Abstract
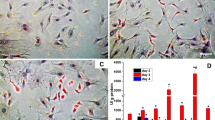
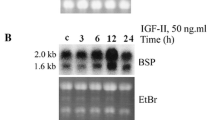
The aim of this study was to explore the effect of lactoferrin (LF) in primary fetal rat osteoblasts proliferation and differentiation and investigate the underlying molecular mechanisms. Primary rat osteoblasts were obtained from the calvarias of neonatal rats. Osteoblasts were treated with LF (0.1–1000 μg/mL), or OSI-906 [a selective inhibitor of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) receptor and insulin receptor]. The IGF-1 was then knocked down by small hairpin RNA (shRNA) technology and then was treated with recombinant human IGF-1 or LF. Cell proliferation and differentiation were measured by MTT assay and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) assay, respectively. The expression of IGF-1 and IGF binding protein 2 (IGFBP2) mRNA were analyzed using real-time PCR. LF promotes the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts in a certain range (1–100 μg/mL) in time- and dose-dependent manner. The mRNA level of IGF-1 was significantly increased, while the expression of IGFBP2 was suppressed by LF treatment. Knockdown of IGF-1 by shRNA in primary rat osteoblast dramatically decreased the abilities of proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts and blocked the proliferation and differentiation effect of LF in osteoblasts. OSI906 (5 μM) blocked the mitogenic and differentiation of LF in osteoblasts. Proliferation and differentiation of primary rat osteoblasts in response to LF are mediated in part by stimulating of IGF-1 gene expression and alterations in the gene expression of IGFBP2.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Metz-Boutigue MH, Jolles J, Mazurier J, Schoentgen F, Legrand D, Spik G, Montreuil J, Jolles P (1984) Human lactotransferrin: amino acid sequence and structural comparisons with other transferrins. Eur J Biochem 145(3):659–676
Lönnerdal B, Iyer S (1995) Lactoferrin: molecular structure and biological function. Annu Rev Nutr 15(1):93–110
Dinauer MC, Lekstrom-Himes JA, Dale DC (2000) Inherited neutrophil disorders molecular basis and new therapies, vol 1. ASH Education Program Book, pp 303–318
Weinberg ED (2001) Human lactoferrin: a novel therapeutic with broad spectrum potential. J Pharm Pharmacol 53(10):1303–1310
Frydecka I, Zimecki M, Bocko D, Kosmaczewska A, Teodorowska R, Ciszak L, Kruzel M, Wlodarska-Polinska J, Kuliczkowski K, Kornafel J (2002) Lactoferrin-induced up-regulation of zeta (ζ) chain expression in peripheral blood T lymphocytes from cervical cancer patients. Anticancer Res 22(3):1897–1901
Ieni A, Barresi V, Grosso M, Rosa MA, Tuccari G (2009) Lactoferrin immuno-expression in human normal and neoplastic bone tissue. J Bone Miner Metab 27(3):364–371
Ieni A, Barresi V, Grosso M, Speciale G, Rosa MA, Tuccari G (2011) Does lactoferrin behave as an immunohistochemical oncofetal marker in bone and cartilage human neoplasms? Pathol Oncol Res 17(2):287–293
Cornish J, Callon KE, Naot D, Palmano KP, Banovic T, Bava U, Watson M, Lin J-M, Tong P, Chen Q (2004) Lactoferrin is a potent regulator of bone cell activity and increases bone formation in vivo. Endocrinology 145(9):4366–4374
Lorget F, Clough J, Oliveira M, Daury M-C, Sabokbar A, Offord E (2002) Lactoferrin reduces in vitro osteoclast differentiation and resorbing activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 296(2):261–266
Blais A, Malet A, Mikogami T, Martin-Rouas C, Tomé D (2009) Oral bovine lactoferrin improves bone status of ovariectomized mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 296(6):E1281–E1288
Grey A, Zhu Q, Watson M, Callon K, Cornish J (2006) Lactoferrin potently inhibits osteoblast apoptosis, via an LRP1-independent pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol 251(1):96–102
Guo HY, Jiang L, Ibrahim SA, Zhang L, Zhang H, Zhang M, Ren FZ (2009) Orally administered lactoferrin preserves bone mass and microarchitecture in ovariectomized rats. J Nutr 139(5):958–964
Cornish J (2004) Lactoferrin promotes bone growth. Biometals 17(3):331–335
Takayama Y, Mizumachi K (2008) Effect of bovine lactoferrin on extracellular matrix calcification by human osteoblast-like cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72(1):226–230
Takayama Y, Mizumachi K (2009) Effect of lactoferrin-embedded collagen membrane on osteogenic differentiation of human osteoblast-like cells. J Biosci Bioeng 107(2):191–195
Bharadwaj S, Naidu A, Betageri G, Prasadarao N, Naidu A (2009) Milk ribonuclease-enriched lactoferrin induces positive effects on bone turnover markers in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int 20(9):1603–1611
