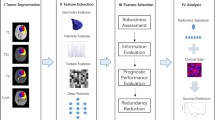
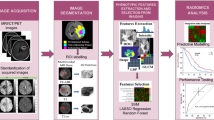
Abstract
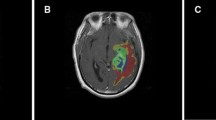
The combination of radiomics and artificial intelligence has emerged as a strong technique for building predictive models in radiology. This study aims to address the clinically important issue of whether a radiomic profile can predict the overall survival (OS) time of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) patients having gross tumor resection (GTR) through pre-operative structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. A retrospective analysis was made using data of glioma patients made publicly available by the University of Pennsylvania. The radiomic characteristics were extracted from pre-operative structural multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) sequences after pre-processing and 3D segmentation using deep learning (DL). After removing irrelevant features, regression models based on machine learning (ML) were developed by considering selected features to predict the OS time of GBM patients within a period of days only. The patients were divided into three survivor groups depending on their projected survival time. To validate the significance of the selected feature set, statistical analysis was performed. As many as 494 patients were considered to improve survival prediction (SP) by using more effective feature extraction and selection techniques. The ridge regressor acquired the highest SpearmanR Rank correlation of 0.635 with an accuracy of 69%, the greatest of all the previous works for categorical predictions of such patients. The researchers in the past who used radiomic characteristics for the OS prognosis of GBM patients could yield limited results only. However, the current research work recorded an enhanced accuracy and SpearmanR rank for the three survivor classes of GBM patients using ML, feature selection, and radiomics. The significance of this work lies in the selection of patients with GTR and the extraction of radiomic characteristics through the use of radiomics and artificial intelligence.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
References
Aftab K, Aamir FB, Mallick S, Mubarak F, Pope WB, Mikkelsen T, Rock JP, Enam SA (2022 Jan 12) Radiomics for precision medicine in glioblastoma. J Neuro-Oncol 156:217–231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03933-1
Agravat RR, Raval MS (2021) 3D Semantic Segmentation of Brain Tumor for Overall Survival Prediction. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, vol 12659. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 215–227. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72087-2_19
Akbar AS, Fatichah C, Suciati N (2021) Modified MobileNet for Patient Survival Prediction. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, vol 12659. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 374–387. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72087-2_33
Ali MJ, Akram MT, Saleem H, Raza B, Shahid AR (2021) Glioma Segmentation Using Ensemble of 2D/3D U-Nets and Survival Prediction Using Multiple Features Fusion. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, vol 12659. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 189–199. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72087-2_17
Anand VK, Grampurohit S, Aurangabadkar P, Kori A, Khened M, Bhat RS, Krishnamurthi G (2021) Brain Tumor Segmentation and Survival Prediction Using Automatic Hard Mining in 3D CNN Architecture. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, vol 12659. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 310–319. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72087-2_27
Bakas S, Akbari H, Sotiras A, Bilello M, Rozycki M, Kirby J, Freymann J, Farahani K, Davatzikos C (2017) Segmentation Labels for the Pre-operative Scans of the TCGA-GBM collection. The Cancer Imaging Archive. https://wiki.cancerimagingarchive.net/x/KoZyAQ
Bakas S, Akbari H, Sotiras A, Bilello M, Rozycki M, Kirby JS, Freymann JB, Farahani K, Davatzikos C (2017) Advancing the Cancer genome atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Scientific Data 4:170117. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2017.117
Bakas S, Reyes M, Jakab A, Bauer S, Rempfler M, Crimi A, Shinohara RT, Berger C, Ha SM, Rozycki M (2018) Identifying the best machine learning algorithms for brain tumor segmentation, progression assessment, and overall survival prediction in the BRATS challenge. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.02629. http://arxiv.org/abs/1811.02629
Bennett IE, Field KM, Hovens CM, Moffat BA, Rosenthal MA, Drummond K, Kaye AH, Morokoff AP (2017) Early perfusion MRI predicts survival outcome in patients with recurrent glioblastoma treated with bevacizumab and carboplatin. J Neuro-Oncol 131(2):321–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2300-0
Bhuyan HK, Ravi V (2021) Analysis of subfeature for classification in data mining. IEEE Trans Eng Manag:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEM.2021.3098463
Bhuyan HK, Reddy CVM (2018) Sub-Feature Selection for Novel Classification. In: 2018 Second International Conference on Inventive Communication and Computational Technologies (ICICCT). p. 477–482. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICCT.2018.8473206
Bhuyan HK, Chakraborty C, Shelke Y, Pani SK (2022) COVID-19 diagnosis system by deep learning approaches. Expert Syst 39(3):e12776. https://doi.org/10.1111/exsy.12776
