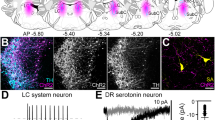
Experiments on rat brainstem sections in membrane potential clamping conditions addressed the effects of serotonin and GABA on serotoninergic neurons in the nucleus raphe magnus. Local application of serotonin stimulated inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSC) in 45% of the serotoninergic neurons studied. This response was not seen in the presence of the fast sodium channel blocker tetrodotoxin. The GABAA receptor antagonist gabazine blocked IPSC in both serotonin-sensitive and serotonin-insensitive neurons. Application of GABA evoked generation of a membrane current (IGABA), which was completely blocked by gabazine. These results indicate self-regulation of the activity of serotoninergic neurons in the nucleus raphe magnus via a negative feedback circuit involving local GABAergic interneurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Yu. Mileikovskii and A. D. Nozdrachev, “Electrophysiological analysis of the interaction of the neuron population of the pons and the medulla oblongata involved in the inhibition of motor activity,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh. im. I. M. Sechenova, 83, No. 11–12, 57–63 (1997).
M. Alreja, “Excitatory actions of serotonin on GABAergic neurons of the medial septum and diagonal band of Broca,” Synapse, 22, 15–27 (1996).
E. Bagdy, I. Kiraly, and L. G. Harsing, “Reciprocal innervation between serotonergic and GABAergic neurons in raphe nuclei of the rat,” Neurochem. Res., 25, 1465–1473 (2000).
N. G. Bowery, A. L. Hudson, and G. W. Price, “GABAA and GABAB receptors site distribution in the rat central nervous system,” Neuroscience, 20, 365–383 (1987).
Y. Cao, K. Matsuyama, Y. Fujito, and M. Aoki, “Involvement of medullary GABAergic and serotonergic raphe neurons in respiratory control: Electrophysiological and immunohistochemical studies in rats,” Neurosci. Res., 56, 322–331 (2006).
G. Chazal and H. J. Ralston II, “Serotonin-containing structures in the nucleus raphe dorsalis of the cat: an ultrastructural analysis of dendrites, presynaptic dendrites, and axon collaterals,” J. Comp. Neurol., 259, 259–317 (1987).
H. J. Cho and A. I. Basbaum, “GABAergic circuitry in the rostral ventral medulla of the rat and its relationship to descending antinociceptive controls,” J. Comp. Neurol., 303, 316–328 (1991).
F. Crespi, J. C. Garratt, A. J. Sleight, and C. A. Marsden, “In vivo evidence that 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) neuronal firing and release are not necessarily correlated with 5-HT metabolism,” Neuroscience, 35, 139–144 (1990).
L. F. S. da Silva and L. Menescal-de-Oliveira, “Role of opioidergic and GABAergic neurotransmission of the nucleus raphe magnus in the modulation of tonic immobility in guinea pigs,” Brain Res. Bull., 72, 25–31 (2007).
C. Davidson and J. A. Stamford, “Evidence that 5-hydroxytryptamine release in rat dorsal raphe nucleus is controlled by 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D autoreceptors,” Brit. J. Pharmacol., 114, 1107–1109 (1995).
H. U. Dodt and W. Zieglgänsberger, “Visualizing unstained neurons in living brain slices by infrared DIC-videomicroscopy,” Brain Res., 537, 333–336 (1990).
K. Gao and P. Mason, “Somatodendritic and axonal anatomy of intracellularly labeled serotonergic neurons in the rat medulla,” J. Comp. Neurol., 389, 309–328 (1997).
D. Gervasconi, C. Peyron, C. Rampon, B. Barbagli, G. Chouvet, N. Urbain, P. Fort, and P. H. Luppi, “Role and origin of the GABAergic innervation of dorsal raphe serotonergic neurons,” J. Neurosci., 20, 4217–4225 (2000).
M. Hajos, S. E. Gartside, A. E. P. Villa, and T. Sharp, “Evidence for a repetitive (burst) firing pattern in a sub-population in the dorsal and median raphe nuclei of the rat,” Neuroscience, 69, 189–197 (1995).
