wang XF, Chen YP, Tang WL, Chen L, Lin ZX (2014) STAT3 Tyr705 phosphorylation affects clinical outcome in patients with newly diagnosed supratentorial glioblastoma. Med Oncol 31(4):924. doi:10.1007/s12032-014-0924-5
Lin GS, Chen YP, Lin ZX, Wang XF, Zheng ZQ, Chen L (2014) STAT3 serine 727 phosphorylation influences clinical outcome in glioblastoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7(6):3141–3149
Tu Y, Zhong Y, Fu J, Cao Y, Fu G, Tian X, Wang B (2011) Activation of JAK/STAT signal pathway predicts poor prognosis of patients with gliomas. Med Oncol 28(1):15–23. doi:10.1007/s12032-010-9435-1
Abou-Ghazal M, Yang DS, Qiao W, Reina-Ortiz C, Wei J, Kong LY, Fuller GN, Hiraoka N, Priebe W, Sawaya R, Heimberger AB (2008) The incidence, correlation with tumor-infiltrating inflammation, and prognosis of phosphorylated STAT3 expression in human gliomas. Clin Cancer Res 14(24):8228–8235. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1329
Kortylewski M, Kujawski M, Wang T, Wei S, Zhang S, Pilon-Thomas S, Niu G, Kay H, Mule J, Kerr WG, Jove R, Pardoll D, Yu H (2005) Inhibiting Stat3 signaling in the hematopoietic system elicits multicomponent antitumor immunity. Nat Med 11(12):1314–1321. doi:10.1038/nm1325
Kinjyo I, Inoue H, Hamano S, Fukuyama S, Yoshimura T, Koga K, Takaki H, Himeno K, Takaesu G, Kobayashi T, Yoshimura A (2006) Loss of SOCS3 in T helper cells resulted in reduced immune responses and hyperproduction of interleukin 10 and transforming growth factor-β1. J Exp Med 203(4):1021–1031
Yu H, Kortylewski M, Pardoll D (2007) Crosstalk between cancer and immune cells: role of STAT3 in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol 7(1):41–51. doi:10.1038/nri1995
Nefedova Y, Huang M, Kusmartsev S, Bhattacharya R, Cheng P, Salup R, Jove R, Gabrilovich D (2004) Hyperactivation of STAT3 is involved in abnormal differentiation of dendritic cells in cancer. J Immunol 172(1):464–474
Gabrilovich DI, Nagaraj S (2009) Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 9(3):162–174. doi:10.1038/nri2506
Diaz-Montero CM, Salem ML, Nishimura MI, Garrett-Mayer E, Cole DJ, Montero AJ (2009) Increased circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells correlate with clinical cancer stage, metastatic tumor burden, and doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide chemotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother 58(1):49–59. doi:10.1007/s00262-008-0523-4
Gorgun GT, Whitehill G, Anderson JL, Hideshima T, Maguire C, Laubach J, Raje N, Munshi NC, Richardson PG, Anderson KC (2013) Tumor-promoting immune-suppressive myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the multiple myeloma microenvironment in humans. Blood 121(15):2975–2987. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-08-448548
Nagaraj S, Gupta K, Pisarev V, Kinarsky L, Sherman S, Kang L, Herber DL, Schneck J, Gabrilovich DI (2007) Altered recognition of antigen is a mechanism of CD8 + T cell tolerance in cancer. Nat Med 13(7):828–835. doi:10.1038/nm1609
Rodriguez PC, Ochoa AC (2008) Arginine regulation by myeloid derived suppressor cells and tolerance in cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Immunol Rev 222:180–191. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00608
Corzo CA, Cotter MJ, Cheng P, Cheng F, Kusmartsev S, Sotomayor E, Padhya T, McCaffrey TV, McCaffrey JC, Gabrilovich DI (2009) Mechanism regulating reactive oxygen species in tumor-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Immunol 182(9):5693–5701. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0900092
Kusmartsev S, Nefedova Y, Yoder D, Gabrilovich DI (2004) Antigen-specific inhibition of CD8+ T cell response by immature myeloid cells in cancer is mediated by reactive oxygen species. J Immunol 172(2):989–999
Raychaudhuri B, Rayman P, Ireland J, Ko J, Rini B, Borden EC, Garcia J, Vogelbaum MA, Finke J (2011) Myeloid-derived suppressor cell accumulation and function in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol 13(6):591–599. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nor042
