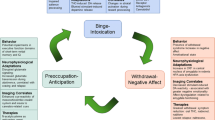
This review provides the first systematic report of the literature on impairments to GABAergic transmission in the basolateral nucleus of the amygdaloid complex of the brain, leading to increases in anxiety levels. Increases in anxiety are regarded as the main factor prompting alcohol cravings and producing the manifestations of alcohol dependence. Structural-functional rearrangements of ionotropic and metabotropic GABA receptors in acute and chronic exposure to ethanol and withdrawal syndrome are discussed. Data in the role of GABA transporters in the pathogenesis of alcoholism are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. G. Akmaev and L. B. Kalimullina, The Amygdaloid Complex of the Brain: Functional Morphology and Neuroendocrinology, Nauka, Moscow (1993).
A. V. Akhmadeev and L. B. Kalimullina, “Impairments to glutamatergic transmission in the basolateral nucleus of the amygdaloid complex on formation of alcohol dependence,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh., 102, No. 4, 385–397 (2016).
A. V. Sem’yanov, “Effects of activation of kainate receptors on tonic and phasic GABAergic inhibition in interneurons in field CA1 in hippocampal slices from guinea pigs,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 53, No. 2, 193–201 (2003).
P. V. Simonov, The Motivated Brain, Nauka, Moscow (1987).
S. A. Chepurnov and N. E. Chepurnova, The Amygdaloid Complex of the Brain, Moscow State University Press, Moscow (1981).
G. Addolorato, F. Caputo, E. Capristo, et al., “Ability of baclofen in reducing alcohol craving and intake: II-preliminary clinical evidence,” Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res., 24, 67–71 (2000).
G. Addolorato, F. Caputo, E. Capristo, et al., “Baclofen efficacy in reducing alcohol craving and intake: a preliminary double-blind randomized controlled study,” Alcohol Alcohol, 37, 504–508 (2002).
G. Addolorato, F. Caputo, E. Capristo, et al., “Rapid suppression of alcohol withdrawal syndrome by baclofen,” Am. J. Med., 112, 226–229 (2002).
G. Addolorato, L. Leggio, R. Agabio, et al., “Suppression of alcohol delirium tremens by baclofen administration: a case report,” Clin. Neuropharmacology, 26, 258–262 (2003).
M. A. Avila, M. A. Real, and S. Guirado, “Patterns of GABA and GABA transporter-1 immunoreactivities in the developing and adult mouse brain amygdala,” Brain Res., 1388, 1–11 (2011).
P. Barbaresi, G. Gazzanelli, and M. Malatesta, “The gamma-aminobutyric acid transporters in the cat periaqueductal gray: a light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical study,” J. Comp. Neurol., 429, No. 2, 337–354 (2001).
N. P. Barrera, J. Betts, and H. You, “Atomic force microscopy reveals the stoichiometry and subunit arrangement of the alpha4beta3delta GABA(A) receptor,” Mol. Pharmacol., 73, No. 3, 960–967 (2008).
B. Bettler, K. Kaupmann, and N. G. Bowery, “GABAb receptors: Drugs meet clones,” Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 8, 345–350 (1998).
B. Bettler, K. Kaupmann, J. Mosbacher, and M. Gassmann, “Molecular structure and physiological functions of GABAB receptors,” Physiol. Rev., 84, 835–867 (2004).
S. Bischoff, S. Leonhard, N. Reymann, et al., “Spatial distribution of GABABR1 receptor mRNA and binding sites in the rat brain,” J. Comp. Neurol., 412, 1–16 (1999).
G. Bonanno, A. Fassio, G. Schmid, et al., “Pharmacologically distinct GABAB receptors that mediate inhibition of GABA and glutamate release in human neocortex,” Br. J. Pharmacol., 120, 60–64 (1997).