Bleeker FE, Molenaar RJ, Leenstra S (2012) Recent advances in the molecular understanding of glioblastoma. J Neuro-Oncol 108(1):11–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0793-0
Carmo D, Rittner L, Lotufo R (2021) MultiATTUNet: Brain Tumor Segmentation and Survival Multitasking. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, vol 12658. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 424–434. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72084-1_38
Cepeda S, Pérez-Nuñez A, García-García S, García-Pérez D, Arrese I, Jiménez-Roldán L, García-Galindo M, González P, Velasco-Casares M, Zamora T, Sarabia R (2021) Predicting short-term survival after gross Total or near Total resection in glioblastomas by machine learning-based Radiomic analysis of preoperative MRI. Cancers. 13(20):5047. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205047
Chambless LB, Kistka HM, Parker SL, Hassam-Malani L, McGirt MJ, Thompson RC (2015) The relative value of postoperative versus preoperative Karnofsky performance scale scores as a predictor of survival after surgical resection of glioblastoma multiforme. J Neuro-Oncol 121(2):359–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1640-x
Choi Y, Nam Y, Jang J, Shin N-Y, Lee YS, Ahn K-J, Kim B, Park J-S, Jeon S, Hong YG (2021) Radiomics may increase the prognostic value for survival in glioblastoma patients when combined with conventional clinical and genetic prognostic models. Eur Radiol 31(4):2084–2093. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07335-1
Çiçek Ö, Abdulkadir A, Lienkamp SS, Brox T, Ronneberger O (2016) 3D U-Net: Learning Dense Volumetric Segmentation from Sparse Annotation. In: Ourselin S, Joskowicz L, Sabuncu MR, Unal G, Wells W (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2016. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 424–432. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_49
Clavreul A, Aubin G, Delion M, Lemée J-M, Ter Minassian A, Menei P (2021) What effects does awake craniotomy have on functional and survival outcomes for glioblastoma patients? J Neuro-Oncol 151(2):113–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03666-7
Czarnek N, Clark K, Peters KB, Mazurowski MA (2017) Algorithmic three-dimensional analysis of tumor shape in MRI improves prognosis of survival in glioblastoma: a multi-institutional study. J Neuro-Oncol 132(1):55–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2359-7
Dai C, Wang S, Raynaud H, Mo Y, Angelini E, Guo Y, Bai W (2021) Self-training for Brain Tumour Segmentation with Uncertainty Estimation and Biophysics-Guided Survival Prediction. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, vol 12658. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 514–523. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72084-1_46
De Barros A, Attal J, Roques M, Nicolau J, Sol J-C, Cohen-Jonathan-Moyal E, Roux F-E (2019) Impact on survival of early tumor growth between surgery and radiotherapy in patients with de novo glioblastoma. J Neuro-Oncol 142(3):489–497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03120-3
De Witt Hamer PC, Ho VKY, Zwinderman AH, Ackermans L, Ardon H, Boomstra S, Bouwknegt W, van den Brink WA, Dirven CM, van der Gaag NA et al (2019) Between-hospital variation in mortality and survival after glioblastoma surgery in the Dutch quality registry for neuro surgery. J Neuro-Oncol 144(2):313–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03229-5
Ferlay J, Shin H-R, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM (2010) Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 127(12):2893–2917. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.25516
Fu J, Singhrao K, Zhong X, Gao Y, Qi SX, Yang Y, Ruan D, Lewis JH (2021) An automatic deep learning–based workflow for glioblastoma survival prediction using preoperative multimodal MR images: a feasibility study. Adv Radiat Oncol 6(5):100746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adro.2021.100746
Fyllingen EH, Bø LE, Reinertsen I, Jakola AS, Sagberg LM, Berntsen EM, Salvesen Ø, Solheim O (2021) Survival of glioblastoma in relation to tumor location: a statistical tumor atlas of a population-based cohort. Acta Neurochir 163(7):1895–1905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-021-04802-6
Gibson E, Li W, Sudre C, Fidon L, Shakir DI, Wang G, Eaton-Rosen Z, Gray R, Doel T, Hu Y, Whyntie T, Nachev P, Modat M, Barratt DC, Ourselin S, Cardoso MJ, Vercauteren T (2018) NiftyNet: a deep-learning platform for medical imaging. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 158:113–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.01.025
Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H (2016) Radiomics: images are more than pictures. They Are Data Radiology 278(2):563–577. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2015151169
González SR, Zemmoura I, Tauber C (2021) 3D Brain Tumor Segmentation and Survival Prediction Using Ensembles of Convolutional Neural Networks. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, vol 12659. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 241–254. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72087-2_21
Han IS (2021) Multimodal Brain Image Analysis and Survival Prediction Using Neuromorphic Attention-Based Neural Networks. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, vol 12658. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 194–206. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72084-1_18