Grey A, Banovic T, Zhu Q, Watson M, Callon K, Palmano K, Ross J, Naot D, Reid IR, Cornish J (2004) The low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 is a mitogenic receptor for lactoferrin in osteoblastic cells. Mol Endocrinol 18(9):2268–2278
Amini AA, Nair LS (2011) Lactoferrin: a biologically active molecule for bone regeneration. Curr Med Chem 18(8):1220–1229
Nakajima K-I, Kanno Y, Nakamura M, Gao X-D, Kawamura A, Itoh F, Ishisaki A (2011) Bovine milk lactoferrin induces synthesis of the angiogenic factors VEGF and FGF2 in osteoblasts via the p44/p42 MAP kinase pathway. Biometals 24(5):847–856
Naot D, Grey A, Reid IR, Cornish J (2005) Lactoferrin—a novel bone growth factor. Clin Med Res 3(2):93–101
Cornish J, Naot D (2010) Lactoferrin as an effector molecule in the skeleton. Biometals 23(3):425–430
Naot D, Chhana A, Matthews BG, Callon KE, Tong PC, Lin J-M, Costa JL, Watson M, Grey AB, Cornish J (2011) Molecular mechanisms involved in the mitogenic effect of lactoferrin in osteoblasts. Bone 49(2):217–224
Grey A, Chen Q, Xu X, Callon K, Cornish J (2003) Parallel phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways subserve the mitogenic and antiapoptotic actions of insulin-like growth factor I in osteoblastic cells. Endocrinology 144(11):4886–4893
Govoni KE, Baylink DJ, Mohan S (2005) The multi-functional role of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in bone. Pediatr Nephrol 20(3):261–268
Jurgens WJ, Oedayrajsingh-Varma MJ, Helder MN, ZandiehDoulabi B, Schouten TE, Kuik DJ, Ritt MJ, van Milligen FJ (2008) Effect of tissue-harvesting site on yield of stem cells derived from adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Cell Tissue Res 332(3):415–426
Yamashita M, Ying S-X, Zhang G-M, Li C, Cheng SY, Deng C-X, Zhang YE (2005) Ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 controls osteoblast activity and bone homeostasis by targeting MEKK2 for degradation. Cell 121(1):101–113
Hansen BH, Altin D, Vang S-H, Nordtug T, Olsen AJ (2008) Effects of naphthalene on gene transcription in Calanus finmarchicus (Crustacea: Copepoda). Aquat Toxicol 86(2):157–165
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods (San Diego, Calif) 25(4):402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Hou J-M, Xue Y, Lin Q-M (2012) Bovine lactoferrin improves bone mass and microstructure in ovariectomized rats via OPG/RANKL/RANK pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33(10):1277–1284
Yakar S, Rosen CJ (2003) From mouse to man: redefining the role of insulin-like growth factor-I in the acquisition of bone mass. Exp Biol Med 228(3):245–252
Zhao G, Monier-Faugere M-C, Langub MC, Geng Z, Nakayama T, Pike JW, Chernausek SD, Rosen CJ, Donahue L-R, Malluche HH (2000) Targeted overexpression of insulin-like growth factor I to osteoblasts of transgenic mice: increased trabecular bone volume without increased osteoblast proliferation. Endocrinology 141(7):2674–2682
Bikle D, Majumdar S, Laib A, Powell-Braxton L, Rosen C, Beamer W, Nauman E, Leary C, Halloran B (2001) The skeletal structure of insulin-like growth factor I-deficient mice. J Bone Miner Res 16(12):2320–2329
Mohan S, Kesavan C (2012) Role of insulin-like growth factor-1 in the regulation of skeletal growth. Curr Osteoporos Rep 10(2):178–186
Zhang M, Xuan S, Bouxsein ML, von Stechow D, Akeno N, Faugere MC, Malluche H, Zhao G, Rosen CJ, Efstratiadis A (2002) Osteoblast-specific knockout of the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor gene reveals an essential role of IGF signaling in bone matrix mineralization. J Biol Chem 277(46):44005–44012
Ogata N, Chikazu D, Kubota N, Terauchi Y, Tobe K, Azuma Y, Ohta T, Kadowaki T, Nakamura K, Kawaguchi H (2000) Insulin receptor substrate-1 in osteoblast is indispensable for maintaining bone turnover. J Clin Investig 105(7):935–943
Yakar S, Courtland HW, Clemmons D (2010) IGF-1 and bone: new discoveries from mouse models. J Bone Miner Res 25(12):2543–2552
LeRoith D (2008) Clinical relevance of systemic and local IGF-I: lessons from animal models. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 5:739–743
Bikle DD, Wang Y (2012) Insulin like growth factor-I: a critical mediator of the skeletal response to parathyroid hormone. Curr Mol Pharmacol 5(2):135–142
Hock JM, Centrella M, Canalis E (1988) Insulin-like growth factor I has independent effects on bone matrix formation and cell replication. Endocrinology 122(1):254–260