J. Bormann, “The ‘ABC’ of GABA receptors,” Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 21, No. 1, 16–19 (2000).
N. G. Bowery, D. R. Hill, A. L. Hudson, et al., “Baclofen decreases neurotransmitter release in the mammalian CNS by an action at a novel GABA receptor,” Nature, 283, 92–94 (1980).
N. G. Bowery, A. L. Hudson, and G. W. Price, “GABAA and GABAB receptor site distribution in the rat central nervous system,” Neuroscience, 20, 365–383 (1987).
K. Brebner, R. Phelan, and D. C. Roberts, “Effect of baclofen on cocaine self-administration in rats reinforced under fixed-ratio 1 and progressive-ratio schedules,” Psychopharmacology, 148, 314–321 (2000).
A. Caitlin, A. Orsini, and S. Maren, “Neural and cellular mechanisms of fear and extinction memory formation,” Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev., 36, No. 7, 1773–1802 (2012).
L. L. Devaud, “Ethanol dependence has limited effects on GABA or glutamate transporters in rat brain,” Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res., 25, No. 4, 606–611 (2001).
M. R. Diaz, D. T. Christian, N. J. Anderson, and B. A. McCoo, “Chronic ethanol and withdrawal differentially modulate lateral/basolateral amygdala paracapsular and local GABAergic synapses,” J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 337, No. 1, 162–170 (2011), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.110.177121.
P. Fadda, M. Scherma, A. Fresu, et al., “Baclofen antagonizes nicotine-, cocaine-, and morphine-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens of rat,” Synapse, 50, 1–6 (2003).
M. Filip and M. Frankowska, “GABA(B) receptors in drug addiction,” Pharmacol. Rep., 60, No. 6, 755–770 (2008).
D. W. Floyd, D. P. Friedman, and J. B. Daunais, “Long-term ethanol self-administration by cynomolgus macaques alters the pharmacology and expression of GABAA receptors in basolateral amygdala,” J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 311, No. 3, 1071–1079 (2004).
J. Fujimura, M. Nagano, and H. Suzuki, “Differential expression of GABA(A) receptor subunits in the distinct nuclei of rat amygdala,” Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res., 138, No. 1, 17–23 (2005).
A. Gadea and A. M. Lopez-Colome, “Glial transporters for glutamate, glycine, and GABA: II. GABA transporters,” J. Neurosci. Res., 63, No. 6, 461–468 (2001).
S. A. Heldt and Ressler K. J. “Training-induced changes in the expression of GABAA-associated genes in the amygdala after the acquisition and extinction of Pavlovian fear,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 26, No. 12, 3631–3644 (2007).
J. H. Hu, Y. H. Ma, and N. Yang, “Up-regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid transporter I mediates ethanol sensitivity in mice,” Neuroscience, 123, No. 4, 807–812 (2004).
A. S. Hwang and G. L. Wilcox, “Baclofen, gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptors and substance P in the mouse spinal cord,” J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 248, 1026–1033 (1989).
Y. Ikarashi, M. Yuzurihara, A. Takahashi, et al., “Modulation of acetylcholine release via GABAA and GABAB receptors in rat striatum,” Brain Res., 816, 238–240 (1999).
R. Imperatore, G. Morello, and L. Luongo, “Genetic deletion of monoacylglycerol lipase leads to impaired cannabinoid receptor CB1R signaling and anxiety-like behavior,” J. Neurochem., 135, No. 4, 799–813 (2015), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13267.
J. H. Jennings, D. R. Sparta, A. M. Stamatakis, et al., “Distinct extended amygdala circuits for divergent motivational states,” Nature, 496, 224–228 (2013).
F. Jursky, S. Tamura, and A. Tamura, “Structure, function and brain localization of neurotransmitter transporters,” J. Exp. Biol., 196, 283–295 (1994).
K. Kaupmann, B. Malitschek, V. Schuler, et al., “GABAB-receptor subtypes assemble into functional heteromeric complexes,” Nature, 396, 683–687 (1998).
