Abstract
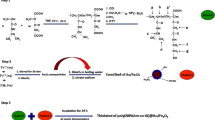
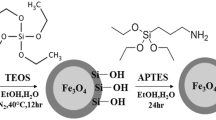
The use of nanoparticles as drug delivery systems for anticancer therapeutics has great potential to revolutionize the future of cancer therapy. The aim of this study is to construct a novel drug delivery platform comprising a magnetic core and biodegradable thermoresponsive shell of tri-block-copolymer. Oleic acid-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles and hydrophilic anticancer drug “doxorubicin” are encapsulated with PEO–PLGA–PEO (polyethylene oxide–poly d, l lactide-co-glycolide–polyethylene oxide) tri-block-copolymer. Structural, magnetic, and physical properties of Fe3O4 core are determined by X-ray diffraction, vibrating sample magnetometer, and transmission electron microscopy techniques, respectively. The hydrodynamic size of composite nanoparticles is determined by dynamic light scattering and is found to be ~36.4 nm at 25 °C. The functionalization of magnetic core with various polymeric chain molecules and their weight proportions are determined by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and thermogravimetric analysis, respectively. Encapsulation of doxorubicin into the polymeric magnetic nanoparticles, its loading efficiency, and kinetics of drug release are investigated by UV–vis spectroscopy. The loading efficiency of drug is 89% with a rapid release for the initial 7 h followed by the sustained release over a period of 36 h. The release of drug is envisaged to occur in response to the physiological temperature by deswelling of thermoresponsive PEO–PLGA–PEO block-copolymer. This study demonstrates that temperature can be exploited successfully as an external parameter to control the release of drug.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexiou C, Arnold W, Klein RJ, Parak FG, Hulin P, Bergemann C, Erhardt W, Wagenpfeil S, Lübbe AS (2000) Locoregional cancer treatment with magnetic drug targeting. Cancer Res 60:6641–6648
Arshady R, Monshipouri M, Arshady R (1999) Microspheres microcapsules and liposomes, vol 2. Citus Books, London
Bergemann C, Muller D, Oster J, Brassard L, Lubbe A (1999) Magnetic ion-exchange nano and microparticles for medical, biochemical and molecular biological applications. J Magn Magn Mater 194:45–52
Bertin P, Smith D, Nguyen S (2005) High-density doxorubicin-conjugated polymeric nanoparticles via ring-opening metathesis polymerization. Chem Commun 3793–3795
Cullity BD (1978) Elements of X-ray diffraction, 2nd edn. Addison-Wesley Publication Company
Fu L, Dravid V, Johnson D (2001) Self-assembled (SA) bilayer molecular coating on magnetic nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 181:173–178
Gu H, Xu K, Yang Z, Cheng C, Xu B (2005) Synthesis and cellular uptake of porphyrin decorated iron oxide nanoparticles—a potential candidate for bimodal anticancer therapy. Chem Commun 4270–4272
Gupta A, Curtis A (2004) Surface modified superparamagnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery: interaction studies with human fibroblasts in culture. J Mater Sci Mater Med 15:493–496
Gupta A, Gupta M (2005) Synthesis and surface engineering of ion oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 26:3995–4021
Gupta A, Wells S (2004) Surface-modified superparamagnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery: preparation, characterization and cytotoxicity studies. IEEE Trans Nanobiosci 3:66–73
Jain T, Morales M, Sahoo S, Pelecky D, Labhasetwar V (2005) Iron oxide nanoparticles for sustained delivery of anticancer agents. Mol Pharm 2:194–205
Jurgons R, Seliger C, Hilpert A, Trahms L, Odenbach S, Alexiou C (2006) Drug loaded magnetic nanoparticles for cancer therapy. J Phys Condens Matter 18:S2893–S2902
Klose D, Siepmann F, Elkharraz K, Krenzlin S, Siepmann J (2006) How porosity and size affect the drug release mechanism from PLGA - based microparticles. Int J Pharm 314:198–206
Kohaler N, Fryxell G, Zhang M (2004) A Bifunctional poly(ethylene glycol) silane immobilized on metallic oxide-based nanoparticles for conjugation with cell targeting agents. J Am Chem Soc 126:7206–7211
