Abstract
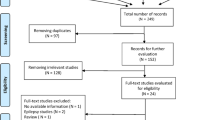
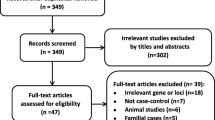
One previous meta-analysis found no evidence that interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) −511 gene polymorphism was associated with febrile seizures (FS) by pooling a limited number of studies. However, it is necessary for the meta-analysis to reevaluate the relationship with more recent findings. Electronic databases were systematically searched for studies published before June 2011. Pooled odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were estimated by means of a genetic model free approach. Subgroup and sensitivity analyses were also performed. All statistical analyses were conducted using Stata 9.0. A total of eight studies, 728 FS cases and 1,223 controls, met the selection criteria. The results show a significant association between IL-1β −511 C/T gene polymorphism and FS (recessive genetic model TT vs. CC + CT: OR = 1.361, 95% CI: 1.065–1.738, P = 0.014). Subgroup analyses show a significant association in Asia (OR = 1.394, 95% CI: 1.005–1.935, P = 0.047), but not in Europe (OR = 1.387, 95% CI: 0.750–2.565, P = 0.298). IL-1β −511 C/T gene polymorphism may play a role in susceptibility to FS, especially in Asia. Geographic differences may be a critical factor in the risk of FS.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Commission on Epidemiology, Prognosis, International League Against Epilepsy (1993) Guidelines for epidemiologic studies on epilepsy. Epilepsia 34:592–596
Hauser WA (1994) The prevalence and incidence of convulsive disorders in children. Epilepsia 35(Suppl 2):S1–S6
Kugler SL, Johnson WG (1998) Genetics of the febrile seizure susceptibility trait. Brain Dev 20:265–274
Chung B, Wat LC, Wong V (2006) Febrile seizures in southern Chinese children: incidence and recurrence. Pediatr Neurol 34:121–126
(1996) Practice parameter: the neurodiagnostic evaluation of the child with a first simple febrile seizure. American Academy of Pediatrics. Provisional Committee on Quality Improvement, Subcommittee on Febrile Seizures. Pediatrics 97: 769–772; discussion 773–775
Hauser WA, Annegers JF, Anderson VE, Kurland LT (1985) The risk of seizure disorders among relatives of children with febrile convulsions. Neurology 35:1268–1273
Rich SS, Annegers JF, Hauser WA, Anderson VE (1987) Complex segregation analysis of febrile convulsions. Am J Hum Genet 41:249–257
Tsuboi T (1987) Genetic analysis of febrile convulsions: twin and family studies. Hum Genet 75:7–14
Corey LA, Berg K, Pellock JM, Solaas MH, Nance WE, DeLorenzo RJ (1991) The occurrence of epilepsy and febrile seizures in Virginian and Norwegian twins. Neurology 41:1433–1436
Tsuboi T, Endo S (1991) Genetic studies of febrile convulsions: analysis of twin and family data. Epilepsy Res Suppl 4:119–128
Kjeldsen MJ, Kyvik KO, Friis ML, Christensen K (2002) Genetic and environmental factors in febrile seizures: a Danish population-based twin study. Epilepsy Res 51:167–177
Gatti S, Vezzani A, Bartfai T (2002) Mechanisms of fever and febrile seizures: putative role of the interleukin-1 system. In: Baram TZ, Shinnar S (eds) Febrile seizures. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 169–188
Haspolat S, Mihci E, Coskun M, Gumuslu S, Ozben T, Yegin O (2002) Interleukin-1beta, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and nitrite levels in febrile seizures. J Child Neurol 17:749–751
Matsuo M, Sasaki K, Ichimaru T, Nakazato S, Hamasaki Y (2006) Increased IL-1beta production from dsRNA-stimulated leukocytes in febrile seizures. Pediatr Neurol 35:102–106
Nothwang HG, Strahm B, Denich D, Kubler M, Schwabe J, Gingrich JC, Jauch A, Cox A, Nicklin MJ, Kurnit DM, Hildebrandt F (1997) Molecular cloning of the interleukin-1 gene cluster: construction of an integrated YAC/PAC contig and a partial transcriptional map in the region of chromosome 2q13. Genomics 41:370–378
Serdaroglu G, Alpman A, Tosun A, Pehlivan S, Ozkinay F, Tekgul H, Gokben S (2009) Febrile seizures: interleukin 1beta and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist polymorphisms. Pediatr Neurol 40:113–116
Nakayama J, Arinami T (2006) Molecular genetics of febrile seizures. Epilepsy Res 70(Suppl 1):S190–S198
Dube C, Vezzani A, Behrens M, Bartfai T, Baram TZ (2005) Interleukin-1beta contributes to the generation of experimental febrile seizures. Ann Neurol 57:152–155
Kanemoto K, Kawasaki J, Yuasa S, Kumaki T, Tomohiro O, Kaji R, Nishimura M (2003) Increased frequency of interleukin-1beta-511T allele in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy, hippocampal sclerosis, and prolonged febrile convulsion. Epilepsia 44:796–799
Kauffman MA, Moron DG, Consalvo D, Bello R, Kochen S (2008) Association study between interleukin 1 beta gene and epileptic disorders: a HuGe review and meta-analysis. Genet Med 10:83–88
Martinez-Carrillo DN, Garza-Gonzalez E, Betancourt-Linares R, Monico-Manzano T, Antunez-Rivera C, Roman–Roman A, Flores-Alfaro E, Illades-Aguiar B, Fernandez-Tilapa G (2010) Association of IL1B–511C/-31T haplotype and Helicobacter pylori vacA genotypes with gastric ulcer and chronic gastritis. BMC Gastroenterol 10:126
