Abstract
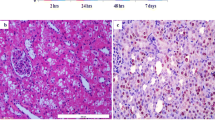
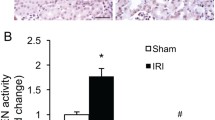
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effects of phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitory drugs, Tadalafil and Sildenafil, on inducible NOS (iNOS), endothelial NOS (eNOS) and p53 genes expressions and apoptosis in ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) induced oxidative injury in rat renal tissue. Eighty Sprague–Dawley rats (300–350 g) were divided into four groups. In ischemia/reperfusion group, rats were subjected to renal ischemia by clamping the left pedicle for 60 min, and then reperfused for 90 min. On the other hand, in other two groups the rats were individually pretreated with Tadalafil and Sildenafil 1 h before the induction of ischemia. Malondialdehyde (MDA) is determined in renal tissue homogenates by high-performance liquid chromatography, the number of apoptotic cell were calculated by TUNEL method and p53 and eNOS expression were detected with immunohistochemistry. On the other hand, myeloperoxidase (MPO) levels were measured by spectrophotometric method and the mRNA level of iNOS in renal tissue was determined by Real-time PCR (RT-PCR). Our results indicate that MDA and MPO levels were increased in the I/R group than those in the control group. Both Tadalafil and Sildenafil treatment decreased the MDA levels in ischemia/reperfusion group, whereas this effect was more potent with Sildenafil. RT-PCR results showed that, iNOS gen expression increased in the I/R group, but decreased in the PDE5 inhibitory drugs treated group. Apoptotic cells, eNOS levels and p53 positive cells were also decreased in PDE5 inhibitory drugs treated group. We suggest that Tadalafil and Sildenafil have beneficial effects against I/R related renal tissue injury and this protective effect is clearer for Sildenafil than Tadalafil.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar V, Abbas AK, Fausto N (2005) Cellular adaptations, cell ınjury, and cell death. In: Kumar V, Abbas AK, Fausto N (eds) Robbins and Cotran Pathologic basis of diseases, 7th edn. Elsevier Saunders, St Louis, pp 1–47
Elahi MM, Kong YX, Matata BM (2009) Oxidative stress as a mediator of cardiovascular disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2:259–269
Lopez-Neblina F, Paez AJ, Toledo AH et al (1995) Role of nitric oxide in ischemia/reperfusion of the rat kidney. Circ Shock 44:91–95
Goligorsky MS, Brodsky SV, Noiri E (2002) Nitric oxide in acute renal failure: NOS versus NOS. Kidney Int 61:855–861
Furchgott R, Zawadzkı J (1980) The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature 288(5789):373–376
Mungrue IN, Husain M, Stewart DJ (2002) The role of NOS in heart failure: lessons from murine genetic model. Heart Fail Rev 7(4):407–422
Oruc O, Inci K, Aki FT et al (2010) Sildenafil attenuates renal ischemia reperfusion injury by decreasing leukocyte infiltration. Acta Histochem 112:337–344
Levine AJ (1997) p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 88:323–331
Ko IG, Shin MS, Kim BK et al (2009) Tadalafil improves short-term memory by suppressing ischemia-induced apoptosis of hippocampal neuronal cells in gerbils. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 91:629–635
Zhang Y, Guan DL, Ou TW et al (2005) Sildenafil citrate treatment for erectile dysfunction after kidney transplantation. Transplantation Proc 37:2100–2103
Ockaili R, Salloum F, Hawkins J et al (2002) Sildenafil (Viagra) induces powerful cardioprotective effect via opening of mitochondrial KATP channels in rabbits. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 283:263–269
Serarslan Y, Yönden Z, Ozgiray E et al (2010) Protective effects of tadalafil on experimental spinal cord injury in rats. J Clin Neurosci 17:349–352
Suzuki K, Ota H, Sasagawa S et al (1983) Assay method for myeloperoxidase in human polymorphonuclear luekocytes. Anal Biochem 132:345
Sobajima S, Shimer AL, Chadderdon RC et al (2005) Quantitative analysis of gene expression in a rabbit model of intervertebral disc degeneration by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Spine J 5:14–23
