Abstract
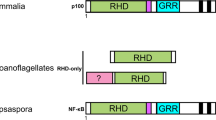
The IκB kinase (IKK) plays a crucial role in activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) by phosphorylating the Inhibitory of NF-κB (IκB), which triggers the subsequent polyubiquitylation and degradation of IκBα through the 26S proteasome. In this study, we reported the cloning of an IKK homologue cDNA (designated as AmphiIKK) from amphioxus, Branchiostoma belcheri. The full-length cDNA consists of 3,087 bp with an ORF that encoded a predicted protein of 777 amino acid residues. The putative amphioxus IKK protein possesses the characteristic organization of the mammalian IKK proteins, which consists of a serine/threonine kinase domain, a leucine zipper motif and a putative helix-loop-helix motif. And the deduced amino acid of AmphiIKK shared 43.8–64.0 % similarity and 23.6–43.3 % identified with the IKKs from other species. Real-time PCR (RT-PCR) analysis indicated that AmphiIKK was ubiquitously expressed in all tissues and we also discovered that the expression of AmphiIKK was affected after lipopolysaccharides stimulation. Our findings help to highlight a potential important regulatory pathway in the innate immune response in the amphioxus and the evolution of the IKK family.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2004) Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev 18:2195–2224
Li Z-W, Omori SA, Labuda T, Karin M, Rickert RC (2003) IKKβ is required for peripheral B cell survival and proliferation. J Immunol 170:4630–4637
Basseres DS, Baldwin AS (2006) Nuclear factor-kappaB and inhibitor of kappaB kinase pathways in oncogenic initiation and progression. Oncogene 25:6817–6830
Gilmore TD (2006) Introduction to NF-kappaB: players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene 25:6680–6684
Perkins ND (2007) Integrating cell-signalling pathways with NF-kappaB and IKK function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:49–62
Karin M, Ben-Neriah Y (2000) Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu Rev Immunol 18:621–663
Phelps CB, Sengchanthalangsy LL, Huxford T, Ghosh G (2000) Mechanism of IκBα binding to NF-κB dimers. J Biol Chem 275:29840–29846
Montagnani C, Labreuche Y, Escoubas JM (2008) Cg-IκB, a new member of the IκB protein family characterized in the pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Dev Comp Immunol 32:182–190
Zhang D, Jiang S, Qiu L, Su T, Wu K, Li Y, Zhu C, Xu X (2009) Molecular characterization and expression analysis of the IκB gene from pearl oyster Pinctada fucata. Fish Shellfish Immunol 26:84–90
Solt L, May M (2008) The IκB kinase complex: master regulator of NF-κB signaling. Immunol Res 42:3–18
Ghosh S, Karin M (2002) Missing pieces in the NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell 109(Suppl):S81–S96
Scheidereit C (2006) IkappaB kinase complexes: gateways to NF-kappaB activation and transcription. Oncogene 25:6685–6705
Silverman N, Zhou R, Stöven S, Pandey N, Hultmark D, Maniatis T (2000) A Drosophila IκB kinase complex required for Relish cleavage and antibacterial immunity. Genes Dev 14:2461–2471
Ertürk-Hasdemir D, Broemer M, Leulier F, Lane WS, Paquette N, Hwang D, Kim CH, Stöven S, Meier P, Silverman N (2009) Two roles for the Drosophila IKK complex in the activation of Relish and the induction of antimicrobial peptide genes. Proc Nat Acad Sci 106:9779
Oshima K, Takeda M, Kuranaga E, Ueda R, Aigaki T, Miura M, Hayashi S (2006) IKKɛ regulates F actin assembly and interacts with Drosophila IAP1 in cellular morphogenesis. Curr Biol 16:1531–1537
Kuranaga E, Kanuka H, Tonoki A, Takemoto K, Tomioka T, Kobayashi M, Hayashi S, Miura M (2006) Drosophila IKK-related kinase regulates nonapoptotic function of caspases via degradation of IAPs. Cell 126:583–596
Escoubas JM, Briant L, Montagnani C, Hez S, Devaux C, Roch P (1999) Oyster IKK-like protein shares structural and functional properties with its mammalian homologues. FEBS Lett 453:293–298
Xiong X, Feng Q, Chen L, Xie L, Zhang R (2008) Cloning and characterization of an IKK homologue from pearl oyster, Pinctada fucata. Dev Comp Immunol 32:15–25
