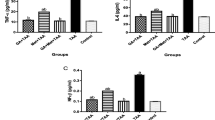
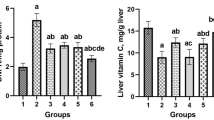
Abstract
Valproic acid (VPA) is known as a common drug in seizure and bipolar disorders treatment. Hepatotoxicity is the most important complication of VPA. Taurine (Tau), an amino acid, has antioxidant effects. The present research was conducted to evaluate the protective mechanisms of Tau on VPA-induced liver injury, especially focusing on the necroptosis signaling pathway. The sixty-four male NMRI mice were divided into eight groups with eight animals per each. The experiment groups pretreated with Tau (250, 500, 1000 mg/kg) and necrostatine-1 (Nec-1, 1.8 mg/kg) and then VPA (500 mg/kg) was administered for 14 consecutive days. The extent of VPA-induced hepatotoxicity was confirmed by elevated ALP (alkaline phosphatase), AST (aspartate aminotransferase), ALT (alanine aminotransferase) levels, and histological changes as steatosis, accumulation of erythrocytes, and inflammation. Additionally, VPA significantly induced oxidative stress in the hepatic tissue by increasing ROS (reactive oxygen species) production and lipid peroxidation level along with decreasing GSH (glutathione). Hepatic TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor) level, mRNA and protein expression of RIPK1 (receptor-interacting protein kinase 1), RIPK3, and MLKL (mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase) were upregulated. Also, the phosphorylation of MLKL and RIPK3 increased in the VPA group. Tau could effectively reverse these events. Our data suggest which necroptosis has a key role in the toxicity of VPA through TNF-α–mediated RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL signaling and oxidative stress. Our findings suggest that Tau protects the liver tissue against VPA toxicity via inhibiting necroptosis signaling pathway mediated by RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL and suppressing oxidative stress, and apoptosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- VPA:
-
Valproic acid
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- MLKL:
-
Mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RIPK1:
-
Receptor-interacting protein kinase 1
- TNFR1:
-
TNF receptor 1
- Tau:
-
Taurine
- Nec-1:
-
Necrostatin-1
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- ALP:
-
Alkaline phosphatase
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- DCFH-DA:
-
Dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate
- DCF:
-
Dichlorofluorescein
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- FADD:
-
Fas-associated death domain
References
Mei S, Feng W, Zhu L, Yu Y, Yang W, Gao B, Wu X, Zhao Z, Fang F (2017) Genetic polymorphisms and valproic acid plasma concentration in children with epilepsy on valproic acid monotherapy. Seizure 51:22–26
Zhu M-M, Li H-L, Shi L-H, Chen X-P, Luo J, Zhang Z-L (2017) The pharmacogenomics of valproic acid. Am J Hum Genet 62(12):1009–1014
Felker D, Lynn A, Wang S, Johnson DE (2014) Evidence for a potential protective effect of carnitine-pantothenic acid co-treatment on valproic acid-induced hepatotoxicity. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 7(2):211–218
Ghodke-Puranik Y, Thorn CF, Lamba JK, Leeder JS, Song W, Birnbaum AK, Altman RB, Klein TE (2013) Valproic acid pathway: pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Pharmacogenet Genom 23(4):236
Schmid M, Freudenmann R, Keller F, Connemann B, Hiemke C, Gahr M, Kratzer W, Fuchs M, Schoenfeldt-Lecuona C (2013) Non-fatal and fatal liver failure associated with valproic acid. Pharmacopsychiatry 46(02):63–68
Nazmy EA, El-Khouly OA, Atef H, Said E (2017) Sulforaphane protects against sodium valproate–induced acute liver injury. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 95(4):420–426
Chang TK, Abbott FS (2006) Oxidative stress as a mechanism of valproic acid-associated hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab Rev 38(4):627–639
Jin J, Xiong T, Hou X, Sun X, Liao J, Huang Z, Zhao Z (2014) Role of Nrf2 activation and NF-κB inhibition in valproic acid induced hepatotoxicity and in diammonium glycyrrhizinate induced protection in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 73:95–104
