Abstract
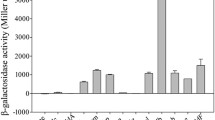
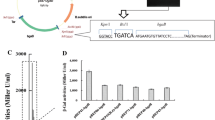
An osmolarity-sensitive promoter fragment, P23423, isolated from Bacillus subtilis was characterized. The expression of β-galactosidase (β-Gal) driven by P23423 was regulated by osmolarity both in Escherichia coli and B. subtilis. The classical conserved region of this prokaryotic promoter was found within the sequence of the cloned fragment, and the putative promoter was identified as the control element of RNA not coding for protein (a RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein). The efficiency and benefit of this promoter was further demonstrated via osmolarity-induced expression of three other heterologous proteins in E. coli. Thus, this approach provided a simple and inexpensive inducible promoter element for the expression of cloned genes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taija K, Alexander DF, Pauli TK (2006) Characterization of heterologous hemoglobin and flavohemoglobin promoter regulation in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 122:161–175
Zhang XZ, Cui ZL, Qing H, Li SP (2005) High-level expression and secretion of methyl parathion hydrolase in Bacillus subtilis WB800. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4101–4103
Nguyen HD, Schumann W (2006) Novel plasmid-based expression vectors for intra- and extracellular production of recombinant proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Protein Expr Purif 46:189–195
Nieto C, Fernández de Palencia P, López P, Espinosa M (2000) Construction of a tightly regulated plasmid vector for Streptococcus pneumoniae: controlled expression of the green fluorescent protein. Plasmid 43:205–213
Kim L, Mogk A, Schumann W (1996) A xylose-inducible Bacillus subtilis integration vector and its application. Gene 87:53–61
Serrano-Heras G, Salas M, Bravo A (2005) A new plasmid vector for regulated gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. Plasmid 54:278–282
Hartl B, Wehrl W, Wiegert T, Homuth G, Schumann W (2001) Development of a new integration site within the Bacillus subtilis chromosome and construction of compatible expression cassettes. J Bacteriol 183:2696–2699
Yang MM, Zhang WW, Zhang XF, Cen PL (2006) Construction and characterization of a novel maltose inducible expression vector in Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol Lett 28:1713–1718
Kosinski MJ, Rinas U, Bailey JE (1992) Isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactopyranoside influences the metabolism of Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 36:782–784
Li W, Li HX, Ji SY, Li S, Gong YS, Yang MM, Chen YL (2007) Characterization of two temperature-inducible promoters newly isolated from Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 358:1148–1153
Paccez JD, Luiz WB, Sbrogio-Almeida ME, Ferreira RCC, Schumannc W, Ferreira LCS (2006) Stable episomal expression system under control of a stress inducible promoter enhances the immunogenicity of Bacillus subtilis as a vector for antigen delivery. Vaccine 24:2935–2943
Schumann W (2007) Production of recombinant proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Adv Appl Microbiol 62:137–189
Scharf C, Riethdorf S, Ernst H, Engelmann S, Völker U, Hecker M (1998) Thioredoxin is an essential protein induced by multiple stresses in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 180:1869–1877
Birgit H, Susanne K, Erhard B (1994) pOSEX: vectors for smotically controlled and finely tuned gene expression in Escherichia coli. Gene 151:137–142
Rajendra JR, Roland WH, Narenara KS (1998) Transcriptional activation of the Aspergillus nidulans gpdA promoter by osmotic signals. Appl Environ Microbiol 7:2229–2231
Palomino MM, Sanchez-Rivas C, Ruzal SM (2009) High salt stress in Bacillus subtilis: involvement of PBP4* as a peptidoglycan hydrolase. Res Microbiol 160:117e124
Ionescu M, Elgrably-Weiss M, Elad T, Rasouly A, Yagur-Kroll S, Belkin S (2011) Negative regulation of σ(70)-driven promoters by σ(70). Res Microbiol 162:461–469
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Bron S (1990) Plasmids. In: Harwood CR, Cutting SM (eds) Molecular biological methods for bacillus. Wiley, New York, pp 75–174
Hirata H, Kzawa T, Negoro S, Okada H (1986) Structure of a bate-galactosidase gene of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol 166:722–727
Dikshit KL, Yutaka O, Navani N, Patel S, Huang H, Stark BC, Webster DA (1998) Site-directed mutagenesis of bacterial hemoglobin: the role of glutamine (T7) in oxygen-binding in the distal heme pocket. Arch Biochem Biophys 349:161–166
Zhang AL, Liu H, Yang MM, Gong YS, Chen H (2007) Assay and characterization of a strong promoter element from Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 354:90–95
Miller JH (1972) Experiments in molecular genetics, 1st edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Ján K, Ševčíkováa B, Halgašováa N, Knirschováa R, Řežuchováa B (2000) Identification and transcriptional characterization of the gene encoding the stress-response c factor cH in Streptomyces coelicolor A3. FEMS Microbiol Lett 189:31–38
Shin-Ichi M, Kaoru I, Shoji M (1984) Promoter exchange between ompF and ompC, genes for osmoregulated major outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol 7:1041–1047
Kullik I, Giachino P (1997) The alternative sigma factor sigB in Staphylococcus aureus: regulation of the sigB operon in response to growth phase and heat shock. Arch Microbiol 167:151–159
Jan K, Beatrica S (2002) Stress-response sigma factor σH directs expression of the gltB gene encoding glutamate synthase in Streptomyces coelicolor A3. BBA 1577:149–154
Hengge-Aronis R (1996) Back to log phase: σS as a global regulator in the osmotic control of gene expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 21:887–893
Benson AK, Haldenwang WG (1993) The σB -dependent promoter of the Bacillus subtilis sigB operon is induced by heat shock. J Bacteriol 175:1929–1935
Petersohn A, Bernhardt J, Gerth U, Hoper D, Koburger T, Voelker U, Hecker M (1999) Identification of σB-dependent genes in Bacillus subtilis using a promoter consensus-directed search and oligonucleotide hybridization. J Bacteriol 181:5718–5724
Zhang S, Reeves A, Woodbury RL, Haldenwang WG (2005) Coexpression patterns of σB regulators in Bacillus subtilis affect σB inducibility. J Bacteriol 187:8520–8525
Acknowledgment
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Bacillus Genetic Stock Centre of Ohio State University for generously providing the study materials. And this study was supported by the grants of NSFC (30872033, 31170609).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, WW., Gao, QR., Yang, MM. et al. Assay and characterization of an osmolarity inducible promoter newly isolated from Bacillus subtilis . Mol Biol Rep 39, 7347–7353 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1566-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1566-3