D. I. Kerr and J. Ong, “GABAB receptors,” Pharmacol. Ther., 67, 187–246 (1995).
M. A. Klitenick, P. DeWitte, and P. W. Kalivas, “Regulation of somatodendritic dopamine release I the ventral tegmental area by opioids and GABA: an in vivo microdialysis study,” J. Neurosci., 12, 2623–2632 (1992).
D. J. Knapp, D. H. Overstreet, and G. R. Breese, “Baclofen blocks expression and sensitization of anxiety-like behavior in an animal model of repeated stress and ethanol withdrawal,” Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res., 31, 582–595 (2007).
G. F. Koob, “Negative reinforcement in drug addiction: the darkness within,” Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 23, 559–563 (2013), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2013.03.011.
P. Koulen, B. Malitschek, R. Kuhn, et al., “Presynaptic and postsynaptic localization of GABAB receptors in neurons of the rat retina,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 10, 1446–1456 (1998).
J. H. Liang, F. Chen, E. Krstew, et al., “The GABAb receptor allosteric modulator CGP7930, like baclofen, reduces operant self-administration of ethanol in alcohol preferring rats,” Neuropharmacology, 50, 632–639 (2006).
F. Liang, Y. Hatanaka, H. Saito, et al., “Differential expression of aminobutyric acid type B receptor-1a and -1b mRNA variants in GABA and nonGABAergic neurons of the rat brain,” J. Comp. Neurol., 416, 475–495 (2000).
A. K. Lindemeyer, J. Liang, and V. N. Marty, “Ethanol-induced plasticity of GABAA receptors in basolateral amygdala,” Neurochem. Res., 39, No. 6, 1162–1170 (2014), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1297-z.
N. J. Mabjeesh, M. Frese, T. Rauen, et al., “Neuronal and glial gamma-aminobutyric acid+ transporters are distinct proteins,” FEBS Lett., 299, 99–102 (1992).
P. Maccioni, D. Pes, A. Orru, et al., “Reducing effect of the positive allosteric modulator of the GABAB receptor, GS39,783, on alcohol self-administration in alcohol-preferring rats,” Psychopharmacology, 193, 171–178 (2007).
A. Marowsky, J. M. Fritschy, and K. E. Vogt, “Functional mapping of GABAA receptor subtypes in the amygdala,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 20, No. 5, 1281–1289 (2004).
F. Mascagni, E. C. Muly, D. G. Rainnie, and A. J. McDonald, “Immunohistochemical characterization of parvalbumin-containing interneurons in the monkey basolateral amygdala,” Neuroscience, 158, No. 4, 1541–1550 (2009).
A. J. McDonald and J. L. Culberson, “Efferent projection of the basolateral amygdala in opossum, Didelphis virginiana,” Brain Res. Bull., 17, No. 3, 335–350 (1986).
A. J. McDonald and F. Mascagni, “Parvalbumin-containing interneurons in the basolateral amygdala express high levels of the alpha1 subunit of GABAA receptor,” J. Comp. Neurol., 473, No. 1, 137–146 (2004).
A. J. McDonald, J. F. Muller, and F. Mascagni, “Postsynaptic targets of GABAergic basal forebrain projection to the basolateral amygdala,” Neuroscience, 183, 144–159 (2011), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.03.027.
A. Minelli, N. C. Brecha, and C. Karschin, “GAT-1, a high-affinity GABA plasma membrane transporter, is localized to neurons and glia in cerebral cortex,” J. Neurosci., 15, No. 11, 7734–7746 (1995).
J. F. Muller, F. Mascagni, and A. J. McDonald, “Pyramidal cells of the rat basolateral amygdala synaptology and innervations by parvalbumin-immunoreactive interneurons,” J. Comp. Neurol., 494, No. 4, 635–650 (2006).