Chen WJ, Guo CJ, Zhou ZC, Yuan LQ, Xiang ZM, Weng SP, Zhang YF, Yu XQ, He JG (2011) Molecular cloning of IKKbeta from the mandarin fish Siniperca chuatsi and its up-regulation in cells by ISKNV infection. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 139:61–66
Putnam NH, Butts T, Ferrier DE, Furlong RF, Hellsten U, Kawashima T, Robinson-Rechavi M, Shoguchi E, Terry A, Yu JK, Benito-Gutierrez EL, Dubchak I, Garcia-Fernandez J, Gibson-Brown JJ, Grigoriev IV, Horton AC, de Jong PJ, Jurka J, Kapitonov VV, Kohara Y, Kuroki Y, Lindquist E, Lucas S, Osoegawa K, Pennacchio LA, Salamov AA, Satou Y, Sauka-Spengler T, Schmutz J, Shin IT, Toyoda A, Bronner-Fraser M, Fujiyama A, Holland LZ, Holland PW, Satoh N, Rokhsar DS (2008) The amphioxus genome and the evolution of the chordate karyotype. Nature 453:1064–1071
Holland LZ, Albalat R, Azumi K, Benito-Gutierrez E, Blow MJ, Bronner-Fraser M, Brunet F, Butts T, Candiani S, Dishaw LJ, Ferrier DE, Garcia-Fernandez J, Gibson-Brown JJ, Gissi C, Godzik A, Hallbook F, Hirose D, Hosomichi K, Ikuta T, Inoko H, Kasahara M, Kasamatsu J, Kawashima T, Kimura A, Kobayashi M, Kozmik Z, Kubokawa K, Laudet V, Litman GW, McHardy AC, Meulemans D, Nonaka M, Olinski RP, Pancer Z, Pennacchio LA, Pestarino M, Rast JP, Rigoutsos I, Robinson-Rechavi M, Roch G, Saiga H, Sasakura Y, Satake M, Satou Y, Schubert M, Sherwood N, Shiina T, Takatori N, Tello J, Vopalensky P, Wada S, Xu A, Ye Y, Yoshida K, Yoshizaki F, Yu JK, Zhang Q, Zmasek CM, de Jong PJ, Osoegawa K, Putnam NH, Rokhsar DS, Satoh N, Holland PW (2008) The amphioxus genome illuminates vertebrate origins and cephalochordate biology. Genome Res 18:1100–1111
Huang S, Yuan S, Guo L, Yu Y, Li J, Wu T, Liu T, Yang M, Wu K, Liu H, Ge J, Yu Y, Huang H, Dong M, Yu C, Chen S, Xu A (2008) Genomic analysis of the immune gene repertoire of amphioxus reveals extraordinary innate complexity and diversity. Genome Res 18:1112–1126
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Schultz J, Milpetz F, Bork P, Ponting CP (1998) SMART, a simple modular architecture research tool: identification of signaling domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5857–5864
Letunic I, Doerks T, Bork P (2012) SMART 7: recent updates to the protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D302–D305
Campanella JJ, Bitincka L, Smalley J (2003) MatGAT: an application that generates similarity/identity matrices using protein or DNA sequences. BMC Bioinformatics 4:29
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Karin M, Delhase M (2000) The I kappa B kinase (IKK) and NF-kappa B: key elements of proinflammatory signalling. Semin Immunol 12:85–98
Ea C-K, Deng L, Xia Z-P, Pineda G, Chen ZJ (2006) Activation of IKK by TNFα requires site-specific ubiquitination of RIP1 and polyubiquitin binding by NEMO. Mol Cell 22:245–257
Adhikari A, Xu M, Chen ZJ (2007) Ubiquitin-mediated activation of TAK1 and IKK. Oncogene 26:3214–3226
Chappell VL, Le LX, LaGrone L, Mileski WJ (2000) Stat proteins play a role in tumor necrosis factor alpha gene expression. Shock 14:400–402 (discussion 402–403)
Bonizzi G, Karin M (2004) The two NF-κB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol 25:280–288
Perkins ND (2003) Oncogenes, tumor suppressors and p52 NF-[kappa]B. Oncogene 22:7553–7556
Sun S-C, Ley SC (2008) New insights into NF-κB regulation and function. Trends Immunol 29:469–478
Beinke S, Ley SC (2004) Functions of NF-κB1 and NF-κB2 in immune cell biology. Biochemical J 382:393
Acknowledgments
I thank Sheng Qin and Wen Chen for help with artwork in the figures. This work was jointly supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30970348), the Project of New Century Excellent Talents in Universities (No. NCET-07-0405), the Major Program of Natural Science Research of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (No.12KJA180005), the Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (No. 20113207110009), and a grant from Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, L., Jin, P., Qian, J. et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of an IKK homologue from amphioxus (Branchiostoma belcheri). Mol Biol Rep 39, 10751–10758 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1967-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1967-3