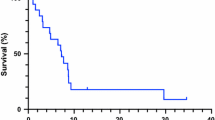
Abstract
Malignant gliomas are highly lethal tumors resistant to current therapies. The standard treatment modality for these tumors, surgical resection followed by radiation therapy and concurrent temozolomide, has demonstrated activity, but development of resistance and disease progression is common. Although oncogenic Ras mutations are uncommon in gliomas, Ras has been found to be constitutively activated through the action of upstream signaling pathways, suggesting that farnesyltransferase inhibitors may show activity against these tumors. We now report the in vitro and orthotopic in vivo results of combination therapy using radiation, temozolomide and lonafarnib (SCH66336), an oral farnesyl transferase inhibitor, in a murine model of glioblastoma. We examined the viability, proliferation, farnesylation of H-Ras, and activation of downstream signaling of combination-treated U87 cells in vitro. Lonafarnib alone or in combination with radiation and temozolomide had limited tumor cell cytotoxicity in vitro although it did demonstrate significant inhibition in tumor cell proliferation. In vivo, lonafarnib alone had a modest ability to inhibit orthotopic U87 tumors, radiation and temozolomide demonstrated better inhibition, while significant anti-tumor activity was found with concurrent lonafarnib, radiation, and temozolomide, with the majority of animals demonstrating a decrease in tumor volume. The use of tumor neurospheres derived from freshly resected adult human glioblastoma tissue was relatively resistant to both temozolomide and radiation therapy. Lonafarnib had a significant inhibitory activity against these neurospheres and could potentate the activity of temozolomide and radiation. These data support the continued research of high grade glioma treatment combinations of farnesyl transferase inhibitors, temozolomide, and radiation therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scott CB, Scarantino C, Urtasun R, Movsas B, Jones CU, Simpson JR, Fischbach AJ, Curran WJ Jr (1998) Validation and predictive power of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) recursive partitioning analysis classes for malignant glioma patients: a report using RTOG 90–06. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 40:51–55
Stupp R, Dietrich PY, Ostermann Kraljevic S, Pica A, Maillard I, Maeder P, Meuli R, Janzer R, Pizzolato G, Miralbell R, Porchet F, Regli L, de Tribolet N, Mirimanoff RO, Leyvraz S (2002) Promising survival for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme treated with concomitant radiation plus temozolomide followed by adjuvant temozolomide. J Clin Oncol 20:1375–1382
Nicholas MK (2007) Glioblastoma multiforme: evidence-based approach to therapy. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 7:S23–S27
Falchetti ML, Mongiardi MP, Fiorenzo P, Petrucci G, Pierconti F, D’Agnano I, D’Alessandris G, Alessandri G, Gelati M, Ricci-Vitiani L, Maira G, Larocca LM, Levi A, Pallini R (2008) Inhibition of telomerase in the endothelial cells disrupts tumor angiogenesis in glioblastoma xenografts. Int J Cancer 122:1236–1242
Falchetti ML, Fiorenzo P, Mongiardi MP, Petrucci G, Montano N, Maira G, Pierconti F, Larocca LM, Levi A, Pallini R (2006) Telomerase inhibition impairs tumor growth in glioblastoma xenografts. Neurol Res 28:532–537
Belda-Iniesta C, de Castro Carpeno J, Sereno M, Gonzalez-Baron M, Perona R (2008) Epidermal growth factor receptor and glioblastoma multiforme: molecular basis for a new approach. Clin Transl Oncol 10:73–77
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P (2007) Genetic pathways to primary and secondary glioblastoma. Am J Pathol 170:1445–1453
