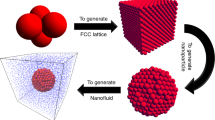
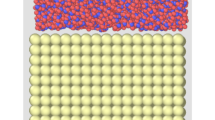
Abstract
The agglomeration of nanoparticles is a key factor which affects the stability of nanofluids. In order to analyze the effect of temperature on the agglomeration of nanoparticles from a micro perspective, molecular dynamics method is adopted to investigate the agglomeration characteristics of Cu nanoparticles in liquid water. Two conditions of stationary state and flow state are considered in the simulation. The results show that the collision and agglomeration accelerate with the increase of fluid temperature for either stationary state or flow state. The aggregation of particles can be divided into the Brown movement stage, the adhesion stage, and the coalescence stage. The centroid distances of nanoparticles no longer change when the aggregation process completes. The potential energy of the system increases with the fluid temperature. The total potential energy of the system decreases with each collision of Cu particles. The total potential energy of the system no longer changes until all the Cu particles collide and agglomerate. The obtained results can provide useful understanding of the stability of nanofluids affected by the temperature. And the stability further affects the thermal behavior of nanofluids.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullaeva Z (2017) Nano- and biomaterials: compounds, properties, characterization, and applications [M]. Chapter 2
Beckers JVL, Lowe CP, Leeuw SWD (1998) An Iterative PPPM method for simulating coulombic systems on distributed memory parallel computers [J]. Mol Simul 20(6):369–383
Berendsen HJC, Grigera JR, Straatsma TP (1987) The missing term in effective pair potentials [J]. J Phys Chem 91(24):6269–6271
Chen ZQ, Wang GX, Xu GY (2001) Colloid and interface chemistry [M]. Colloid and Interface Chemistry. High Education Press, Beijing
Chen J, Shi L, An QS (2010) Effective thermal conductivity of nanofluid form molecular dynamics simulations [J]. Tsing hua Univ(SCi&Tech) 50(12):1983–1987
Choi SUS, Eastman JA (1995) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles [J]. ASME FED 231(1):99–105
Cui W, Shen Z, Yang J, Wu S (2016) Molecular dynamics simulation on the microstructure of absorption layer at the liquid-solid interface in nanofluids [J]. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer 71:75–85
Dippong T, Toloman D, Levei EA, Cadar O, Mesaros A (2018a) A possible formation mechanism and photocatalytic properties of CoFe2O4/PVA-SiO2 nanocomposites [J]. Thermochim Acta 666:103–115
Dippong T, Cadar O, Levei EA, Deac IG, Borodi G (2018b) Formation of CoFe2O4/PVA-SiO2 nanocomposites: effect of diol chain length on the structure and magnetic properties [J]. Ceram Int 44(9):10478–10485
Dippong T, Levei EA, Cadar O et al (2019a) Thermal behavior of Ni, Co and Fe succinates embedded in silica matrix [J]. J Therm Anal Calorim 97(1):245–250
Dippong T, Cadar O, Levei EA, Deac IG, Goga F, Borodi G, Barbu-Tudoran L (2019b) Influence of polyol structure and molecular weight on the shape and properties of Ni0.5 Co0.5 Fe2O4 nanoparticles obtained by sol-gel synthesis [J]. Ceram Int 45(6):7458–7467
Dippong T, Levei EA, Deac IG, Neag E, Cadar O (2020a) Influence of Cu2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+ ions doping on the structure, morphology, and magnetic properties of co-ferrite embedded in SiO2 matrix obtained by an innovative sol-gel route [J]. Nanomaterials 10(3):580
Dippong T, Deac IG, Cadar O, Levei EA, Petean I (2020b) Impact of Cu2+ substitution by Co2+ on the structural and magnetic properties of CuFe2O4 synthesized by sol-gel route [J]. Mater Charact 163:110248
Farzaneh H, Behzadmehr A, Yaghoubi M, Samimi A, Sarvari SMH (2016) Stability of nanofluids: molecular dynamic approach and experimental study [J]. Energy Convers Manag 111:1–14
Habib A, Mohammad AJ, Nayyer R (2014) Nanoparticles aggregation in nanofluid flow through nanochannels: insights from molecular dynamic study [J]. Int J Modern Physics C 25(11):145066
