Abstract
Chronic liver diseases are attributed to liver injury. Development of fibrosis from chronic liver diseases is a dynamic process that involves multiple molecular and cellular processes. As the first to be impacted by injury, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) are involved in the pathogenesis of liver diseases caused by a variety of etiologies. Moreover, capillarization of LSECs has been recognized as an important event in the development of chronic liver diseases and fibrosis. Studies have reported that various cytokines (such as vascular endothelial growth factor, transforming growth factor-β), and pathways (such as hedgehog, and Notch), as well as epigenetic and metabolic factors are involved in the development of LSEC-mediated liver fibrosis. This review describes the complexity and plasticity of LSECs in fibrotic liver diseases from several perspectives, including the cross-talk between LSECs and other intra-hepatic cells. Moreover, it summarizes the mechanisms of several kinds of LSECs-targeting anti-fibrosis chemicals, and provides a theoretical basis for future studies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Poisson J, Lemoinne S, Boulanger C et al (2017) Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: physiology and role in liver diseases. J Hepatol 66(1):212–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2016.07.009
Steffan AM, Gendrault JL, McCuskey RS, McCuskey PA, Kirn A (1986) Phagocytosis, an unrecognized property of murine endothelial liver cells. Hepatology 6(5):830–836
Wilkinson AL, Qurashi M, Shetty S (2020) The role of sinusoidal endothelial cells in the axis of inflammation and cancer within the liver. Front Physiol 11:990. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.00990
Liu L, You Z, Yu H et al (2017) Mechanotransduction-modulated fibrotic microniches reveal the contribution of angiogenesis in liver fibrosis. Nat Mater 16(12):1252–1261. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat5024
Xie G, Wang X, Wang L et al. Role of differentiation of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in progression and regression of hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gastroenterology. 2012;142(4). doi:https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.017.
Leo CH, Jelinic M, Ng HH et al (2017) Vascular actions of relaxin: nitric oxide and beyond. Br J Pharmacol 174(10):1002–1014. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13614
Yan Z, Qu K, Zhang J et al (2015) CD147 promotes liver fibrosis progression via VEGF-A/VEGFR2 signalling-mediated cross-talk between hepatocytes and sinusoidal endothelial cells. Clin Sci (Lond) 129(8):699–710. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20140823
Kantari-Mimoun C, Castells M, Klose R et al (2015) Resolution of liver fibrosis requires myeloid cell-driven sinusoidal angiogenesis. Hepatology (Baltimore, MD) 61(6):2042–2055. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.27635
Shi M, Zhu J, Wang R et al (2011) Latent TGF-β structure and activation. Nature 474(7351):343–349. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10152
Henderson NC, Arnold TD, Katamura Y et al (2013) Targeting of αv integrin identifies a core molecular pathway that regulates fibrosis in several organs. Nat Med 19(12):1617–1624. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3282
Sakata K, Eda S, Lee E-S, Hara M, Imoto M, Kojima S (2014) Neovessel formation promotes liver fibrosis via providing latent transforming growth factor-β. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 443(3):950–956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.12.074
Caja L, Dituri F, Mancarella S et al (2018) TGF-β and the tissue microenvironment: relevance in fibrosis and cancer. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051294
Pardali E, Sanchez-Duffhues G, Gomez-Puerto MC, Ten Dijke P (2017) TGF-β-induced endothelial-mesenchymal transition in fibrotic diseases. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102157
Ribera J, Pauta M, Melgar-Lesmes P et al (2017) A small population of liver endothelial cells undergoes endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in response to chronic liver injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 313(5):G492–G504. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00428.2016
Tillet E, Ouarné M, Desroches-Castan A et al (2018) A heterodimer formed by bone morphogenetic protein 9 (BMP9) and BMP10 provides most BMP biological activity in plasma. J Biol Chem 293(28):10963–10974. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.002968
Breitkopf-Heinlein K, Meyer C, König C et al (2017) BMP-9 interferes with liver regeneration and promotes liver fibrosis. Gut 66(5):939–954. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313314
Desroches-Castan A, Tillet E, Ricard N et al (2019) Bone morphogenetic protein 9 is a paracrine factor controlling liver sinusoidal endothelial cell fenestration and protecting against hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology (Baltimore, MD) 70(4):1392–1408. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30655