Mohan S, Baylink D (1996) Insulin-like growth factor system components and the coupling of bone formation to resorption. Horm Res Paediatr 45(Suppl. 1):59–62
Rosen CJ, Donahue LR (1998) Insulin-like growth factors and bone: the osteoporosis connection revisited. In: Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine (New York, NY). Royal Society of Medicine, pp 1–7
Giustina A, Mazziotti G, Canalis E (2008) Growth hormone, insulin-like growth factors, and the skeleton. Endocr Rev 29(5):535–559
Cao JJ, Kurimoto P, Boudignon B, Rosen C, Lima F, Halloran BP (2007) Aging impairs IGF-I receptor activation and induces skeletal resistance to IGF-I. J Bone Miner Res 22(8):1271–1279
Bonewald L, Dallas S (1994) Role of active and latent transforming growth factor β in bone formation. J Cell Biochem 55(3):350–357
Zapf J, Froesch E (1986) Insulin-like growth factors/somatomedins: structure, secretion, biological actions and physiological role. Horm Res Paediatr 24(2–3):121–130
Celil AB, Campbell PG (2005) BMP-2 and insulin-like growth factor-I mediate Osterix (Osx) expression in human mesenchymal stem cells via the MAPK and protein kinase D signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 280(36):31353–31359
Ernst M, Rodan GA (1991) Estradiol regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I expression in osteoblastic cells: evidence for transcriptional control. Mol Endocrinol 5(8):1081–1089
Canalis E, Avioli L (1992) Effects of deflazacort on aspects of bone formation in cultures of intact calvariae and osteoblast-enriched cells. J Bone Miner Res 7(9):1085–1092
Scharla SH, Strong DD, Mohan S, Baylink DJ, Linkhart TA (1991) 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 differentially regulates the production of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein-4 in mouse osteoblasts. Endocrinology 129(6):3139–3146
Fox EM, Miller TW, Balko JM, Kuba MG, Sánchez V, Smith RA, Liu S, González-Angulo AM, Mills GB, Ye F (2011) A kinome-wide screen identifies the insulin/IGF-I receptor pathway as a mechanism of escape from hormone dependence in breast cancer. Cancer Res 71(21):6773–6784
Cortot AB, Repellin CE, Shimamura T, Capelletti M, Zejnullahu K, Ercan D, Christensen JG, Wong K-K, Gray NS, Jänne PA (2013) Resistance to irreversible EGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors through a multistep mechanism involving the IGF1R pathway. Cancer Res 73(2):834–843
Ferry R Jr, Katz L, Grimberg A, Cohen P, Weinzimer S (1999) Cellular actions of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Horm Metab Res 31(02/03):192–202
Baxter RC (2000) Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding proteins: interactions with IGFs and intrinsic bioactivities. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 278(6):E967–E976
Collett-Solberg PF, Cohen P (2000) Genetics, chemistry, and function of the IGF/IGFBP system. Endocrine 12(2):121–136
Jones JI, Clemmons DR (1995) Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr Rev 16(1):3–34
Wetterau LA, Moore MG, Lee K-W, Shim ML, Cohen P (1999) Novel aspects of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Mol Genet Metab 68(2):161–181
Spagnoli A, Hwa V, Horton WA, Lunstrum GP, Roberts CT, Chiarelli F, Torello M, Rosenfeld RG (2001) Antiproliferative effects of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 in mesenchymal chondrogenic cell line RCJ3. 1C5. 18 relationship to differentiation stage. J Biol Chem 276(8):5533–5540
Kream BE, Tetradis S, Lafrancis D, Fall PM, Feyen JH, Raisz LG (1997) Modulation of the effects of glucocorticoids on collagen synthesis in fetal rat calvariae by insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2. J Bone Miner Res 12(6):889–895
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China 81270968.
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jian-ming Hou, Man Wu and Qing-ming Lin are regarded as co-first author.
Jian-ming Hou, Man Wu and Qing-ming Lin contributed equally to this work.
The Publisher and Editor retract this article in accordance with the recommendations of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE). After a thorough investigation we have strong reason to believe that the peer review process was compromised.
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, Jm., Wu, M., Lin, Qm. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Lactoferrin promote primary rat osteoblast proliferation and differentiation via up-regulation of insulin-like growth factor-1 expression. Mol Biol Rep 41, 5019–5030 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3368-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3368-2