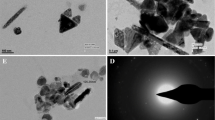
Abstract
We report a total “green” chemical method in aqueous solution for synthesizing stable narrowly distributed copper nanoparticles with average diameter less than 5 nm in the presence of Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as a stabilizer and without any inert gas protection. In our synthesis route, ascorbic acid, natural vitamin C (VC), an excellent oxygen scavenger, acts as both reducing agent and antioxidant, to reduce the metallic ion precursor, and to effectively prevent the common oxidation process of the newborn pure copper nanoclusters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anastas P.T., Warner J.C. (1998). Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice. Oxford University Press, Inc., New York
Avyappan S., Gopalan R.S., Subbanna G.N. (1997). Nanoparticles of Ag, Au, Pd, and Cu produced by alcohol reduction of the salts. J. Mater. Res. 12 (2): 398–401
Condorelli G.G., Costanzo L.L., Fragalà I.L., Giuffrida S., Ventimiglia G. (2003). A single photochemical route for the formation of both copper nanoparticles and patterned nanostructured films. J. Mater. Chem. 13: 2409–2411
Dhas N.A., Raj C.P., Gedanken A. (1998). Synthesis, characterization, and properties of metallic copper nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 10:1446–1452
Eastman J.A., Choi S.U.S., Li S., Yu W., Thompson L.J. (2001). Anomalously increased effective thermal conductivities of ethylene glycol-based nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78: 718–720
Gates B.C. (1995). Supported metal-clusters-synthesis, structure, and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 95(3): 511–522
Henglein A. (1993). Physicochemical properties of small metal particles in solution: “microelectrode” reactions, chemisorption, composite metal particles, and the atom-to-metal transition. J. Phys. Chem. 97: 5457–5471
Hwang C.-B., Fu Y.-S., Lu Y.-L., Jang S.-W., Chou P.-T., Chris Wang C. R., Yu S.J. (2000). Synthesis, characterization, and highly efficient catalytic reactivity of suspended palladium nanoparticles. J. Catal. 195: 336–341
Joshi S.S., Patil S.F., Iyer V., Mahumuni S. (1998). Radiation induced synthesis and characterization of copper nanoparticles. Nanostruct. Mater. 10: 1135–1144
Kapoor S., Mukherjee T. (2003). Photochemical formation of copper nanoparticles in poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone). Chem. Phys. Lett. 370: 83–87
Kruis F.E., Fissan H., Peled A. (1998). Synthesis of nanoparticles in the gas phase for electronic, optical and magnetic applications – a review. J. Aerosol Sci. 29: 511–535
Liu J., Raveendran P., Qin G., Ikushima Y. (2005). Self-assembly of β-D glucose-stabilized Pt nanocrystals into nanowire-like structures. Chem. Commun. (23): 2972–2974
Liu X., Cai W.P., Bi H.J. (2002). Optical absorption of copper nanoparticles dispersed within pores of monolithic mesoporous silica. J. Mater. Res. 17: 1125–1128
Lu Q., Gao F., Komarneni S. (2005). A green chemical approach to the synthesis of Tellurium nanowires. Langmuir 21: 6002–6005
Matlack A.S. (2001). Introduction to Green Chemistry. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York
Narayanan R., El-Sayed M.A. (2003). Effect of Catalysis on the Stability of Metallic Nanoparticles: Suzuki Reaction Catalyzed by PVP-Palladium Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125: 8340–8347
Nasibulin A.G., Ahonen P.P., Richard O., Kauppinen E.I., Altman I.S. (2001). Copper and copper oxide nanoparticle formation by chemical vapor nucleation from copper (II) acetylacetonate. J. Nanopart. Res. 3: 383–398
Poliakoff M., Anastas P. (2001). A principled stance. Nature 413: 257
Raveendran P., Fu J., Wallen S.L. (2003). Completely “Green” synthesis and stabilization of metal nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125: 13940–13941
Reetz M.T., Helbig W. (1994). Size-selective synthesis of nanostructured transition metal clusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 116: 7401–7402
Schmid G. (1992). Large clusters and colloids-metals in the embryonic state. Chem. Rev. 92: 1709–1727
Song X.Y., Sun S.X., Zhang W.M., Yin Z.L. (2004). A method for the synthesis of spherical copper nanoparticles in the organic phase. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 273: 463–469
Sun L., Zhang Z.J., Dang H.X. (2003). A novel method for preparation of silver nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 57: 3874–3879
Sun Y.G., Xia Y.N. (2002). Shape-controlled synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. Science 298: 2176–2179
Tatasov S., Kolubaev A., Belyaev S., Lerner M., Tepper F. (2002). Study of friction reduction by nanocopper additives to motor oil. Wear 252: 63–69
Tsai K.L., Dye J.L. (1991). Nanoscale metal particles by homogeneous reduction with alkalides or electrides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 113: 1650–1652
Tsai K.L., Dye J.L. (1993). Synthesis, properties, and characterization of nanometer-size metal particles by homogeneous reduction with alkalides and electrides in aprotic solvents. Chem. Mater. 5: 540–546
Weare W.W., Reed S.M., Warner M.G., Hutchison J.E. (2000). Improved synthesis of small (dCORE ≈ 1.5 nm) phosphine-stabilized gold nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122: 12890–12891
Wei Q., Kang S.Z., Mu J. (2004). “Green” synthesis of starch capped CdS nanoparticles. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 247: 125–127
Wu S.-H., Chen D.-H. (2004). Synthesis of high-concentration Cu nanoparticles in aqueous CTAB solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 273: 165–169
Xie S.-Y., Ma Z.-J., Wang C.-F., Lin S.-C., Jiang Z.-Y., Huang R.-B., Zheng L.-S. (2004). Preparation and self-assembly of copper nanoparticles via discharge of copper rod electrodes in a surfactant solution: a combination of physical and chemical processes. J. Solid State Chem. 177: 3743–3747
Xuan Y., Li Q. (2000). Heat transfer enhancement of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat and Fluid Flow 21: 58–64
Zhang Y.C., Xing R., Hu X.Y. (2004). A green hydrothermal route to copper nanocrystallites. J. Crystal Growth 273: 280–284
Zheng H.G., Liang J.H., Zeng J.H. (2001). Preparation of nickel nanopowders in ethanol-water system (EWS). Mater. Res. Bull. 36: 947–952
Zhu H.T., Zhang C.Y., Yin Y.S. (2004). Rapid synthesis of copper nanoparticles by sodium hypophosphite reduction in ethylene glycol under microwave irradiation. J. Crystal Growth 270: 722–728
Zhu Y.J., Qian Y.T., Zhang M.W., Chen Z.Y., Xu D.F. (1994). Preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline powders of cuprous oxide by using γ-radiation. Mater. Res. Bull. 29: 377–383
Acknowledgements
This project is funded by NASA/Space Grant and NSF (CTS-0500402).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, C., Mosher, B.P. & Zeng, T. One-step green route to narrowly dispersed copper nanocrystals. J Nanopart Res 8, 965–969 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-005-9065-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-005-9065-2