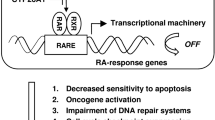
Abstract
Cellular Retinol Binding Protein 1 (CRBP1) gene is a protein coding gene located on human chromosome 3q21, which codifies a protein named CRBP1. CRBP1 is widely expressed in many tissues as a chaperone protein to regulate the uptake, subsequent esterification and bioavailability of retinol. CRBP1 combines retinol and retinaldehyde with high affinity to protect retinoids from non-specific oxidation, and transports retinoids to specific enzymes to promote the biosynthesis of retinoic acid. The vital role of CRBP1 in retinoids metabolism has been gradually discovered, which has been implicated in tumorigenesis. However, the precise functions of CRBP1 in different diseases are still poorly understood. The purpose of this review is to provide an overview of the role of CRBP1 in various diseases, especially in both the promotion and inhibition of cancers, which may also offer a novel biomarker and potential therapeutic target for human diseases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dowling JE (1966) Night blindness. Sci Am 215:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1038/scientificamerican1066-78
De Luca LM (1991) Retinoids and their receptors in differentiation, embryogenesis, and neoplasia. Faseb j 5:2924–2933
Mark M, Ghyselinck NB, Chambon P (2006) Function of retinoid nuclear receptors: lessons from genetic and pharmacological dissections of the retinoic acid signaling pathway during mouse embryogenesis. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 46:451–480. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.46.120604.141156
Molotkov A, Ghyselinck NB, Chambon P et al (2004) Opposing actions of cellular retinol-binding protein and alcohol dehydrogenase control the balance between retinol storage and degradation. Biochem J 383:295–302. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20040621
Saari JC, Nawrot M, Garwin GG et al (2002) Analysis of the visual cycle in cellular retinol-binding protein type I (CRBPI) knockout mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:1730–1735
Budhu AS, Noy N (2002) Direct channeling of retinoic acid between cellular retinoic acid-binding protein II and retinoic acid receptor sensitizes mammary carcinoma cells to retinoic acid-induced growth arrest. Mol Cell Biol 22:2632–2641. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.22.8.2632-2641.2002
Chambon P (1996) A decade of molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors. Faseb J 10:940–954
Vogel S, Mendelsohn CL, Mertz JR et al (2001) Characterization of a new member of the fatty acid-binding protein family that binds all-trans-retinol. J Biol Chem 276:1353–1360. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M005118200
Napoli JL (2017) Cellular retinoid binding-proteins, CRBP, CRABP, FABP5: effects on retinoid metabolism, function and related diseases. Pharmacol Ther 173:19–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.01.004
Chou AP, Chowdhury R, Li S et al (2012) Identification of retinol binding protein 1 promoter hypermethylation in isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 mutant gliomas. J Natl Cancer Inst 104:1458–1469. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djs357
LiCata VJ, Bernlohr DA (1998) Surface properties of adipocyte lipid-binding protein: Response to lipid binding, and comparison with homologous proteins. Proteins 33:577–589
Menozzi I, Polverini E, Berni R (2018) Deciphering protein dynamics changes along the pathway of retinol uptake by cellular retinol-binding proteins 1 and 2. Arch Biochem Biophys 645:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2018.03.020
Li E, Qian SJ, Winter NS et al (1991) Fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of the ligand binding properties of two homologous rat cellular retinol-binding proteins expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 266:3622–3629
Ghyselinck NB, Båvik C, Sapin V et al (1999) Cellular retinol-binding protein I is essential for vitamin A homeostasis. Embo J 18:4903–4914. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.18.4903
Shutoh M, Oue N, Aung PP et al (2005) DNA methylation of genes linked with retinoid signaling in gastric carcinoma: expression of the retinoid acid receptor beta, cellular retinol-binding protein 1, and tazarotene-induced gene 1 genes is associated with DNA methylation. Cancer 104:1609–1619. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.21392
He D, Zhang YW, Zhang NN et al (2015) Aberrant gene promoter methylation of p16, FHIT, CRBP1, WWOX, and DLC-1 in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinomas. Med Oncol 32:92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-015-0525-y
Colvin EK, Susanto JM, Kench JG et al (2011) Retinoid signaling in pancreatic cancer, injury and regeneration. PLoS ONE 6:e29075. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0029075