Gaitantzi H, Karch J, Germann L et al (2020) BMP-9 modulates the hepatic responses to LPS. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030617
Maretti-Mira AC, Wang X, Wang L, DeLeve LD (2019) Incomplete differentiation of engrafted bone marrow endothelial progenitor cells initiates hepatic fibrosis in the rat. Hepatology 69(3):1259–1272. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30227
Kaur S, Tripathi D, Dongre K et al (2012) Increased number and function of endothelial progenitor cells stimulate angiogenesis by resident liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (SECs) in cirrhosis through paracrine factors. J Hepatol 57(6):1193–1198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2012.07.016
Choi SS, Omenetti A, Syn W-K, Diehl AM (2011) The role of Hedgehog signaling in fibrogenic liver repair. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43(2):238–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2010.10.015
Pereira TA, Xie G, Choi SS et al (2013) Macrophage-derived Hedgehog ligands promotes fibrogenic and angiogenic responses in human schistosomiasis mansoni. Liver Int 33(1):149–161. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.12016
Witek RP, Yang L, Liu R et al (2009) Liver cell-derived microparticles activate hedgehog signaling and alter gene expression in hepatic endothelial cells. Gastroenterology. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2008.09.066
Xie G, Choi SS, Syn W-K et al (2013) Hedgehog signalling regulates liver sinusoidal endothelial cell capillarisation. Gut 62(2):299–309. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301494
Dill MT, Rothweiler S, Djonov V et al (2012) Disruption of Notch1 induces vascular remodeling, intussusceptive angiogenesis, and angiosarcomas in livers of mice. Gastroenterology. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.052
Duan J-L, Ruan B, Yan X-C et al (2018) Endothelial Notch activation reshapes the angiocrine of sinusoidal endothelia to aggravate liver fibrosis and blunt regeneration in mice. Hepatology 68(2):677–690. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29834
Shen Z, Liu Y, Dewidar B et al (2016) Delta-like ligand 4 modulates liver damage by down-regulating chemokine expression. Am J Pathol 186(7):1874–1889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.03.010
Chen L, Gu T, Li B et al (2019) Delta-like ligand 4/DLL4 regulates the capillarization of liver sinusoidal endothelial cell and liver fibrogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1866(10):1663–1675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.06.011
Resnick N, Yahav H, Shay-Salit A et al (2003) Fluid shear stress and the vascular endothelium: for better and for worse. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 81(3):177–199
Yoshizumi M, Abe J-I, Tsuchiya K, Berk BC, Tamaki T (2003) Stress and vascular responses: atheroprotective effect of laminar fluid shear stress in endothelial cells: possible role of mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Pharmacol Sci 91(3):172–176
Kumar A, Lin Z, SenBanerjee S, Jain MK (2005) Tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated reduction of KLF2 is due to inhibition of MEF2 by NF-kappaB and histone deacetylases. Mol Cell Biol 25(14):5893–5903
Gracia-Sancho J, Russo L, García-Calderó H, García-Pagán JC, García-Cardeña G, Bosch J (2011) Endothelial expression of transcription factor Kruppel-like factor 2 and its vasoprotective target genes in the normal and cirrhotic rat liver. Gut 60(4):517–524. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2010.220913
Marrone G, Maeso-Díaz R, García-Cardena G et al (2015) KLF2 exerts antifibrotic and vasoprotective effects in cirrhotic rat livers: behind the molecular mechanisms of statins. Gut 64(9):1434–1443. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308338
Zeng X-Q, Li N, Pan D-Y et al (2015) Kruppel-like factor 2 inhibit the angiogenesis of cultured human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells through the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 464(4):1241–1247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.07.113
Natarajan V, Harris EN, Kidambi S (2017) SECs (sinusoidal endothelial cells), liver microenvironment, and fibrosis. Biomed Res Int 2017:4097205. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4097205
Hilscher MB, Sehrawat T, Arab JP et al (2019) Mechanical stretch increases expression of CXCL1 in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells to recruit neutrophils, generate sinusoidal microthombi, and promote portal hypertension. Gastroenterology. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2019.03.013
Maher JJ, McGuire RF (1990) Extracellular matrix gene expression increases preferentially in rat lipocytes and sinusoidal endothelial cells during hepatic fibrosis in vivo. J Clin Invest 86(5):1641–1648
Neubauer K, Krüger M, Quondamatteo F, Knittel T, Saile B, Ramadori G (1999) Transforming growth factor-beta1 stimulates the synthesis of basement membrane proteins laminin, collagen type IV and entactin in rat liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. J Hepatol 31(4):692–702