Nefedova Y, Nagaraj S, Rosenbauer A, Muro-Cacho C, Sebti SM, Gabrilovich DI (2005) Regulation of dendritic cell differentiation and antitumor immune response in cancer by pharmacologic-selective inhibition of the janus-activated kinase 2/signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 pathway. Cancer Res 65(20):9525–9535
Sica A, Schioppa T, Mantovani A, Allavena P (2006) Tumour-associated macrophages are a distinct M2 polarised population promoting tumour progression: potential targets of anti-cancer therapy. Eur J Cancer 42(6):717–727. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2006.01.003
Yang I, Han SJ, Kaur G, Crane C, Parsa AT (2010) The role of microglia in central nervous system immunity and glioma immunology. J Clin Neurosci 17(1):6–10. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2009.05.006
Mantovani A, Schioppa T, Porta C, Allavena P, Sica A (2006) Role of tumor-associated macrophages in tumor progression and invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25(3):315–322. doi:10.1007/s10555-006-9001-7
Lievense LA, Bezemer K, Aerts JG, Hegmans JP (2013) Tumor-associated macrophages in thoracic malignancies. Lung Cancer 80(3):256–262. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.02.017
Ding P, Wang W, Wang J, Yang Z, Xue L (2014) Expression of Tumor-Associated Macrophage in Progression of Human Glioma. Cell Biochem Biophys. doi:10.1007/s12013-014-0105-3
Komohara Y, Ohnishi K, Kuratsu J, Takeya M (2008) Possible involvement of the M2 anti-inflammatory macrophage phenotype in growth of human gliomas. J Pathol 216(1):15–24
Zhang L, Alizadeh D, Van Handel M, Kortylewski M, Yu H, Badie B (2009) Stat3 inhibition activates tumor macrophages and abrogates glioma growth in mice. Glia 57(13):1458–1467. doi:10.1002/glia.20863
Fujiwara Y, Komohara Y, Kudo R, Tsurushima K, Ohnishi K, Ikeda T, Takeya M (2011) Oleanolic acid inhibits macrophage differentiation into the M2 phenotype activation of STAT3. Oncol Rep 26(6):1533–1537. doi:10.3892/or.2011.1454
Wu A, Wei J, Kong LY, Wang Y, Priebe W, Qiao W, Sawaya R, Heimberger AB (2010) Glioma cancer stem cells induce immunosuppressive macrophages/microglia. Neuro Oncol 12(11):1113–1125. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noq082
Gao Q, Qiu SJ, Fan J, Zhou J, Wang XY, Xiao YS, Xu Y, Li YW, Tang ZY (2007) Intratumoral balance of regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. J Clin Oncol 25(18):2586–2593
Hiraoka N, Onozato K, Kosuge T, Hirohashi S (2006) Prevalence of FOXP3 + regulatory T cells increases during the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its premalignant lesions. Clin Cancer Res 12(18):5423–5434
El Andaloussi A, Lesniak MS (2007) CD4 + CD25 + FoxP3 + T-cell infiltration and heme oxygenase-1 expression correlate with tumor grade in human gliomas. J Neurooncol 83(2):145–152
Heimberger AB, Abou-Ghazal M, Reina-Ortiz C, Yang DS, Sun W, Qiao W, Hiraoka N, Fuller GN (2008) Incidence and prognostic impact of FoxP3 + regulatory T cells in human gliomas. Clin Cancer Res 14(16):5166–5172. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0320
Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X, Cheng P, Mottram P, Evdemon-Hogan M, Conejo-Garcia JR, Zhang L, Burow M, Zhu Y, Wei S, Kryczek I, Daniel B, Gordon A, Myers L, Lackner A, Disis ML, Knutson KL, Chen L, Zou W (2004) Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat Med 10(9):942–949. doi:10.1038/nm1093
Shen Z, Zhou S, Wang Y, Li RL, Zhong C, Liang C, Sun Y (2010) Higher intratumoral infiltrated Foxp3+ Treg numbers and Foxp3+/CD8+ ratio are associated with adverse prognosis in resectable gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136(10):1585–1595. doi:10.1007/s00432-010-0816-9