I. D. Hentall, P. J. Furle, and T. R. White, “Correlations between serotonin level and single-cell firing in the rat’s nucleus raphe magnus,” Neuroscience, 95, 1081–1088 (2000).
F. Hery, M. Faudon, and J. P. Ternaux, “In vivo release of serotonin in two raphe nuclei (raphe dorsalis and magnus) of cat,” Brain Res. Bull., 8, 123–129 (1982).
J.-P. Hornung, “The human raphe nuclei and the serotonergic system,” J. Chem. Neuroanat., 26, 331–343 (2003).
I. A. Kerman, C. Shabrang, L. Taylor, H. Akil, and S. J. Watson, “Relationship of presympathetic-premotor neurons to the serotonergic transmitter system in the brainstem,” J. Comp. Neurol., 499, 882–896 (2006).
Y. W. Li and D. A. Bayliss, “Electrophysical properties, synaptic transmission and neuromodulation in serotonergic caudal raphe neurons,” Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol., 25, 468–473 (1998).
A. H. Li and H.-L. Wang, “G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 mediated μ-opioid receptor desensitization in GABAergic neurons of the nucleus raphe magnus,” J. Neurochem., 77, 435–444 (2001).
R. Liu, T. Jolas, and G. K. Aghajanian, “Serotonin 5-HT2 receptors activate local GABA inhibitory inputs to serotonergic neurons of the dorsal raphe nucleus,” Brain Res., 873, 34–45 (2000).
P. Mason, “Contributions of the medullary raphe and ventromedial reticular region to pain modulation and other homeostatic functions,” Ann. Rev. Neurosci., 24, 737–777 (2001).
P. Mason, “Deconstructing endogenous pain modulations,” J. Neurophysiol., 94, 1659–1663 (2005).
P. Mason, K. Gao, and J. R. Gensen, “Serotonergic raphe magnus cell discharge reflects ongoing autonomic and respiratory activities,” J. Neurophysiol., 98, 1919–1927 (2007).
L. L. McMahon and J. A. Kauer, “Hippocampal interneurons are excited via serotonin-gated ion channels,” J. Neurophysiol., 78, 2493–2502 (1997).
J. A. Mico, E. Berrocoso, A. Ortega-Alvaro, J. Gibert-Rahola, and M. O. Rojas-Corrales, “The role of 5-HT1A receptors in research strategy for extensive pain treatment,” Curr. Top. Med. Chem., 18, 1997–2003 (2006).
D. E. Millhorn, T. Hokfelt, K. Seroogy, and A. A. Verhofstad, “Extent of colocalization of serotonin and GABA in neurons of the ventral medulla oblongata in rat,” Brain Res., 461, 169–174 (1988).
M. K. Mundey, A. Fletcher, and C. A. Marsden, “Effect of the putative 5-HT]A antagonists WAY 100135 and SDZ 216-525 on 5-HT neuronal firing in the guinea-pig dorsal raphe nucleus,” Neuropharmacol., 33, 61–66 (1994).
K. T. Muneoka and M. Takigawa, “5-Hydroxytryptamine7 (5-HT7) receptor immunoreactivity-positive ‘stigmoid body’-like structure in developing rat brains,” Int. J. Dev. Neurosci., 21, 133–143 (2003).
T. Nagai, T. Maeda, H. Imai, P. L. McGeer, and E. G. McGeer, “Distribution of GABA-T-intensive neurons in the rat hindbrain,” J. Comp. Neurol., 231, 260–269 (1985).
M. W. Nason and P. Mason, “Medullary raphe neurons facilitate brown adipose tissue activation,” J. Neurosci., 26, 1190–1198 (2006).
Z. Z. Pan, S. A. Tershner, and H. L. Fields, “Cellular mechanism for anti-analgesic action of agonists of the kappa-opioid receptor,” Nature, 389, 382–385 (1997).
N. J. Penington, J. S. Kelly, and A. P. Fox, “Whole cell recordings of inwardly rectifying K+ currents activated by 5-HT1A receptors on dorsal raphe neurons of the adult rat,” J. Physiol., 469, 387–406 (1993).
