Abstract
Background
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is the process by which epithelial cells transform into mesenchymal cells, which plays a significant role in lung fibrotic disease. Transforming growth factor-β1(TGF-β1) is considered to be the most effective EMT inducer. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of the proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) on TGF-β1-induced EMT and the underlying mechanisms in the human bronchial epithelial cell line BEAS-2B.
Methods
Human bronchial epithelial BEAS-2B cells were treated with TGF-β1 and TNF-α separately or in combination for 24 h, and qRT–PCR, western blotting, immunofluorescence staining, and migration assays were used to investigate the EMT process. Moreover, to further explore the effect of the NF-κB pathway on the EMT process, inhibitor assays (BAY-117082, NF-κB inhibitor), wound healing assays, and western blotting were performed.
Results
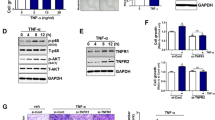
The results showed that both cytokines enhanced the transformation of BEAS-2B cells from epithelial to mesenchymal cells. In addition, combined treatment with TNF-α and TGF-β1 further reduced E-cadherin expression, which conversely elevated α-SMA and vimentin mRNA and protein levels. Correspondingly, the migration rate of BEAS-2B cells was also increased. Furthermore, inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway blocked the expression of EMT-related markers and NOX4 induced by TGF-β1 and TNF-α, as well as cell migration.
Conclusion
Taken together, TNF-α and TGF-β1 cooperatively promoted EMT and cell migration in BEAS-2B cells through the NF-κB/NOX4 signaling pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee HW, Jose CC, Cuddapah S (2021) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: insights into nickel-induced lung diseases. Semin Cancer Biol 76:99–109
Huang Z, Zhang Z, Zhou C, Liu L, Huang C (2022) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: the history, regulatory mechanism, and cancer therapeutic opportunities. MedComm 3(2):e144
Ribatti D, Tamma R, Annese T (2020) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: a historical overview. Transl Oncol 13(6):100773
Liu L, Sun Q, Davis F, Mao J, Zhao H, Ma D (2022) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in organ fibrosis development: current understanding and treatment strategies. Burns Trauma 10:tkac011
Jiang Z, Zhang Y, Zhu Y, Li C, Zhou L, Li X, Zhang F, Qiu X, Qu Y (2021) Cathelicidin induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition to promote airway remodeling in smoking-related chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann Transl Med 9(3):223
Di Gregorio J, Robuffo I, Spalletta S, Giambuzzi G, De Iuliis V, Toniato E, Martinotti S, Conti P, Flati V (2020) The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition as a possible therapeutic target in fibrotic disorders. Front Cell Dev Biol 21(8):607483
Epstein Shochet G, Brook E, Bardenstein-Wald B, Shitrit D (2020) TGF-beta pathway activation by idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) fibroblast derived soluble factors is mediated by IL-6 trans-signaling. Respir Res 21(1):56
Zhang KW, Wang D, Cai H, Cao MQ, Zhang YY, Zhuang PY, Shen J (2021) IL-6 plays a crucial role in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and pro-metastasis induced by sorafenib in liver cancer. Oncol Rep 45(3):1105–1117
Cruceriu D, Baldasici O, Balacescu O, Berindan-Neagoe I (2020) The dual role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in breast cancer: molecular insights and therapeutic approaches. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 43(1):1–18
Sisto M, Ribatti D, Lisi S (2021) Organ fibrosis and autoimmunity: the role of inflammation in TGFβ-dependent EMT. Biomolecules 11(2):310
Yuan Q, Tan RJ, Liu Y (2019) Myofibroblast in kidney fibrosis: origin, activation, and regulation. Adv Exp Med Biol 1165:253–283
Xue R, Li Y, Li X, Ma J, An C, Ma Z (2019) miR-185 affected the EMT, cell viability, and proliferation via DNMT1/MEG3 pathway in TGF-β1-induced renal fibrosis. Cell Biol Int 43(10):1152–1162
Chen K, Li Z, Zhang M, Wang B, Peng T, Shen Y, Zhang J, Ye J, Liu Y, Tang D, Peng M, Ma D, Xiao Z, Zhang Y, Jin W, Li X (2020) miR-876 inhibits EMT and liver fibrosis via POSTN to suppress metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Res Int 5(2020):1964219
Özel M, Baskol M, Akalın H, Baskol G (2021) Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid (SAHA) reduces fibrosis markers and deactivates human stellate cells via the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Cell Biochem Biophys 79(2):349–357
Zhang D, Yang H, Dong XL, Zhang JT, Liu XF, Pan Y, Zhang J, Xu JW, Wang ZH, Cui WJ, Dong L (2022) TL1A/DR3 axis, a key target of TNF-a, augments the epithelial-mesenchymal transformation of epithelial cells in OVA-induced asthma. Front Immunol 14(13):854995
Wu EK, Henkes ZI, McGowan B, Bell RD, Velez MJ, Livingstone AM, Ritchlin CT, Schwarz EM, Rahimi H (2019) TNF-induced interstitial lung disease in a murine arthritis model: accumulation of activated monocytes, conventional dendritic cells, and CD21(+)/CD23(-) B cell follicles is prevented with Anti-TNF therapy. J Immunol 203(11):2837–2849
Shao S, Qu Z, Liang Y, Xu Y, Zhou D, Li D, Zhang Y, Yin S (2021) Iguratimod decreases bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in association with inhibition of TNF-α in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 99:107936.19