Yue Q, Zhang X, Ye HX, Wang Y, Du ZG, Yao Y, Mao Y (2014) The prognostic value of Foxp3 + tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 116(2):251–259. doi:10.1007/s11060-013-1314-0
Doucette TA, Rao G, Rao A, Shen L, Aldape K, Wei J, Dziurzynski K, Gilbert M, Heimberger AB (2013) Immune heterogeneity of glioblastoma subtypes: extrapolation from the cancer genome atlas. Cancer Immunol Res 1(2):112–122
Zorn E, Nelson EA, Mohseni M, Porcheray F, Kim H, Litsa D, Bellucci R, Raderschall E, Canning C, Soiffer RJ, Frank DA, Ritz J (2006) IL-2 regulates FOXP3 expression in human CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells through a STAT-dependent mechanism and induces the expansion of these cells in vivo. Blood 108(5):1571–1579. doi:blood-2006-02-004747
Bailey SR, Nelson MH, Himes RA, Li Z, Mehrotra S, Paulos CM (2014) Th17 cells in cancer: the ultimate identity crisis. Front Immunol 5:276. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00276
Gomez-Rodriguez J, Wohlfert EA, Handon R, Meylan F, Wu JZ, Anderson SM, Kirby MR, Belkaid Y, Schwartzberg PL (2014) Itk-mediated integration of T cell receptor and cytokine signaling regulates the balance between Th17 and regulatory T cells. J Exp Med 211(3):529–543. doi:10.1084/jem.20131459
Chalmin F, Mignot G, Bruchard M, Chevriaux A, Vegran F, Hichami A, Ladoire S, Derangere V, Vincent J, Masson D, Robson SC, Eberl G, Pallandre JR, Borg C, Ryffel B, Apetoh L, Rebe C, Ghiringhelli F (2012) Stat3 and Gfi-1 transcription factors control Th17 cell immunosuppressive activity via the regulation of ectonucleotidase expression. Immunity 36(3):362–373. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2011.12.019
Albesiano E, Han JE, Lim M (2010) Mechanisms of local immunoresistance in glioma. Neurosurg Clin N Am 21(1):17–29. doi:10.1016/j.nec.2009.08.008
Rolle CE, Sengupta S, Lesniak MS (2012) Mechanisms of immune evasion by gliomas. Adv Exp Med Biol 746:53–76. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-3146-6_5
Fujita M, Zhu X, Sasaki K, Ueda R, Low KL, Pollack IF, Okada H (2008) Inhibition of STAT3 promotes the efficacy of adoptive transfer therapy using type-1 CTLs by modulation of the immunological microenvironment in a murine intracranial glioma. J Immunol 180(4):2089–2098. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.180.4.2089
Bao JJ, Fokt I, Szymanski S, Priebe W (2005) Inhibition of constitutively active STAT3 by WP1066 suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 11(24):9026S–9027S
Kupferman ME, Zhou G, Zhao M, Jasser S, Dakak-Yazici Y, Priebe W, Myers JN (2006) A novel inhibitor of STAT3 signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. In: 97th American Association of Cancer Research Annual Meeting, Washington, DC
Kong LY, Abou-Ghazal MK, Wei J, Chakraborty A, Sun W, Qiao W, Fuller GN, Fokt I, Grimm EA, Schmittling RJ, Archer GE Jr, Sampson JH, Priebe W, Heimberger AB (2008) A novel inhibitor of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 activation is efficacious against established central nervous system melanoma and inhibits regulatory T cells. Clin Cancer Res 14(18):5759–5768
Hatiboglu MA, Kong LY, Wei J, Wang Y, McEnery KA, Fuller GN, Qiao W, Davies MA, Priebe W, Heimberger AB (2012) The tumor microenvironment expression of p-STAT3 influences the efficacy of cyclophosphamide with WP1066 in murine melanoma models. Int J Cancer 131(1):8–17. doi:10.1002/ijc.26307
Iwamaru A, Szymanski S, Iwado E, Aoki H, Yokoyama T, Fokt I, Hess K, Conrad C, Madden T, Sawaya R, Kondo S, Priebe W, Kondo Y (2007) A novel inhibitor of the STAT3 pathway induces apoptosis in malignant glioma cells both in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 26(17):2435–2444. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210031
Kong LY, Wu AS, Doucette T, Wei J, Priebe W, Fuller GN, Qiao W, Sawaya R, Rao G, Heimberger AB (2010) Intratumoral mediated immunosuppression is prognostic in genetically engineered murine models of glioma and correlates to immunotherapeutic responses. Clin Cancer Res 16(23):5722–5733. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1693