Juin A, Planus E, Guillemot F et al (2013) Extracellular matrix rigidity controls podosome induction in microvascular endothelial cells. Biol Cell 105(1):46–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/boc.201200037
Marrone G, Shah VH, Gracia-Sancho J (2016) Sinusoidal communication in liver fibrosis and regeneration. J Hepatol 65(3):608–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2016.04.018
Hammoutene A, Biquard L, Lasselin J et al (2020) A defect in endothelial autophagy occurs in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and promotes inflammation and fibrosis. J Hepatol 72(3):528–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2019.10.028
Hernández-Gea V, Ghiassi-Nejad Z, Rozenfeld R et al (2012) Autophagy releases lipid that promotes fibrogenesis by activated hepatic stellate cells in mice and in human tissues. Gastroenterology 142(4):938–946. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.044
Ruart M, Chavarria L, Campreciós G et al (2019) Impaired endothelial autophagy promotes liver fibrosis by aggravating the oxidative stress response during acute liver injury. J Hepatol 70(3):458–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.10.015
Guixé-Muntet S, de Mesquita FC, Vila S et al (2017) Cross-talk between autophagy and KLF2 determines endothelial cell phenotype and microvascular function in acute liver injury. J Hepatol 66(1):86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2016.07.051
Miyao M, Kotani H, Ishida T et al (2015) Pivotal role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in NAFLD/NASH progression. Lab Invest 95(10):1130–1144. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2015.95
Hammoutene A, Rautou P-E (2019) Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol 70(6):1278–1291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2019.02.012
Cogger VC, Mohamad M, Solon-Biet SM et al (2016) Dietary macronutrients and the aging liver sinusoidal endothelial cell. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 310(9):H1064–H1070. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00949.2015
Pourhoseini S, Seth RK, Das S et al (2015) Upregulation of miR21 and repression of Grhl3 by leptin mediates sinusoidal endothelial injury in experimental nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. PLoS ONE 10(2):e0116780. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0116780
Wang BY, Ju XH, Fu BY, Zhang J, Cao YX (2005) Effects of ethanol on liver sinusoidal endothelial cells-fenestrae of rats. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 4(3):422–426
Witte MH, Borgs P, Way DL, Ramirez G, Bernas MJ, Witte CL (1992) Alcohol, hepatic sinusoidal microcirculation, and chronic liver disease. Alcohol 9(6):473–480
Deaciuc D, Fortunato H, Sarphie McClain (2001) Alcohol-induced sinusoidal endothelial cell dysfunction in the mouse is associated with exacerbated liver apoptosis and can be reversed by caspase inhibition. Hepatol Res 19(1):85–97
Miller AM, Wang H, Park O et al (2010) Anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic roles of endothelial cell STAT3 in alcoholic liver injury. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34(4):719–725. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2009.01141.x
McCuskey RS, Bethea NW, Wong J et al (2005) Ethanol binging exacerbates sinusoidal endothelial and parenchymal injury elicited by acetaminophen. J Hepatol 42(3):371–377
Maeso-Díaz R, Ortega-Ribera M, Fernández-Iglesias A et al (2018) Effects of aging on liver microcirculatory function and sinusoidal phenotype. Aging Cell 17(6):e12829. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12829
Ito Y, Sørensen KK, Bethea NW et al (2007) Age-related changes in the hepatic microcirculation in mice. Exp Gerontol 42(8):789–797
Yeligar S, Tsukamoto H, Kalra VK (2009) Ethanol-induced expression of ET-1 and ET-BR in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and human endothelial cells involves hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and microrNA-199. J Immunol 183(8):5232–5243. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0901084
Wang Q, Zhang F, Lei Y, Liu P, Liu C, Tao Y (2020) microRNA-322/424 promotes liver fibrosis by regulating angiogenesis through targeting CUL2/HIF-1α pathway. Life Sci 266:118819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118819
Zhu A, Chu L, Ma Q, Li Y (2018) WITHDRAWN: Long non-coding RNA H19 promotes angiogenesis in microvascular endothelial cells by down-regulating miR-181a. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.08.091
Ye Y, Shen A, Liu A (2019) Long non-coding RNA H19 and cancer: a competing endogenous RNA. Bull Cancer 106(12):1152–1159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bulcan.2019.08.011
Zhu Y, Ni T, Lin J, Zhang C, Zheng L, Luo M (2019) Long non-coding RNA H19, a negative regulator of microRNA-148b-3p, participates in hypoxia stress in human hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells via NOX4 and eNOS/NO signaling. Biochimie 163:128–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2019.04.006
Guo C, Qi Y, Qu J, Gai L, Shi Y, Yuan C (2020) Pathophysiological functions of the lncRNA TUG1. Curr Pharm Des 26(6):688–700. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612826666191227154009