N. Nayeem, T. P. Green, I. L. Martin, and E. A. Barnard, “Quaternary structure of the native GABAA receptor determined by electron microscopic image analysis,” J. Neurochem., 62, No. 2, 815–818 (1994).
A. Orru, P. Lai, C. Lobina, et al., “Reducing effect of the positive allosteric modulators of the GABAB receptor, CGP7930 and GS39783, on alcohol intake in alcohol-preferring rats,” Eur. J. Pharmacol., 525, 105–111 (2005).
N. E. Paterson, S. Vlachou, S. Query, et al., “Positive modulation of GABAB receptors decreased nicotine self-administration and counteracted nicotine-induced enhancement of brain reward function in rats,” J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 326, 306–314 (2008).
C. R. Pinard, J. F. Muller, F. Mascagni, and A. J. McDonald, “Dopaminergic innervation of interneurons in the rat basolateral amygdala,” Neuroscience, 157, No. 4, 850–863 (2008).
A. P. Princivalle, M. N. Pangalos, N. G. Bowery, and R. Spreafico, “Distribution of GA-BABla, GABABlb and GABAB2 receptor protein in cerebral cortex and thalamus of adult rats,” Neuroreport, 12, 591–595 (2001).
R. Radian, O. P. Ottersen, J. Storm-Mathisen, et al., “Immunocytochemical localization of the GABA transporter in rat brain,” J. Neurosci., 10, 1319–1330 (1990).
P. S. Rao, R. L. Bell, E. A. Engleman, and Y. Sar, “Targeting glutamate uptake to treat alcohol use disorders,” Front. Neurosci., 9, 144–149 (2015).
A. Sarup, O. M. Larsson, and A. Schousboe, “GABA transporters and GABA-transaminase as drug targets,” Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord., 2, No. 4, 269–277 (2003).
A. Schousboe, A. Sarup, O. M. Larsson, and H. S. White, “GABA transporters as drug targets for modulation of GABAergic activity,” Biochem. Pharmacol., 68, No. 8, 1557–1563 (2004).
Y. Silberman, O. J. Ariwodola, and J. L. Weiner, “Differential effect of GABAB autoreceptor activation on ethanol potentiation of local and lateral paracapsular GABAergic synapses in the rat basolateral amygdala,” Neuropharmacology, 56, No. 5, 886–895 (2009), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.01.013.
J. Spampanato, J. Polepalli, and P. Sah, “Interneurons in the basolateral amygdala,” Neuropharmacology, 60, No. 5, 765–773 (2011).
B. H. Westerink, H. F. Kwint, and J. B. de Vries, “Eating-induced dopamine release from mesolimbic neurons is mediated by NMDA receptors in the ventral tegmental area: a dual-probe microdialysis study,” J. Neurochem., 69, 662–668 (1997).
D. Wirtshafter and A. C. Sheppard, “Localization of GABAB receptors in midbrain monoamine containing neurons in the rat,” Brain Res. Bull., 56, 1–5 (2001).
Z. X. Xi and E. A. Stein, “Baclofen inhibits heroin self-administration behavior and mesolimbic dopamine release,” J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 290, 1369–1374 (1999).
M. Yoshida, H. Yokoo, T. Tanaka, et al., “Opposite changes in the mesolimbic dopamine metabolism in the nerve terminal and cell body sites induced by locally infused baclofen in the rat,” Brain Res., 636, 111–114 (1994).
L. Zhu, “Ethanol potentiates GABAergic synaptic transmission in a postsynaptic neuron/synaptic bouton preparation from basolateral amygdala,” J. Neurophysiol., 96, No. 1, 433–441 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 103, No. 9, pp. 978–986, September, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akhmadeev, A.V., Kalimullina, L.B. The GABAergic System of the Basolateral Nucleus of the Amygdaloid Complex of the Brain in Formation of Alcohol Dependence. Neurosci Behav Physi 49, 463–467 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-019-00756-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-019-00756-6