Linkermann A, Green DR (2014) Necroptosis. N Engl J Med 370(5):455–465
Seo M-J, Hong J-M, Kim S-J, Lee S-M (2017) Genipin protects d-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatic injury through suppression of the necroptosis-mediated inflammasome signaling. Eur J Pharmacol 812:128–137
Schneider P, Tschopp J (2000) Apoptosis induced by death receptors. Pharmacochem Libr 31:281–286
Lourenco R, Camilo M (2002) Taurine: a conditionally essential amino acid in humans? An overview in health and disease. Nutr Hosp 17(6):262–270
Santangelo F (2002) The regulation of sulphurated amino acid junctionsFact or fiction in the field of inflammation? Amino Acids 23(4):359–365
Kim C, Cha Y-N (2014) Taurine chloramine produced from taurine under inflammation provides anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective effects. Amino Acids 46(1):89–100
Devi SL, Anuradha C (2010) Mitochondrial damage, cytotoxicity and apoptosis in iron-potentiated alcoholic liver fibrosis: amelioration by taurine. Amino Acids 38(3):869–879
Marcinkiewicz J, Kontny E (2014) Taurine and inflammatory diseases. Amino Acids 46(1):7–20
Karamikhah R, Jamshidzadeh A, Azarpira N, Saeedi A, Heidari R (2015) Propylthiouracil-induced liver injury in mice and the protective role of taurine. Pharm Sci 21(2):94–101
Saleh AAS, Shahin MI, Kelada NA (2017) Hepatoprotective effect of taurine and coenzyme Q10 and their combination against acrylamide-induced oxidative stress in rats. Trop J Pharm Res 16(8):1849–1855
Kim S-J, Lee S-M (2017) Necrostatin-1 protects against D-Galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatic injury by preventing TLR4 and RAGE signaling. Inflammation 40(6):1912–1923
Najafi N, Jamshidzadeh A, Fallahzadeh H, Omidi M, Abdoli N, Najibi A, Azarpira N, Heidari R, Niknahad H (2017) Valproic acid-induced hepatotoxicity and the protective role of thiol reductants. Trends Pharm Sci 3(2):63–70
Tong V, Teng XW, Chang TK, Abbott FS (2005) Valproic acid I: time course of lipid peroxidation biomarkers, liver toxicity, and valproic acid metabolite levels in rats. Toxicol Sci 86(2):427–435
Sokmen BB, Tunali S, Yanardag R (2012) Effects of vitamin U (S-methyl methionine sulphonium chloride) on valproic acid induced liver injury in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 50(10):3562–3566
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82(1):70–77
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–310
Shaaban AA, El-Agamy DS (2017) Cytoprotective effects of diallyl trisulfide against valproate-induced hepatotoxicity: new anticonvulsant strategy. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 390(9):919–928
Al-Amoudi WM (2017) Protective effects of fennel oil extract against sodium valproate-induced hepatorenal damage in albino rats. Saudi J Biol Sci 24(4):915–924
Abd El Latif EA, Sanad RA, Abdallah OM, Ismail YM (2015) Protective effect of Nigella sativa against cerebral ischemia and sodium valproate-induced hepatotoxicity. Benha Med J 32(1):41
Nagai K, Fukuno S, Oda A, Konishi H (2016) Protective effects of taurine on doxorubicin-induced acute hepatotoxicity through suppression of oxidative stress and apoptotic responses. Anticancer Drugs 27(1):17–23
Abdel-Moneim AM, Al-Kahtani MA, El-Kersh MA, Al-Omair MA (2015) Free radical-scavenging, anti-inflammatory/anti-fibrotic and hepatoprotective actions of taurine and silymarin against CCl4 induced rat liver damage. PLoS ONE 10(12):e0144509
Rashid K, Das J, Sil PC (2013) Taurine ameliorate alloxan induced oxidative stress and intrinsic apoptotic pathway in the hepatic tissue of diabetic rats. Food Chem Toxicol 51:317–329
Wu G, Yang J, Lv H, Jing W, Zhou J, Feng Y, Lin S, Yang Q, Hu J (2018) Taurine prevents ethanol-induced apoptosis mediated by mitochondrial or death receptor pathways in liver cells. Amino Acids 50(7):863–875
Abdelkader NF, Elyamany M, Gad AM, Assaf N, Fawzy HM, Elesawy WH (2020) Ellagic acid attenuates liver toxicity induced by valproic acid in rats. J Pharmacol Sci 143(1):23–29