Zhang R, Huang X-Q, Jiang Y-Y, Li N, Wang J, Chen S-Y (2020) LncRNA TUG1 regulates autophagy-mediated endothelial-mesenchymal transition of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells by sponging miR-142-3p. Am J Transl Res 12(3):758–772
Shao J, Xu Y, Fang M (2020) BRG1 deficiency in endothelial cells alleviates thioacetamide induced liver fibrosis in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 521(1):212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.10.109
Sun L-J, Yu J-W, Shi Y-G, Zhang X-Y, Shu M-N, Chen M-Y (2018) Hepatitis C virus core protein induces dysfunction of liver sinusoidal endothelial cell by down-regulation of silent information regulator 1. J Med Virol 90(5):926–935. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25034
Verbeke L, Farre R, Trebicka J et al (2014) Obeticholic acid, a farnesoid X receptor agonist, improves portal hypertension by two distinct pathways in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 59(6):2286–2298. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26939
Verbeke L, Mannaerts I, Schierwagen R et al (2016) FXR agonist obeticholic acid reduces hepatic inflammation and fibrosis in a rat model of toxic cirrhosis. Sci Rep 6:33453. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep33453
Schwabl P, Hambruch E, Seeland BA et al (2017) The FXR agonist PX20606 ameliorates portal hypertension by targeting vascular remodelling and sinusoidal dysfunction. J Hepatol 66(4):724–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2016.12.005
Xing Y, Zhao T, Gao X, Wu Y (2016) Liver X receptor α is essential for the capillarization of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in liver injury. Sci Rep 6:21309. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21309
Baiocchini A, Del Nonno F, Taibi C et al (2019) Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) modifications in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Sci Rep 9(1):8760. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45114-1
Tsai H-C, Li T-H, Huang C-C et al (2018) Beneficial effects of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α/γ agonist aleglitazar on progressive hepatic and splanchnic abnormalities in cirrhotic rats with portal hypertension. Am J Pathol 188(7):1608–1624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.03.018
Boyer-Diaz Z, Aristu-Zabalza P, Andrés-Rozas M et al (2020) Pan-PPAR agonist lanifibranor improves portal hypertension and hepatic fibrosis in experimental advanced chronic liver disease. J Hepatol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2020.11.045
Ding B-S, Liu CH, Sun Y et al (2016) HDL activation of endothelial sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-1 (S1P) promotes regeneration and suppresses fibrosis in the liver. JCI insight 1(21):e87058. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.87058
Keitel V, Reinehr R, Gatsios P et al (2007) The G-protein coupled bile salt receptor TGR5 is expressed in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Hepatology 45(3):695–704
Klindt C, Reich M, Hellwig B et al (2019) The G protein-coupled bile acid receptor TGR5 (Gpbar1) modulates endothelin-1 signaling in liver. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8111467
Schmid CD, Schledzewski K, Mogler C et al (2018) GPR182 is a novel marker for sinusoidal endothelial differentiation with distinct GPCR signaling activity in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 497(1):32–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.01.185
Liu D, Chen J, Wang J et al (2010) Increased expression of urotensin II and GPR14 in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Int J Mol Med 25(6):845–851
Wang R, Ding Q, Yaqoob U et al (2015) Exosome adherence and internalization by hepatic stellate cells triggers sphingosine 1-phosphate-dependent migration. J Biol Chem 290(52):30684–30696. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.671735
Hong F, Tuyama A, Lee TF et al (2009) Hepatic stellate cells express functional CXCR4: role in stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha-mediated stellate cell activation. Hepatology 49(6):2055–2067. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.22890
Liu Y, Yang X, Jing Y et al (2015) Contribution and mobilization of mesenchymal stem cells in a mouse model of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis. Sci Rep 5:17762. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17762
Liepelt A, Tacke F (2016) Stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) as a target in liver diseases. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 311(2):G203–G209. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00193.2016
Ramirez-Pedraza M, Fernández M (2019) Interplay between macrophages and angiogenesis: a double-edged sword in liver disease. Front Immunol 10:2882. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02882
Wu M-H, Chen Y-L, Lee K-H et al (2017) Glycosylation-dependent galectin-1/neuropilin-1 interactions promote liver fibrosis through activation of TGF-β- and PDGF-like signals in hepatic stellate cells. Sci Rep 7(1):11006. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11212-1