Hussain SF, Kong LY, Jordan J, Conrad C, Madden T, Fokt I, Priebe W, Heimberger AB (2007) A novel small molecule inhibitor of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 reverses immune tolerance in malignant glioma patients. Cancer Res 67(20):9630–9636. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1243
Wei J, Barr J, Kong LY, Wang Y, Wu A, Sharma AK, Gumin J, Henry V, Colman H, Priebe W, Sawaya R, Lang FF, Heimberger AB (2010) Glioblastoma cancer-initiating cells inhibit T-cell proliferation and effector responses by the signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 pathway. Mol Cancer Ther 9(1):67–78. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0734
Sen M, Grandis JR (2012) Nucleic acid-based approaches to STAT inhibition. JAKSTAT 1(4):285–291. doi:10.4161/jkst.22312
Wang X, Crowe PJ, Goldstein D, Yang JL (2012) STAT3 inhibition, a novel approach to enhancing targeted therapy in human cancers (review). Int J Oncol 41(4):1181–1191. doi:10.3892/ijo.2012.1568
Gu J, Li G, Sun T, Su Y, Zhang X, Shen J, Tian Z, Zhang J (2008) Blockage of the STAT3 signaling pathway with a decoy oligonucleotide suppresses growth of human malignant glioma cells. J Neurooncol 89(1):9–17. doi:10.1007/s11060-008-9590-9
Herrmann A, Priceman SJ, Kujawski M, Xin H, Cherryholmes GA, Zhang W, Zhang C, Lahtz C, Kowolik C, Forman SJ, Kortylewski M, Yu H (2014) CTLA4 aptamer delivers STAT3 siRNA to tumor-associated and malignant T cells. J Clin Invest 124(7):2977–2987. doi:10.1172/JCI73174
See AP, Han JE, Phallen J, Binder Z, Gallia G, Pan F, Jinasena D, Jackson C, Belcaid Z, Jeong SJ, Gottschalk C, Zeng J, Ruzevick J, Nicholas S, Kim Y, Albesiano E, Pardoll DM, Lim M (2012) The role of STAT3 activation in modulating the immune microenvironment of GBM. J Neurooncol 110(3):359–368. doi:10.1007/s11060-012-0981-6
Wei J, Wang F, Kong LY, Xu S, Doucette T, Ferguson SD, Yang Y, McEnery K, Jethwa K, Gjyshi O, Qiao W, Levine NB, Lang FF, Rao G, Fuller GN, Calin GA, Heimberger AB (2013) miR-124 inhibits STAT3 signaling to enhance T cell-mediated immune clearance of glioma. Casncer Res 73(13):3913–3926. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4318
Fuh B, Sobo M, Cen L, Josiah D, Hutzen B, Cisek K, Bhasin D, Regan N, Lin L, Chan C, Caldas H, DeAngelis S, Li C, Li PK, Lin J (2009) LLL-3 inhibits STAT3 activity, suppresses glioblastoma cell growth and prolongs survival in a mouse glioblastoma model. Br J Cancer 100(1):106–112. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604793.6604793
Molavi O, Ma Z, Hamdy S, Lai R, Lavasanifar A, Samuel J (2008) Synergistic antitumor effects of CpG oligodeoxynucleotide and STAT3 inhibitory agent JSI-124 in a mouse melanoma tumor model. Immunol Cell Biol 86(6):506–514. doi:10.1038/icb.2008.27
Molavi O, Ma Z, Hamdy S, Lavasanifar A, Samuel J (2009) Immunomodulatory and anticancer effects of intra-tumoral co-delivery of synthetic lipid A adjuvant and STAT3 inhibitor, JSI-124. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 31(2):214–221. doi:10.1080/08923970802380452
Kong LY, Gelbard A, Wei J, Reina-Ortiz C, Wang Y, Yang EC, Hailemichael Y, Fokt I, Jayakumar A, Qiao W, Fuller GN, Overwijk WW, Priebe W, Heimberger AB (2010) Inhibition of p-STAT3 enhances IFN-alpha efficacy against metastatic melanoma in a murine model. Clin Cancer Res 6(9):2550–2561. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0279
Acknowledgments
We thank Audria Patrick for assistance with manuscript preparation and David M. Wildrick, Ph.D. for editorial assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferguson, S.D., Srinivasan, V.M. & Heimberger, A.B. The role of STAT3 in tumor-mediated immune suppression. J Neurooncol 123, 385–394 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1731-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1731-3