Koneracka M, Kopcansky P, Antalik M, Timko M, Ramchand C, Lobo D, Mehta R, Upadhyay R (1999) Immobilization of proteins and enzymes to fine magnetic particles. J Magn Mang Mater 201:427–430
Koneracka M, Kopcansky P, Timko M, Ramchand C, Sequeira A, Trevan M (2002) Direct binding procedure of proteins and enzymes to fine magnetic particles. J Mol Catal B Enzym 18:13–18
Koneracka M, Muckova M, Zavisova V, Tomasovicova N, Kopcansky P, Timko M, Jurikova A, Csach K, Kavecansky V, Lancz G (2008) Encapsulation of anticancer drug and magnetic particles in biodegradable polymer nanospheres. J Phys Condens Matter 20:204151
Kwon K, Park M, Bae Y, Kim H, Char K (2002) Geletation behaviours of PEO–PLGA–PEO triblock copolymers in water. Polymer 43:3353–3358
Lübbe AS, Bergemann C, Huhnt W, Fricke T, Riess H, Brock JW, Huhn D (1996) Preclinical experiences with magnetic drug targeting: tolerance and efficacy. Cancer Res 56:4694–4701
Lübbe AS, Alexiou C, Bergemann C (2001) Clinical applications of magnetic drug targetting. J Surg Res 95:200–206
Mann J (1999) The elusive magic bullet. Oxford University Press, New York
Mehta RV, Upadhyay RV, Charles SW, Ramchand CN (1997) Direct binding of protein to magnetic particles. Biotechnol Tech 11:493–496
Mohapatra S, Mallck S, Maiti T, Ghosh S, Pramanik P (2007) Synthesis of highly stable folic acid conjugated magnetite nanoparticles for targeting cancer cells. Nanotechnology 18:385102
Saiyed ZM, Telang SD, Ramchand CN (2003) Application of magnetic techniques in the field of drug discovery and biomedicine. Biomagn Res Technol 1:2
Sastry MD, Babu Y, Goyal PS, Mehta RV, Upadhyay RV, Srinivas D (1995) Electron magnetic resonance of ferrofluids: evidence for anisotropic resonance at 77 K in samples cooled in a magnetic field. J Magn Magn Mater 149:64–66
Shameem M, Lee H, DeLuca PP (1999) A short-term (accelerated release) approach to evaluate peptide release from PLGA depot formulations. AAPS Pharmsci 1:7
Sun C, Sze R, Zhang M (2006) Folic acid–PEG conjugated superparamagnetic nanoparticles for targeted cellular uptake and detection by MRI. J Biomed Mater Res A 78A:550–557
Vasir JK, Labhasetwar V (2005) Targeted drug delivery in cancer therapy. Technol Cancer Res Treat 4:363–374
Wooding A, Kilner M, Labrick BD (1992) Stripped magnetic particles. Applications of the double surfactant layer principle in the preparation of water-based magnetic fluids. J Colloid Interface Sci 149:98–104
Xu Q, Xubu Y, Jin C (2005) Self-aggregates of cholic acid hydrazide-dextran conjugates as drug carriers. J Appl Polym Sci 95:487–493
Yu W, Chang E, Sayes C, Drezek R, Colvin V (2006) Aqueous dispersion of monodisperse magnetic iron oxide nanocrystals through phase transfer. Nanotechnology 17:4483–4487
Zhang J, Misra R (2007) Magnetic drug-targeting carrier encapsulated with thermosensitive smart polymer: core-shell nanoparticle carrier and drug release response. Actabiomaterialia 3:838–850
Zhang J, Srivastava R, Misra R (2007) Core-shell magnetite nanoparticles surface encapsulated with smart stimuli-responsive polymer: synthesis, characterization and LCST of viable drug-targeting delivery system. Langmuir 23:6342–6351
Zhang J, Rana S, Srivastava R, Misra R (2008) On the chemical synthesis and drug delivery response of folate receptor-activated, polyethylene glycol-functionalized magnetite nanoparticles. Actabiomaterialia 4:40–48
Acknowledgments
The work was carried out under Ramanna Fellowship Project awarded to Prof. R.V. Mehta by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi. Authors are thankful to K. Padmanabhan, Beckman Coulter India Pvt Ltd. for his help in temperature dependent DLS measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andhariya, N., Chudasama, B., Mehta, R.V. et al. Biodegradable thermoresponsive polymeric magnetic nanoparticles: a new drug delivery platform for doxorubicin. J Nanopart Res 13, 1677–1688 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-9921-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-9921-6