N. J. Penington and J. S. Kelly, “Serotonin receptor activation reduces calcium current in an acutely dissociated adult central neuron,” Neuron, 4, 751–758 (1990).
M. Pompeiano, J. M. Palacios, and G. Mengod, “Distribution and cellular localization of mRNA coding for 5-HT1A receptor in the rat brain: correlation with receptor binding,” J. Neurosci., 12, 440–453 (1992).
S. B. Potrebic, H. L. Fields, and P. Mason, “Serotonin immunoreactivity is contained in one physiological cell class in the rat rostral ventromedial medulla,” J. Neurosci., 14, 1655–1665 (1994).
D. B. Reichling and A. I. Basbaum, “Contribution of brainstem GABAergic circuitry to descending antinociceptive controls: II. Electronic microscopic immunocytochemical evidence, of GABAergic control over the projection from the periaqueductal gray to the nucleus raphe magnus in the rat,” J. Comp. Neurol., 302, 378–393 (1990).
W. M. Renno, M. Alkhalaf, A. Mousa, and R. A. Kanaan, “A comparative study of excitatory and inhibitory amino acids in three different brainstem nuclei,” Neurochem. Res., 33, 150–159 (2008).
J. Serrats, F. Artigas, G. Mengod, and R. Cortes, “GABAB receptor mRNA in the raphe nuclei: co-expression with serotonin transporter and glutamic acid decarboxylase,” J. Neurochem., 84, 743–752 (2003).
C. Sotelo, B. Cholley, S. E. Mestikawy, H. Gozlan, and M. Hamon, “Direct immunohistochemical evidence of the existence of 5-HT1A autoreceptors on serotoninergic neurons in the midbrain raphe nuclei,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 2, 144–154 (1990).
L. M. Sharkey, S. G. Madamba, G. Siggins, and T. Bartfai, “Galanin alters GABAergic neurotransmission in the dorsal raphe nucleus,” Neurochem. Res., 33, 285–291 (2008).
R. Tao, Z. Ma, and S. B. Auerbach, “Differential regulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine release by GABAA and GABAB receptors in midbrain raphe nuclei and forebrain of rats,” Brit. J. Pharmacol., 119, 1375–1384 (1996).
Y. Tohyama, D. Muck-Seler, and M. Diksic, “Acute flesinoxan treatment produces a different effect on rat brain serotonin synthesis than chronic treatment: An α-methyl-L-tryptophan autoradiographic study,” Neurochem. Int., 51, 486–495 (2007).
N. Urbain, K. Creamer, and G. Debonnel, “Electrophysiological diversity of the dorsal raphe cells across the sleep-wake cycle of the rat,” J. Physiol., 573, 679–695 (2006).
C. P. Candermaelen and G. K. Aghajanian, “Electrophysiological and pharmacological characterization of serotonergic dorsal raphe neurons recorded extracellularly and intracellularly in rat brain slices,” Brain Res., 289, 109–119 (1983).
T. A. Verner, A. K. Goodchild, and P. M. Pokowsky, “A mapping study of cardiorespiratory responses to chemical stimulation of the midline medulla oblongata in ventilated and freely breathing rats,” Am. J. Physiol., 287, R411–R421 (2004).
D. M. L. Vianna, C. Allen, and P. Carrive, “Cardiovascular and behavioral responses to conditioned fear after medullary raphe neuronal blockade,” Neuroscience, 153, 1344–1353 (2008).
L. Zhang, K. T. Sykes, A. V. Vuhler, and D. L. Hammond, “Electrophysiological heterogeneity of spinally projecting serotonergic and nonserotonergic neurons in the rostral ventromedial medulla,” J. Neurophysiol., 95, 1853–1863 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 95, No. 7, pp. 750–761, July, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inyushkin, A.N., Merkulova, N.A., Orlova, A.O. et al. Local Gabaergic Modulation of the Activity of Serotoninergic Neurons in the Nucleus Raphe Magnus. Neurosci Behav Physi 40, 885–893 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-010-9337-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-010-9337-x