Henker C, Hiepel MC, Kriesen T, Scherer M, Glass Ä, Herold-Mende C, Bendszus M, Langner S, Weber M-A, Schneider B, Unterberg A, Piek J (2019) Volumetric assessment of glioblastoma and its predictive value for survival. Acta Neurochir 161(8):1723–1732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-019-03966-6
Isensee F, Kickingereder P, Wick W, Bendszus M, Maier-Hein KH (2018) Brain Tumor Segmentation and Radiomics Survival Prediction: Contribution to the BRATS 2017 Challenge. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Menze B, Reyes M (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 287–297. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75238-9_25
Jun W, Haoxiang X, Wang Z (2021) Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Dual-Path Attention U-Net in 3D MRI Images. In: Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, vol 12658. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 183–193. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72084-1_17
Kudulaiti N, Zhou Z, Luo C, Zhang J, Zhu F, Wu J (2021) A nomogram for individualized prediction of overall survival in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma: a real-world retrospective cohort study. BMC Surg 21(1):238. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-021-01233-z
Li H, Li A, Wang M (2019) A novel end-to-end brain tumor segmentation method using improved fully convolutional networks. Comput Biol Med 108:150–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.03.014
Liu L, Zhang H, Wu J, Yu Z, Chen X, Rekik I, Wang Q, Lu J, Shen D (2019) Overall survival time prediction for high-grade glioma patients based on large-scale brain functional networks. Brain Imaging Behav 13(5):1333–1351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9949-2
Liu L, Jiang H, He P, Chen W, Liu X, Gao J, Han J (2020 Apr 17) On the Variance of the Adaptive Learning Rate and Beyond. arXiv:1908.03265 [cs, stat]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1908.03265
Menze BH, Jakab A, Bauer S, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Farahani K, Kirby J, Burren Y, Porz N, Slotboom J, Wiest R, Lanczi L, Gerstner E, Weber MA, Arbel T, Avants BB, Ayache N, Buendia P, Collins DL, Cordier N, … van Leemput K (2015) The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34(10):1993–2024. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2014.2377694
Miron R, Albert R, Breaban M (2021) A Two-Stage Atrous Convolution Neural Network for Brain Tumor Segmentation and Survival Prediction. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, vol 12659. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 290–299. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72087-2_25
Naceur MB, Saouli R, Akil M, Kachouri R (2018) Fully automatic brain tumor segmentation using end-to-end incremental deep neural networks in MRI images. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 166:39–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.09.007
Nair V, Hinton GE (2010) Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In: Icml
Nestler U, Lutz K, Pichlmeier U, Stummer W, Franz K, Reulen H-J, Bink A (2015) On behalf of the 5-ALA glioma study group. Anatomic features of glioblastoma and their potential impact on survival. Acta Neurochir 157(2):179–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-014-2271-x
Ostrom QT, Bauchet L, Davis FG, Deltour I, Fisher JL, Langer CE, Pekmezci M, Schwartzbaum JA, Turner MC, Walsh KM, Wrensch MR, Barnholtz-Sloan JS (2014) The epidemiology of glioma in adults: a “state of the science” review. Neuro-Oncol 16(7):896–913. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nou087
Pang E, Shi W, Li X, Wu Q (2021) Glioma Segmentation Using Encoder-Decoder Network and Survival Prediction Based on Cox Analysis. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, vol 12658. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 318–326. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72084-1_29
Parmar B, Parikh M (2021) Brain Tumor Segmentation and Survival Prediction Using Patch Based Modified 3D U-Net. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, vol 12659. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 398–409. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72087-2_35
Patel J, Chang K, Hoebel K, Gidwani M, Arun N, Gupta S, Aggarwal M, Singh P, Rosen BR, Gerstner ER et al (2021) Segmentation, Survival Prediction, and Uncertainty Estimation of Gliomas from Multimodal 3D MRI Using Selective Kernel Networks. In: Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, vol 12659. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 228–240. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72087-2_20
Pei L, Vidyaratne L, Rahman MM, Iftekharuddin KM (2020) Context aware deep learning for brain tumor segmentation, subtype classification, and survival prediction using radiology images. Sci Rep 10(1):19726. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-74419-9
Pei L, Murat AK, Colen R (2021) Multimodal Brain Tumor Segmentation and Survival Prediction Using a 3D Self-ensemble ResUNet. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, vol 12658. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 367–375. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72084-1_33