Yokoi K, Yamashita K, Ishii S et al (2017) Comprehensive molecular exploration identified promoter DNA methylation of the CRBP1 gene as a determinant of radiation sensitivity in rectal cancer. Br J Cancer 116:1046–1056. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2017.65
Schmitt-Gräff A, Ertelt V, Allgaier HP et al (2003) Cellular retinol-binding protein-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with beta-catenin, Ki-67 index, and patient survival. Hepatology 38:470–480. https://doi.org/10.1053/jhep.2003.50321
Liu X, Shan W, Li T et al (2021) Cellular retinol binding protein-1 inhibits cancer stemness via upregulating WIF1 to suppress Wnt/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 21:1224. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-021-08967-2
Mizuiri H, Yoshida K, Toge T et al (2005) DNA methylation of genes linked to retinoid signaling in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: DNA methylation of CRBP1 and TIG1 is associated with tumor stage. Cancer Sci 96:571–577. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2005.00082.x
Toki K, Enokida H, Kawakami K et al (2010) CpG hypermethylation of cellular retinol-binding protein 1 contributes to cell proliferation and migration in bladder cancer. Int J Oncol 37:1379–1388. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo_00000789
Jerónimo C, Henrique R, Oliveira J et al (2004) Aberrant cellular retinol binding protein 1 (CRBP1) gene expression and promoter methylation in prostate cancer. J Clin Pathol 57:872–876. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.2003.014555
Mendoza-Rodriguez M, Arreola H, Valdivia A et al (2013) Cellular retinol binding protein 1 could be a tumor suppressor gene in cervical cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 6:1817–1825
Badary DM, Abou-Taleb H (2020) Vitamin D receptor and cellular retinol-binding protein-1 immunohistochemical expression in normal, hyperplastic and neoplastic endometrium: Possible diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Ann Diagn Pathol 48:151569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2020.151569
Roberts D, Williams SJ, Cvetkovic D et al (2002) Decreased expression of retinol-binding proteins is associated with malignant transformation of the ovarian surface epithelium. DNA Cell Biol 21:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1089/10445490252810276
Cvetković D, Williams SJ, Hamilton TC (2003) Loss of cellular retinol-binding protein 1 gene expression in microdissected human ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res 9:1013–1020
Li H, Lei Y, Li S et al (2022) MicroRNA-20a-5p inhibits the autophagy and cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer via regulating DNMT3B-mediated DNA methylation of RBP1. Reprod Toxicol 109:93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2021.12.011
Doldo E, Costanza G, Ferlosio A et al (2014) CRBP-1 expression in ovarian cancer: a potential therapeutic target. Anticancer Res 34:3303–3312
Orlandi A, Ferlosio A, Ciucci A et al (2004) Cellular retinol-binding protein-1 expression in endometrial stromal cells: physiopathological and diagnostic implications. Histopathology 45:511–517. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2559.2004.01963.x
Orlandi A, Ferlosio A, Ciucci A et al (2006) Cellular retinol binding protein-1 expression in endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma: diagnostic and possible therapeutic implications. Mod Pathol 19:797–803. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.3800586
Malik M, Webb J, Catherino WH (2008) Retinoic acid treatment of human leiomyoma cells transformed the cell phenotype to one strongly resembling myometrial cells. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 69:462–470. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.2008.03207.x
Peralta R, Baudis M, Vazquez G et al (2010) Increased expression of cellular retinol-binding protein 1 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136:931–938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-009-0735-9
Peralta R, Valdivia A, Alvarado-Cabrero I et al (2012) Correlation between expression of cellular retinol-binding protein 1 and its methylation status in larynx cancer. J Clin Pathol 65:46–50. https://doi.org/10.1136/jclinpath-2011-200304
Gao L, Wang Q, Ren W et al (2020) The RBP1-CKAP4 axis activates oncogenic autophagy and promotes cancer progression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 11:488. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2693-8
Chen Y, Tian T, Mao MJ et al (2018) CRBP-1 over-expression is associated with poor prognosis in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 18:514. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4249-1
Bistulfi G, Pozzi S, Ren M et al (2006) A repressive epigenetic domino effect confers susceptibility to breast epithelial cell transformation: implications for predicting breast cancer risk. Cancer Res 66:10308–10314. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-06-1052