Kacmaz A, Polat A, User Y et al (2003) Octreotide: a new approach to the management of acute abdominal hypertension. Peptides 24:1381–1386
Sahna E, Parlakpinar H, Turkoz Y et al (2005) Protective effects of melatonin on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion induced infarct size and oxidative changes. Physiol Res 54:491–495
Beckman JS, Beckman TW, Chen J et al (1995) Apparent hydroxyl radical production by peroxynitrite: implications for endothelial injury from nitric oxide and superoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci 87:1620–1624
Radi R, Beckman JS, Bush KM et al (1991) Peroxynitrite oxidation of sulfhydryls: the cytotoxic potential of superoxide and nitric oxide. J Biol Chem 266:4244–4250
Radi R, Beckman JS, Bush KM et al (1991) Peroxynitrite-induced membrane lipid peroxidation: the cytotoxic potential of superoxide and nitric oxide. Arch Biochem Biophys 288(2):481–487
Walker LM, Walker PD, Imam SZ et al (2000) Evidence for peroxynitrite formation in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury: studies with the inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor L-N6-(1-Iminoethyl)lysine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295:417–422
Weight SC, Nicholson ML (1998) Nitric oxide and renal reperfusion injury: a review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 16:98–103
Noiri E, Nakao A, Uchida K et al (2001) Oxidative and nitrosative stress in acute renal ischemia. Am J Physiol 281:948–957
Chatterjee PK, Patel NSA, Kvale EO et al (2002) Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase reduces renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Kidney Int 61:862–871
Tisi P, Shearman CP (1999) Systemic consequences of reperfusion injury. In: Grace PA, Mathie RT (eds) Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Blackwell Science, London, pp 20–30
Kucuk A, Kabadere S, Tosun M et al (2009) Protective effects of doxycycline in ischemia/reperfusion injury on kidney. J Physiol Biochem 65:183–191
Kucuk A, Erkasap N, Tosun M et al (2010) Effects of leptin on p53 expression and apoptosis in ischemia reperfusion induced renal injury. Cent Eur J Urol 63(1):36–39
Cengiz SL, Erdi MF, Tosun M et al (2010) Beneficial effects of levosimendan on cerebral vasospasm induced by subarachnoid haemorrhage: an experimental study. Brain Inj 24(6):877–885
Kalkan E, Keskin F, Kaya B et al (2011) Effects of iloprost and piracetam in spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rabbit. Spinal Cord 49(1):81–86
Choi DE, Jeong JY, Lim BJ et al (2009) Pretreatment of sildenafil attenuates ischemia-reperfusion renal injuryin rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297(2):362–370
Medeiros PJ, Villarim Neto A, Lima FP et al (2010) Effect of sildenafil in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Acta Cir Bras 25(6):490–495
Lledo-Garcia E, Subira-Rios D, Ogaya-Pinies G et al (2011) Intravenous sildenafil as a preconditioning drug against hemodynamic consequences of warm ischemia-reperfusion on the kidney. J Urol 186(1):331–333
Goldberg DM, Hanh SE, Parkes JG (1995) Beyond alcohol: beverage consumption and cardiovascular mortality. Clin Chim Acta 237:155–187
Morales AI, Vicente-Sanchez C, Jerkic M (2006) Effect of quercetin on metallothionein, nitric oxide synthases and cyclooxygenase-2 expression on experimental chronic cadmium nephrotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 210:128–135
Vinas JL, Sola A, Genseca M et al (2006) NO and NOS isoforms in the development of apoptosis in renal ischemia/reperfusion. Free Radic Biol Med 40:992–1003
Schneider R, Meusel M, Betz B et al (2011) Nitric oxide induced regulation of renal organic cation transport after renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 301(5):997–1004
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Küçük, A., Yucel, M., Erkasap, N. et al. The effects of PDE5 inhibitory drugs on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Mol Biol Rep 39, 9775–9782 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1843-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1843-1