Ribalta Lorenzo P, Nalepa J, Bobek-Billewicz B, Wawrzyniak P, Mrukwa G, Kawulok M, Ulrych P, Hayball MP (2019) Segmenting brain tumors from FLAIR MRI using fully convolutional neural networks. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 176:135–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.05.006
Russo C, Liu S, Di Ieva A (2021) Impact of Spherical Coordinates Transformation Pre-processing in Deep Convolution Neural Networks for Brain Tumor Segmentation and Survival Prediction. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, vol 12658. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 295–306. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72084-1_27
Selvapandian A, Manivannan K (2018) Fusion based glioma brain tumor detection and segmentation using ANFIS classification. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 166:33–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.09.006
Sfifou F, Hakkou EM, Bouaiti EA, Slaoui M, Errihani H, Al Bouzidi A, Abouqal R, El Ouahabi A, Cherradi N (2021) Correlation of immunohistochemical expression of HIF-1alpha and IDH1 with clinicopathological and therapeutic data of moroccan glioblastoma and survival analysis. Annals of Medicine and Surgery 69:102731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102731
Sharma N, Aggarwal LM (2010) Automated medical image segmentation techniques. J Medical Phys 35(1):3–14. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-6203.58777
Sharma A, Mishra PK (2020) State-of-the-Art in Performance Metrics and Future Directions for Data Science Algorithms. J Sci Res 64(02):221–238. https://doi.org/10.37398/JSR.2020.640232
Soltaninejad M, Yang G, Lambrou T, Allinson N, Jones TL, Barrick TR, Howe FA, Ye X (2018) Supervised learning based multimodal MRI brain tumour segmentation using texture features from supervoxels. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 157:69–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.01.003
Soltaninejad M, Pridmore T, Pound M (2021) Efficient MRI Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Multi-resolution Encoder-Decoder Networks. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, vol 12659. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 30–39. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72087-2_3
Suter Y, Knecht U, Alão M, Valenzuela W, Hewer E, Schucht P, Wiest R, Reyes M (2020) Radiomics for glioblastoma survival analysis in pre-operative MRI: exploring feature robustness, class boundaries, and machine learning techniques. Cancer Imaging 20(1):55. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40644-020-00329-8
van Griethuysen JJM, Fedorov A, Parmar C, Hosny A, Aucoin N, Narayan V, Beets-Tan RGH, Fillion-Robin J-C, Pieper S, Aerts HJWL (2017) Computational Radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype. Cancer Res 77(21):e104–e107. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0339
Wang G, Li W, Ourselin S, Vercauteren T (2018) Automatic Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Cascaded Anisotropic Convolutional Neural Networks. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Menze B, Reyes M (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 178–190. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75238-9_16
Whitmire P, Rickertsen CR, Hawkins-Daarud A, Carrasco E, Lorence J, De Leon G, Curtin L, Bayless S, Clark-Swanson K, Peeri NC et al (2020) Sex-specific impact of patterns of imageable tumor growth on survival of primary glioblastoma patients. BMC Cancer 20(1):447. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-020-06816-2
Wu Y, He K (2018) Group Normalization. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). p. 3–19. https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ECCV_2018/html/Yuxin_Wu_Group_Normalization_ECCV_2018_paper.html
Zhao G, Jiang B, Zhang J, Xia Y (2021) Segmentation then Prediction: A Multi-task Solution to Brain Tumor Segmentation and Survival Prediction. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, vol 12658. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 492–502. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72084-1_44
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization—Gurinderjeet Kaur.
Methodology—Gurinderjeet Kaur.
Formal analysis and investigation—Gurinderjeet Kaur, Prashant Singh Rana, Vinay Arora.
Writing (original draft preparation)— Gurinderjeet Kaur.
Writing (review and editing)— Gurinderjeet Kaur, Prashant Singh Rana, Vinay Arora.
Resources— Gurinderjeet Kaur, Prashant Singh Rana, Vinay Arora.
Supervision—Prashant Singh Rana, Vinay Arora.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Data is publicly available and contains no patient identities; thus, no institutional review board permission was necessary. The source of data is correctly cited in the manuscript.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable. No data, which could lead to the identification of the patient (photographs, names), was used.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 150 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, G., Rana, P.S. & Arora, V. Extracting Radiomic features from pre-operative and segmented MRI scans improved survival prognosis of glioblastoma Multiforme patients through machine learning: a retrospective study. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 30003–30038 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-14223-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-14223-x