Farias EF, Ong DE, Ghyselinck NB et al (2005) Cellular retinol-binding protein I, a regulator of breast epithelial retinoic acid receptor activity, cell differentiation, and tumorigenicity. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/dji004
Kuppumbatti YS, Bleiweiss IJ, Mandeli JP et al (2000) Cellular retinol-binding protein expression and breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:475–480. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/92.6.475
Zhang XK (2002) Vitamin A and apoptosis in prostate cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 9:87–102. https://doi.org/10.1677/erc.0.0090087
Yu J, Perri M, Jones JW et al (2022) Altered RBP1 gene expression impacts epithelial cell retinoic acid, proliferation, and microenvironment. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050792
Kuppumbatti YS, Rexer B, Nakajo S et al (2001) CRBP suppresses breast cancer cell survival and anchorage-independent growth. Oncogene 20:7413–7419. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204749
Soares J, Pinto AE, Cunha CV et al (1999) Global DNA hypomethylation in breast carcinoma: correlation with prognostic factors and tumor progression. Cancer 85:112–118
Farias EF, Marzan C, Mira-y-Lopez R (2005) Cellular retinol-binding protein-I inhibits PI3K/Akt signaling through a retinoic acid receptor-dependent mechanism that regulates p85–p110 heterodimerization. Oncogene 24:1598–1606. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208347
Wu W, Wang Y, Niu C et al (2022) Retinol binding protein 1-dependent activation of NF-κB signaling enhances the malignancy of non-glioblastomatous diffuse gliomas. Cancer Sci 113:517–528. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.15233
Campos B, Centner FS, Bermejo JL et al (2011) Aberrant expression of retinoic acid signaling molecules influences patient survival in astrocytic gliomas. Am J Pathol 178:1953–1964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.01.051
Doldo E, Costanza G, Ferlosio A et al (2015) High expression of cellular retinol binding protein-1 in lung adenocarcinoma is associated with poor prognosis. Genes Cancer 6:490–502. https://doi.org/10.18632/genesandcancer.89
Ferlosio A, Doldo E, Agostinelli S et al (2020) Cellular retinol binding protein 1 transfection reduces proliferation and AKT-related gene expression in H460 non-small lung cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep 47:6879–6886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05744-5
Bansal N, Bosch A, Leibovitch B et al (2016) Blocking the PAH2 domain of Sin3A inhibits tumorigenesis and confers retinoid sensitivity in triple negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 7:43689–43702. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.9905
Silvaroli JA, Widjaja-Adhi MAK, Trischman T et al (2019) Abnormal Cannabidiol modulates vitamin A metabolism by acting as a competitive inhibitor of CRBP1. ACS Chem Biol 14:434–448. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.8b01070
Elmaadawy E, Elgarhy LH, Shareef M (2019) Cellular retinol-binding protein-1 expression increases with increasing clinical severity of alopecia areata. J Cosmet Dermatol 18:659–664. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12833
Aktuna D, Buchinger W, Langsteger W et al (1993) Beta-carotene, vitamin A and carrier proteins in thyroid diseases. Acta Med Austriaca 20:17–20
Forga L, Bolado F, Goñi MJ et al (2016) Low serum levels of prealbumin, retinol binding protein, and retinol are frequent in adult type 1 diabetic patients. J Diabetes Res 2016:2532108. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2532108
Saurat JH (1999) Retinoids and psoriasis: novel issues in retinoid pharmacology and implications for psoriasis treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol 41:S2-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0190-9622(99)70358-0
Phelan JK, Bok D (2000) A brief review of retinitis pigmentosa and the identified retinitis pigmentosa genes. Mol Vis 6:116–124
Voigt AP, Mullin NK, Whitmore SS et al (2021) Human photoreceptor cells from different macular subregions have distinct transcriptional profiles. Hum Mol Genet 30:1543–1558. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddab140
Funding
This work was supported by Scientific and technological key project in Henan Province (No. 222102310244).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that this review was written in the absence of any potential confict of interest.
Consent to publish
All authors state their permission for the publication of this manuscript.
Research involving human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Z., Zhao, Y., Wu, Y. et al. Cellular retinol-binding protein 1: a therapeutic and diagnostic tumor marker. Mol Biol Rep 50, 1885–1894 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-08179-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-08179-2