Sarkar C, Karak AK, Nath N, Sharma MC, Mahapatra AK, Chattopadhyay P, Sinha S (2005) Apoptosis and proliferation: correlation with p53 in astrocytic tumours. J Neurooncol 73:93–100
Voelzke WR, Petty WJ, Lesser GJ (2008) Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor in high-grade astrocytomas. Curr Treat Options Oncol 9:23–31
Failly M, Korur S, Egler V, Boulay JL, Lino MM, Imber R, Merlo A (2007) Combination of sublethal concentrations of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor and microtubule stabilizer induces apoptosis of glioblastoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther 6:773–781
Knobbe CB, Reifenberger J, Reifenberger G (2004) Mutation analysis of the Ras pathway genes NRAS, HRAS, KRAS and BRAF in glioblastomas. Acta Neuropathol 108:467–470
Feldkamp MM, Lala P, Lau N, Roncari L, Guha A (1999) Expression of activated epidermal growth factor receptors, Ras-guanosine triphosphate, and mitogen-activated protein kinase in human glioblastoma multiforme specimens. Neurosurgery 45:1442–1453
Widemann BC, Salzer WL, Arceci RJ, Blaney SM, Fox E, End D, Gillespie A, Whitcomb P, Palumbo JS, Pitney A, Jayaprakash N, Zannikos P, Balis FM (2006) Phase I trial and pharmacokinetic study of the farnesyltransferase inhibitor tipifarnib in children with refractory solid tumors or neurofibromatosis type I and plexiform neurofibromas. J Clin Oncol 24:507–516
Haas-Kogan DA, Banerjee A, Kocak M, Prados MD, Geyer JR, Fouladi M, McKnight T, Poussaint TY, Broniscer A, Blaney SM, Boyett JM, Kun LE (2008) Phase I trial of tipifarnib in children with newly diagnosed intrinsic diffuse brainstem glioma. Neuro Oncol 10:341–347
Kieran MW, Packer RJ, Onar A, Blaney SM, Phillips P, Pollack IF, Geyer JR, Gururangan S, Banerjee A, Goldman S, Turner CD, Belasco JB, Broniscer A, Zhu Y, Frank E, Kirschmeier P, Statkevich P, Yver A, Boyett JM, Kun LE (2007) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of the oral farnesyltransferase inhibitor lonafarnib administered twice daily to pediatric patients with advanced central nervous system tumors using a modified continuous reassessment method: a Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium Study. J Clin Oncol 25:3137–3143
Morgillo F, Lee HY (2006) Lonafarnib in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Invest Drugs 15:709–719
Bernhard EJ, McKenna WG, Hamilton AD, Sebti SM, Qian Y, Wu JM, Muschel RJ (1998) Inhibiting Ras prenylation increases the radiosensitivity of human tumor cell lines with activating mutations of Ras oncogenes. Cancer Res 58:1754–1761
Ling CC, Endlich B (1989) Radioresistance induced by oncogenic transformation. Radiat Res 120:267–279
McKenna WG, Weiss MC, Bakanauskas VJ, Sandler H, Kelsten ML, Biaglow J, Tuttle SW, Endlich B, Ling CC, Muschel RJ (1990) The role of the H-Ras oncogene in radiation resistance and metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 18:849–859
Miller AC, Gafner J, Clark EP, Samid D (1993) Differences in radiation-induced micronuclei yields of human cells: influence of Ras gene expression and protein localization. Int J Radiat Biol 64:547–554
Gupta AK, Bakanauskas VJ, McKenna WG, Bernhard EJ, Muschel RJ (2001) Ras regulation of radioresistance in cell culture. Methods Enzymol 333:284–290
Glass TL, Liu TJ, Yung WK (2000) Inhibition of cell growth in human glioblastoma cell lines by farnesyltransferase inhibitor SCH66336. Neuro-Oncol 2:151–158
Szentirmai O, Baker CH, Lin N, Szucs S, Takahashi M, Kiryu S, Kung AL, Mulligan RC, Carter BS (2006) Noninvasive bioluminescence imaging of luciferase expressing intracranial U87 xenografts: correlation with magnetic resonance imaging determined tumor volume and longitudinal use in assessing tumor growth and antiangiogenic treatment effect. Neurosurgery 58:365–372 (discussion 365–372)