Mu Y, Liu J, Wang B, Wen Q, Wang J, Yan J, Zhou S, Ma X, Cao Y (2010) Interleukin 1 beta (IL-1beta) promoter C [−511] T polymorphism but not C [+3953] T polymorphism is associated with polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocrine 37:71–75
Corleto VD, Pagnini C, Margagnoni G, Guagnozzi D, Torre MS, Martorelli M, Latiano A, Annese V, Caprilli R, Delle FG (2010) IL-1beta-511 and IL-1RN*2 polymorphisms in inflammatory bowel disease: An Italian population study and meta-analysis of European studies. Dig Liver Dis 42:179–184
Guo SW, Thompson EA (1992) Performing the exact test of Hardy–Weinberg proportion for multiple alleles. Biometrics 48:361–372
Cleves M (1999) Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium test and allele frequency estimation. Stata Tech Bull 48:34–37
Cui J (2000) Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium test in case–control studies. Stata Tech Bull 57:17–19
Thakkinstian A, McElduff P, D’Este C, Duffy D, Attia J (2005) A method for meta-analysis of molecular association studies. Stat Med 24:1291–1306
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21:1539–1558
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327:557–560
Bagos PG, Nikolopoulos GK (2007) A method for meta-analysis of case-control genetic association studies using logistic regression. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 6: Article 17
Begg CB, Mazumdar M (1994) Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50:1088–1101
Egger M, Davey SG, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
Kira R, Torisu H, Takemoto M, Nomura A, Sakai Y, Sanefuji M, Sakamoto K, Matsumoto S, Gondo K, Hara T (2005) Genetic susceptibility to simple febrile seizures: interleukin-1beta promoter polymorphisms are associated with sporadic cases. Neurosci Lett 384:239–244
Chou IC, Tsai CH, Hsieh YY, Peng CT, Tsai FJ (2003) Association between polymorphism of interleukin-1beta −511 promoter and susceptibility to febrile convulsions in Taiwanese children. Acta Paediatr 92:1356
Li SH, Hu CF, Liu TC (2006) Relationship between the children interleukin 1β (−511) gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to febrile seizures. Chin J Pathophysiol 22:1168–1170
Chou IC, Lin WD, Wang CH, Tsai CH, Li TC, Tsai FJ (2010) Interleukin (IL)-1beta, IL-1 receptor antagonist, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, and tumor necrosis factor alpha gene polymorphisms in patients with febrile seizures. J Clin Lab Anal 24:154–159
Kira R, Ishizaki Y, Torisu H, Sanefuji M, Takemoto M, Sakamoto K, Matsumoto S, Yamaguchi Y, Yukaya N, Sakai Y, Gondo K, Hara T (2010) Genetic susceptibility to febrile seizures: case–control association studies. Brain Dev 32:57–63
Virta M, Hurme M, Helminen M (2002) Increased frequency of interleukin-1beta (−511) allele 2 in febrile seizures. Pediatr Neurol 26:192–195
Haspolat S, Baysal Y, Duman O, Coskun M, Tosun O, Yegin O (2005) Interleukin-1alpha, interleukin-1beta, and interleukin-1Ra polymorphisms in febrile seizures. J Child Neurol 20:565–568
Tilgen N, Pfeiffer H, Cobilanschi J, Rau B, Horvath S, Elger CE, Propping P, Heils A (2002) Association analysis between the human interleukin 1beta (−511) gene polymorphism and susceptibility to febrile convulsions. Neurosci Lett 334:68–70
Heida JG, Moshe SL, Pittman QJ (2009) The role of interleukin-1beta in febrile seizures. Brain Dev 31:388–393
Helminen M, Vesikari T (1990) Increased interleukin-1 (IL-1) production from LPS-stimulated peripheral blood monocytes in children with febrile convulsions. Acta Paediatr Scand 79:810–816
Heida JG, Boisse L, Pittman QJ (2004) Lipopolysaccharide-induced febrile convulsions in the rat: short-term sequelae. Epilepsia 45:1317–1329
Nelson KB, Ellenberg JH (1976) Predictors of epilepsy in children who have experienced febrile seizures. N Engl J Med 295:1029–1033
Annegers JF, Hauser WA, Shirts SB, Kurland LT (1987) Factors prognostic of unprovoked seizures after febrile convulsions. N Engl J Med 316:493–498
Verity CM, Golding J (1991) Risk of epilepsy after febrile convulsions: a national cohort study. BMJ 303:1373–1376
Berg AT, Shinnar S (1996) Unprovoked seizures in children with febrile seizures: short-term outcome. Neurology 47:562–568
MacDonald BK, Johnson AL, Sander JW, Shorvon SD (1999) Febrile convulsions in 220 children–neurological sequelae at 12 years follow-up. Eur Neurol 41:179–186
Shinnar S (2003) Febrile seizures and mesial temporal sclerosis. Epilepsy Curr 3:115–118
Chomba E, Taylor TE, Hauser W, Wasterlain C, Organek N, Birbeck G (2008) Seizure recurrence in rural Zambian children admitted with febrile seizures. Open Trop Med J 1:101–107
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhen-Qiang Wu and Liang Sun contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, ZQ., Sun, L., Sun, YH. et al. Interleukin 1 beta −511 C/T gene polymorphism and susceptibility to febrile seizures: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep 39, 5401–5407 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1340-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1340-y