Hou J, Ma T, Cao H, Chen Y, Wang C, Chen X, Xiang Z, Han X (2018) TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation promotes myofibroblast differentiation of LR-MSCs and exacerbates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Cell Physiol 233(3):2409–2419
Malaviya R, Laskin JD, Laskin DL (2017) Anti-TNFα therapy in inflammatory lung diseases. Pharmacol Ther 180:90–98
Shyam Prasad Shetty B, Chaya SK, Kumar VS, Mahendra M, Jayaraj BS, Lokesh KS, Ganguly K, Mahesh PA (2021) Inflammatory biomarkers interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) and tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) are differentially elevated in tobacco smoke associated COPD and biomass smoke associated COPD. Toxics 9(4):72
Venosa A, Gow JG, Taylor S, Golden TN, Murray A, Abramova E, Malaviya R, Laskin DL, Gow AJ (2021) Myeloid cell dynamics in bleomycin-induced pulmonary injury in mice; effects of anti-TNFα antibody. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 15(417):115470
Losa Garcia JE, Rodriguez FM, de Cabo MRM, Garcia Salgado MJ, Losada JP, Villaron LG, Lopez AJ, Arellano JL (1999) Evaluation of inflammatory cytokine secretion by human alveolar macrophages. Mediators Inflamm 8(1):43–51
Lozo Vukovac E, Lozo M, Mise K, Gudelj I, Puljiz Z, Jurcev-Savicevic A, Bradaric A, Kokeza J, Mise J (2014) Bronchoalveolar pH and inflammatory biomarkers in newly diagnosed IPF and GERD patients: a case-control study. Med Sci Monit 20:255–261
Cu A, Ye Q, Sarria R, Nakamura S, Guzman J, Costabel U (2009) N-acetylcysteine inhibits TNF-alpha, sTNFR, and TGF-beta1 release by alveolar macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in vitro. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 26(2):147–154
Piguet PF, Collart MA, Grau GE, Sappino AP, Vassalli P (1990) Requirement of tumour necrosis factor for development of silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Nature 344(6263):245–247
Piguet PF, Ribaux C, Karpuz V, Grau GE, Kapanci Y (1993) Expression and localization of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and its mRNA in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol 143(3):651–655
Borthwick LA, McIlroy EI, Gorowiec MR, Brodlie M, Johnson GE, Ward C, Lordan JL, Corris PA, Kirby JA, Fisher AJ (2010) Inflammation and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in lung transplant recipients: role in dysregulated epithelial wound repair. Am J Transplant 10(3):498–509
Bates RC, Mercurio AM (2003) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulates the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of human colonic organoids. Mol Biol Cell 14(5):1790–1800
Borthwick LA, Gardner A, De Soyza A, Mann DA, Fisher AJ (2012) Transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) driven epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) is accentuated by tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) via CROSSTALK BETWEEN the SMAD and NF-kappaB pathways. Cancer Microenviron 5(1):45–57
Ma M, Shi F, Zhai R, Wang H, Li K, Xu C, Yao W, Zhou F (2021) TGF-beta promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition via NF-kappaB/NOX4/ROS signal pathway in lung cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep 48(3):2365–2375
Liao SJ, Luo J, Li D, Zhou YH, Yan B, Wei JJ, Tu JC, Li YR, Zhang GM, Feng ZH (2019) TGF-beta1 and TNF-alpha synergistically induce epithelial to mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells by enhancing TAK1 activation. J Cell Commun Signal 13(3):369–380
Bradding P, Roberts JA, Britten KM et al (1994) Interleukin-4, -5, and -6 and thmor necrosis factor-a in normal and asthmatic airways: evidence for the human mast cell as a source of these cytokines. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 10(5):471–480
Franchimont D, Martens H, Hagelstein MT, Louis E, Dewe W, Chrousos GP, Belaiche J, Geenen V (1999) Tumor necrosis factor alpha decreases, and interleukin-10 increases, the sensitivity of human monocytes to dexamethasone: potential regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84(8):2834–2839
Epstein Shochet G, Brook E, Israeli-Shani L, Edelstein E, Shitrit D (2017) Fibroblast paracrine TNF-alpha signaling elevates integrin A5 expression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Respir Res 18(1):122
Cuadrado A, Pajares M, Benito C, Jiménez-Villegas J, Escoll M, Fernández-Ginés R, Garcia Yagüe AJ, Lastra D, Manda G, Rojo AI, Dinkova-Kostova AT (2020) Can activation of NRF2 be a strategy against COVID-19? Trends Pharmacol Sci 41(9):598–610
Nga HT, Moon JS, Tian J, Lee HY, Kim SH, Lee YS, Jeon JH, Yi HS (2021) Interleukin-10 attenuates liver fibrosis exacerbated by thermoneutrality. Front Med (Lausanne) 26(8):672658
Funding
This work received support from The Ministry of Education of Science and Technology research foundation of Henan province (Grant No. 222300420537).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, K., Zhou, R., Ma, M. et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α coordinates with transforming growth factor-β1 to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration via the NF-κB/NOX4 pathway in bronchial epithelial cells. Mol Biol Rep 49, 9325–9333 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07777-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07777-4