Rubin JB, Kung AL, Klein RS, Chan JA, Sun Y, Schmidt K, Kieran MW, Luster AD, Segal RA (2003) A small-molecule antagonist of CXCR4 inhibits intracranial growth of primary brain tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13513–13518
Ligon KL, Huillard E, Mehta S, Kesari S, Liu H, Alberta JA, Bachoo RM, Kane M, Louis DN, Depinho RA, Anderson DJ, Stiles CD, Rowitch DH (2007) Olig2-regulated lineage-restricted pathway controls replication competence in neural stem cells and malignant glioma. Neuron 53:503–517
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE, Hawkins C, Squire J, Dirks PB (2003) Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res 63:5821–5828
Desrosiers RR, Cusson MH, Turcotte S, Beliveau R (2005) Farnesyltransferase inhibitor SCH-66336 downregulates secretion of matrix proteinases and inhibits carcinoma cell migration. Int J Cancer 114:702–712
Laks DR, Masterman-Smith M, Visnyei K, Angenieux B, Orozco NM, Foran I, Yong WH, Vinters HV, Liau LM, Lazareff JA, Mischel PS, Cloughesy TF, Horvath S, Kornblum HI (2009) Neurosphere formation is an independent predictor of clinical outcome in malignant glioma. Stem Cells 27:980–987
Dowlati A, Kluge A, Nethery D, Halmos B, Kern JA (2008) SCH66336, inhibitor of protein farnesylation, blocks signal transducer and activators of transcription 3 signaling in lung cancer and interacts with a small molecule inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2. Anticancer Drugs 19:9–16
Feldkamp MM, Lau N, Guha A (1999) Growth inhibition of astrocytoma cells by farnesyl transferase inhibitors is mediated by a combination of anti-proliferative, pro-apoptotic and anti-angiogenic effects. Oncogene 18:7514–7526
Sepp-Lorenzino L, Ma Z, Rands E, Kohl NE, Gibbs JB, Oliff A, Rosen N (1995) A peptidomimetic inhibitor of farnesyl:protein transferase blocks the anchorage-dependent and -independent growth of human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res 55:5302–5309
Pollack IF, Bredel M, Erff M, Hamilton AD, Sebti SM (1999) Inhibition of Ras and related guanosine triphosphate-dependent proteins as a therapeutic strategy for blocking malignant glioma growth: II–preclinical studies in a nude mouse model. Neurosurgery 45:1208–1214 (discussion 1214–1205)
Liu M, Bishop WR, Nielsen LL, Bryant MS, Kirschmeier P (2001) Orally bioavailable farnesyltransferase inhibitors as anticancer agents in transgenic and xenograft models. Methods Enzymol 333:306–318
Shi Y, Wu J, Mick R, Cerniglia GJ, Cohen-Jonathan E, Rhim JS, Koch CJ, Bernhard EJ (2005) Farnesyltransferase inhibitor effects on prostate tumor micro-environment and radiation survival. Prostate 62:69–82
Lustig R, Mikkelsen T, Lesser G, Grossman S, Ye X, Desideri S, Fisher J, Wright J (2008) Phase II preradiation R115777 (tipifarnib) in newly diagnosed GBM with residual enhancing disease. Neuro Oncol 10:1004–1009
Loprevite M, Favoni RE, De Cupis A, Scolaro T, Semino C, Mazzanti P, Ardizzoni A (2004) In vitro study of farnesyltransferase inhibitor SCH 66336, in combination with chemotherapy and radiation, in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep 11:407–414
Lerner EC, Qian Y, Blaskovich MA, Fossum RD, Vogt A, Sun J, Cox AD, Der CJ, Hamilton AD, Sebti SM (1995) Ras CAAX peptidomimetic FTI-277 selectively blocks oncogenic Ras signaling by inducing cytoplasmic accumulation of inactive Ras–Raf complexes. J Biol Chem 270:26802–26806
Chakravarti A, Chakladar A, Delaney MA, Latham DE, Loeffler JS (2002) The epidermal growth factor receptor pathway mediates resistance to sequential administration of radiation and chemotherapy in primary human glioblastoma cells in a RAS-dependent manner. Cancer Res 62:4307–4315