Semela D, Das A, Langer D, Kang N, Leof E, Shah V (2008) Platelet-derived growth factor signaling through ephrin-b2 regulates hepatic vascular structure and function. Gastroenterology 135(2):671–679. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2008.04.010
Venkatraman L, Tucker-Kellogg L (2013) The CD47-binding peptide of thrombospondin-1 induces defenestration of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Liver Int 33(9):1386–1397. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.12231
Lao Y, Li Y, Zhang P et al (2018) Targeting endothelial Erk1/2-Akt axis as a regeneration strategy to bypass fibrosis during chronic liver injury in mice. Mol Ther 26(12):2779–2797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.08.016
Rautou P-E, Bresson J, Sainte-Marie Y et al (2012) Abnormal plasma microparticles impair vasoconstrictor responses in patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2012.03.040
Tegge AN, Rodrigues RR, Larkin AL, Vu L, Murali TM, Rajagopalan P (2018) Transcriptomic analysis of hepatic cells in multicellular organotypic liver models. Sci Rep 8(1):11306. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-29455-x
Lafoz E, Ruart M, Anton A, Oncins A, Hernández-Gea V (2020) The endothelium as a driver of liver fibrosis and regeneration. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040929
Ford AJ, Jain G, Rajagopalan P (2015) Designing a fibrotic microenvironment to investigate changes in human liver sinusoidal endothelial cell function. Acta Biomater 24:220–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2015.06.028
Abraldes JG, Rodríguez-Vilarrupla A, Graupera M et al (2007) Simvastatin treatment improves liver sinusoidal endothelial dysfunction in CCl4 cirrhotic rats. J Hepatol 46(6):1040–1046
Bravo M, Raurell I, Hide D et al (2019) Restoration of liver sinusoidal cell phenotypes by statins improves portal hypertension and histology in rats with NASH. Sci Rep 9(1):20183. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-56366-2
Hu L, Su L, Dong Z et al (2019) AMPK agonist AICAR ameliorates portal hypertension and liver cirrhosis via NO pathway in the BDL rat model. J Mol Med (Berl) 97(3):423–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-019-01746-4
Hunt NJ, Lockwood GP, Kang SWS et al (2020) The effects of metformin on age-related changes in the liver sinusoidal endothelial cell. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 75(2):278–285. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glz153
Kong L-J, Li H, Du Y-J et al (2017) Vatalanib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, decreases hepatic fibrosis and sinusoidal capillarization in CCl4-induced fibrotic mice. Mol Med Rep 15(5):2604–2610. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6325
Piguet A-C, Majumder S, Maheshwari U et al (2014) Everolimus is a potent inhibitor of activated hepatic stellate cell functions in vitro and in vivo, while demonstrating anti-angiogenic activities. Clin Sci (Lond) 126(11):775–784. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20130081
Ling L, Li G, Meng D, Wang S, Zhang C (2018) Carvedilol ameliorates intrahepatic angiogenesis, sinusoidal remodeling and portal pressure in cirrhotic rats. Med Sci Monit 24:8290–8297. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.913118
Wu Y, Li Z, Xiu A-Y, Meng D-X, Wang S-N, Zhang C-Q (2019) Carvedilol attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis and hepatic sinusoidal capillarization in mice. Drug Des Dev Ther 13:2667–2676. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S210797
Di Martino J, Mascalchi P, Legros P et al (2019) Actin depolymerization in dedifferentiated liver sinusoidal endothelial cells promotes fenestrae re-formation. Hepatol Commun 3(2):213–219. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep4.1301
Bi Y, Mukhopadhyay D, Drinane M et al (2014) Endocytosis of collagen by hepatic stellate cells regulates extracellular matrix dynamics. Am J Physiol, Cell Physiol 307(7):C622–C633. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00086.2014
Funding
This manuscript is supported by no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11033_2021_6269_MOESM1_ESM.png
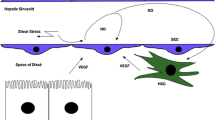
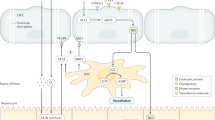
Supplementary Fig. 1 The LSECs-HSCs cross-talk and changes of markers in Normal or Fibrotic Livers. Several cytokines and pathways are involved in the cross-talk between LSECs and HSCs. ECM, extracellular matrix; ET-1, endothelin-1; NO, nitric oxide; KLF2, Kruppel-like factor 2; PDGF, Platelet derived growth factor; SDF-1, stromal cell derived factor 1; SK-1, sphingosine kinase-1; S1P, sphingosine 1-phosphate; TSP-1, thrombospondin-1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor. (PNG 218 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, H., Liu, X., Zhang, M. et al. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells are implicated in multiple fibrotic mechanisms. Mol Biol Rep 48, 2803–2815 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06269-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06269-1