Oztopuz O, Turkon H, Buyuk B, Coskun O, Sehitoglu MH, Ovali MA, Uzun M (2020) Melatonin ameliorates sodium valproate-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Mol Bio Rep 47(1):317–325
Zhang F, Mao Y, Qiao H, Jiang H, Zhao H, Chen X, Tong L, Sun X (2010) Protective effects of taurine against endotoxin-induced acute liver injury after hepatic ischemia reperfusion. Amino Acids 38(1):237–245
Antosiewicz J, Ziolkowski W, Kaczor JJ, Herman-Antosiewicz A (2007) Tumor necrosis factor-α-induced reactive oxygen species formation is mediated by JNK1-dependent ferritin degradation and elevation of labile iron pool. Free Radic Biol Med 43(2):265–270
Ventura J-J, Cogswell P, Flavell RA, Baldwin AS, Davis RJ (2004) JNK potentiates TNF-stimulated necrosis by increasing the production of cytotoxic reactive oxygen species. Genes Dev 18(23):2905–2915
Liu Y, Liu T, Lei T, Zhang D, Du S, Girani L, Qi D, Lin C, Tong R, Wang Y (2019) RIP1/RIP3-regulated necroptosis as a target for multifaceted disease therapy. Int J Mol Med 44(3):771–786
Shirley S, Morizot A, Micheau O (2011) Regulating TRAIL receptor-induced cell death at the membrane: a deadly discussion. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov 6(3):311–323
Schwabe RF, Luedde T (2018) Apoptosis and necroptosis in the liver: a matter of life and death. Nat Rev Gastroenterol 15(12):738–752
Lee EW, Seo JH, Jeong MH, Lee SS, Song JW (2014) Invited mini review: the roles of FADD in extrinsic apoptosis and necroptosis. BMB Rep 45(9):496–508
Duprez L, Takahashi N, Van Hauwermeiren F, Vandendriessche B, Goossens V, Berghe TV, Declercq W, Libert C, Cauwels A, Vandenabeele P (2011) RIP kinase-dependent necrosis drives lethal systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Immunity 35(6):908–918
Ramachandran A, McGill MR, Xie Y, Ni HM, Ding WX, Jaeschke H (2013) Receptor interacting protein kinase 3 is a critical early mediator of acetaminophen-induced hepatocyte necrosis in mice. Hepatology 58(6):2099–2108
Ni H-M, Chao X, Kaseff J, Deng F, Wang S, Shi Y-H, Li T, Ding WX, Jaeschke H (2019) Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 (RIPK3)–mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL)–mediated necroptosis contributes to ischemia-reperfusion injury of steatotic livers. Am J Pathol 189(7):1363–1374
Bollino D, Balan I, Aurelian L (2015) Valproic acid induces neuronal cell death through a novel calpain-dependent necroptosis pathway. J Neurochem 133(2):174–186
Zhou Y, Dai W, Lin C, Wang F, He L, Shen M, Chen P, Wang C, Lu J, Xu L, Xu X (2013) Protective effects of necrostatin-1 against concanavalin A-induced acute hepatic injury in mice. Mediat Inflamm 2013:706156
Lin B, Jin Z, Chen X, Zhao L, Weng C, Chen B, Tang Y, Lin L (2020) Necrostatin-1 protects mice from acute lung injury by suppressing necroptosis and reactive oxygen species. Mol Med Rep 21(5):2171–2181
Takemoto K, Hatano E, Iwaisako K, Takeiri M, Noma N, Ohmae S, Toriguchi K, Tanabe K, Tanaka H, Seo S, Taura K (2014) Necrostatin-1 protects against reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced hepatotoxicity in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. FEBS Open Bio 4:777–787
Lin CY, Chang TW, Hsieh WH, Hung MC, Lin IH, Lai SC, Tzeng YJ (2016) Simultaneous induction of apoptosis and necroptosis by Tanshinone IIA in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Cell Death Discov 2(1):1–1
Li S, Yang L, Dong G, Wang X (2017) Taurine protects mouse liver against arsenic-induced apoptosis through JNK pathway. Adv Exp Med Biol 10:855–862
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This work is related to the thesis of HA and was granted (MPRC-9721) by the Medicinal Plant Research Center of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khodayar, M.J., Kalantari, H., Khorsandi, L. et al. Taurine attenuates valproic acid-induced hepatotoxicity via modulation of RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL-mediated necroptosis signaling in mice. Mol Biol Rep 48, 4153–4162 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06428-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06428-4