Abounader R, Ranganathan S, Kim BY, Nichols C, Laterra J (2001) Signaling pathways in the induction of c-met receptor expression by its ligand scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor in human glioblastoma. J Neurochem 76:1497–1508
Elowe S, Holland SJ, Kulkarni S, Pawson T (2001) Downregulation of the Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by the EphB2 receptor tyrosine kinase is required for ephrin-induced neurite retraction. Mol Cell Biol 21:7429–7441
Holland SJ, Gale NW, Gish GD, Roth RA, Songyang Z, Cantley LC, Henkemeyer M, Yancopoulos GD, Pawson T (1997) Juxtamembrane tyrosine residues couple the Eph family receptor EphB2/Nuk to specific SH2 domain proteins in neuronal cells. EMBO J 16:3877–3888
Tong J, Elowe S, Nash P, Pawson T (2003) Manipulation of EphB2 regulatory motifs and SH2 binding sites switches MAPK signaling and biological activity. J Biol Chem 278:6111–6119
Kim I, Ryu YS, Kwak HJ, Ahn SY, Oh JL, Yancopoulos GD, Gale NW, Koh GY (2002) EphB ligand, ephrinB2, suppresses the VEGF- and angiopoietin 1-induced Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in venous endothelial cells. FASEB J 16:1126–1128
Klemke RL, Cai S, Giannini AL, Gallagher PJ, de Lanerolle P, Cheresh DA (1997) Regulation of cell motility by mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Cell Biol 137:481–492
Scott AN, Hetheridge C, Reynolds AR, Nayak V, Hodivala-Dilke K, Mellor H (2008) Farnesyltransferase inhibitors target multiple endothelial cell functions in angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 11:337–346
Basso AD, Mirza A, Liu G, Long BJ, Bishop WR, Kirschmeier P (2005) The farnesyl transferase inhibitor (FTI) SCH66336 (lonafarnib) inhibits Rheb farnesylation and mTOR signaling Role in FTI enhancement of taxane and tamoxifen anti-tumor activity. J Biol Chem 280:31101–31108
Sebti SM, Hamilton AD (2000) Farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase I inhibitors and cancer therapy: lessons from mechanism and bench-to-bedside translational studies. Oncogene 19:6584–6593
Whyte DB, Kirschmeier P, Hockenberry TN, Nunez-Oliva I, James L, Catino JJ, Bishop WR, Pai JK (1997) K- and N-Ras are geranylgeranylated in cells treated with farnesyl protein transferase inhibitors. J Biol Chem 272:14459–14464
Lu C, Shervington A (2008) Chemoresistance in gliomas. Mol Cell Biochem 312:71–80
Rich JN (2007) Cancer stem cells in radiation resistance. Cancer Res 67:8980–8984
Sauvageot CM, Kesari S, Stiles CD (2007) Molecular pathogenesis of adult brain tumors and the role of stem cells. Neurol Clin 25:891–924 (vii)
Acknowledgments
Funding was provided by the Stop & Shop Family Pediatric Brain Tumor Fund, the C.J. Buckley Fund (J.W.B., D.C., D.P., E.R.G., M.W.K.), the Kyle Johnson Fund (J.W.B., M.W.K.), the Pediatric Low-Grade Astrocytoma Foundation (C.S., M.W.K.), the Solomon and Marlene Finvarb Brain Tumor Research Fund (P.Y.W., C.S.), the Brudnick Foundation (N.R.), by NIH K08 (SK: K08CA124804) and by Sontag Foundation Distinguished Scientist Award (SK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11060_2010_502_MOESM1_ESM.ppt
Supplemental Figure 1 Combination treatment influences activation of MAPK and RTK pathways. (A) Representative Proteome Profiler (R&D Systems, Minneapolis MN) dot blot is shown for pEGF receptor (pEGFR), pHGFR, pEphA7, pP38 and ERK1. The optical density of duplicate dots were normalized to control and plotted as the mean ± s.e.m. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). (PPT 443 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaponis, D., Barnes, J.W., Dellagatta, J.L. et al. Lonafarnib (SCH66336) improves the activity of temozolomide and radiation for orthotopic malignant gliomas. J Neurooncol 104, 179–189 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0502-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0502-4