Izadkhah MS, Heris SZ (2019) Influence of Al2O3 nanoparticles on the stability and viscosity of nanofluids: insights from molecular dynamics simulation [J]. J Therm Anal Calorim 138(1):623–631
Jiang HF, Li H, Zan C et al (2014) Temperature dependence of the stability and thermal conductivity of and oil-based nanofluid [J]. Thermochim Acta 579:27–30
Kumar PG, Kumaresan V, Velraj R (2017) Stability, viscosity, thermal conductivity, and electrical conductivity enhancement of multi-walled carbon nanotube nanofluid using gum arabic [J]. Fullerenes Nanotubes Carbon Nanostructures 25(4):230–240
Li L, Zhang YW, Ma HB et al (2010a) Molecular dynamics simulation of effect of liquid layering around the nanoparticle on the enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids [J]. J Nanopart Res 12:811–821
Li L, Guo L, Yang M et al (2010b) Molecular dynamics simulation of the thermal conductivity of nanofluids [J]. J Eng Thermophys 11:135–138
Li Y, Xu J, Li D (2010c) Molecular dynamics simulation of nanoscale liquid flows [J]. Microfluid Nanofluid 9(6):1011–1031
Liu Z, Chen Y, Mo S, Cheng Z, Li H (2015) Stability of TiO2 nanoparticles in deionized water with ZrP nanoplatelets [J]. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 15(4):3271–3275
Lu J (2016) Research on aggregation and deposition characteristics of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in aqueous systems under different scales [D]. Harbin Institute Technology, Harbin
Lv JZ, Cui WZ, Bai ML et al (2011a) Molecular dynamics simulation on flow behavior of nanofluids between flat plates under shear flow condition [J]. Microfluid Nanofluid 10:475–480
Lv JZ, Bai ML, Cui WZ et al (2011b) The molecular dynamic simulation on impact and friction characters of nanofluids with many nanoparticles system [J]. Nanoscale Res Lett 6(1):200–200
Plimpton S (1995) Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics [J]. J Comput Phys 117(1):1–19
Rudyak V, Krasnolutskii S, Belkin A et al (2020) Molecular dynamics simulation of water-based nanofluids viscosity [J]. J Therm Anal Calorim 6
Song QS, Guo XL, Yuan SL et al (2009) Molecular dynamics simulation of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate aggregation on silica surface [J]. Acta Phys -Chim Sin 25(6):1053–1058(6)
Varilly P, Chandler D (2013) Water evaporation: a transition path sampling study [J]. J Phys Chem B 117(5):1419–1428
Wang X, Jing DW (2019) Determination of thermal conductivity of interfacial layer in nanofluids by equilibrium molecular dynamics simulation [J]. Int J Heat Mass Transf 128:199–207
Wang N, Chen J, An QS et al (2011) Elementary research on the dispersion and stability of nanofluids by molecular dynamics simulations [J]. J Eng Thermophys 32(07):1107–1110
Wang JT, Xu ZM, Han ZM et al (2018) Effect of heat flux and inlet temperature on the fouling characteristics of nanoparticles [J]. Chin J Chem Eng 26(3):623–630
Xiong HL, Yuan YZ, Li H et al (2007) Computer simulation of colloidal aggregation induced by directionalism of long range van der Waals forces [J]. Acta Phys -Chim Sin 23(08):1241–1246
Yin XY, Hu CZ, Bai ML et al (2019) Molecular dynamic simulation of rapid boiling of nanofluids on different wetting surfaces with depositional nanoparticles [J]. Int J Multiphase Flow 115:9–18
Zhang LX, Hong G, Cai SY (2019) Molecular dynamics simulation of aggregation of monocrystal and polycrystal copper nanoparticles [J]. Int J Modern Physics B 33(16):1950168
Zheng HG, Li YD, Li CW et al (1997) Preparation of colloid and It’s absorption spectrum [J]. Acta Phys -Chim Sin 13(11):974–977
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51476025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Li, Z., Jia, Y. et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of effect of temperature on Cu nanoparticles agglomeration of nanofluids. J Nanopart Res 23, 28 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-05131-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-05131-y