Abstract
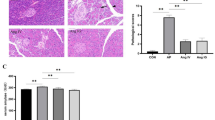
To explore the influence of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) on the gut barrier function in severe acute pancreatitis (SAP). Fifty four SD rats were randomly divided into three groups: sham operated (SO) group, SAP group and VIP intervention group. Each group was further divided into three time points: 1, 6 and 12 h after operation with 6 rats for each treatment point. SAP models were induced by retrograde injection of 4% sodium taurocholate into the bili-pancreatic duct. VIP intervention group was made by 5 nmol VIP intraperitoneal injection within 5 min after SAP model successfully obtained. The VIP in plasma and intestinal homogenate were detected with ELISA. The endotoxin in plasma of all groups was also tested. The expression levels of TLR4, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 in gut mucosa were measured by RT-PCR. Meanwhile intestinal samples were harvested for pathological examination. Compared to SO group, the VIP in plasma and intestinal homogenate of SAP group were significantly decreased at 1 h after induction, and then gradually increased to beyond the level of SO group at 12 h. The endotoxin of SAP group was continually increased. The mRNA levels of TLR4, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 were also increased with obvious pathological injuries in the intestine. In the VIP group, endotoxin in plasma was obviously decreased compared to SAP group. The expressions of TNF-α, IL-6 mRNA were suppressed while IL-10mRNA was increased. The intestinal pathological injuries were also markedly alleviated. These results suggested that VIP had protective effects on SAP gut barrier function through inhibiting intestinal mucosal inflammatory responses.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mann DV, Hershman MJ, Hittinger R, Glazer G (1994) Multicentre audit of death in acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg 81:890–893
Norman J (1998) The role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Am J Surg 175:76–83
Shi C, Zhao X, Lagergren A, Sigvardsson M, Wang X, Andersson R (2006) Immune status and inflammatory response differ locally and systemically in severe acute pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol 41:472–480
Swank GM, Deitch EA (1996) Role of the gut in multiple organ failure: bacterial translocation and permeability changes. World J Surg 20:411–417
MacFie J, O’Boyle C, Mitchell CJ, Buckley PM, Johnstone D, Sudworth P (1999) Gut origin of sepsis: a prospective study investigating associations between bacterial translocation, gastric microflora, and septic morbidity. Gut 45:223–228
Matheus AS, Coelho AM, Sampietre S, Patzina R, Jukemura J, Cunha JE, Machado MC (2007) Effect of inhibition of prostaglandin E2 production on pancreatic infection in experimental acute pancreatitis. HPB (Oxford) 9:392–397
Leveau P, Wang X, Sun Z, Börjesson A, Andersson E, Andersson R (2005) Severity of pancreatitis-associated gut barrier dysfunction is reduced following treatment with the PAF inhibitor lexipafant. Biochem Pharmacol 69:1325–1331
Ammori BJ (2003) Role of the gut in the course of severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 26:122–129
Delgado M, Abad C, Martinez C, Juarranz MG, Arranz A, Gomariz RP, Leceta J (2002) Vasoactive intestinal peptide in the immune system: potential therapeutic role in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. J Mol Med 80:16–24
Chorny A, Gonzalez-Rey E, Varela N, Robledo G, Delgado M (2006) Signaling mechanisms of vasoactive intestinal peptide in inflammatory conditions. Regul Pept 137:67–74
Besselink MG, van Santvoort HC, Renooij W, de Smet MB, Boermeester MA, Fischer K et al (2009) Intestinal barrier dysfunction in a randomized trial of specific probiotic composition in acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg 250:712–719
Zhang Y, Cai D, Cai W, Geng S, Chen L, Han T (2009) Protective effect of galactooligosaccharide-supplemented enteral nutrition on intestinal barrier function in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Clin Nutr 28:575–580
Kojima M, Ito T, Oono T, Hisano T, Lgarashi H, Arita Y, Kawabe K, Coy DH, Jensen RT, Nawata H (2005) VIP attenuation of the severity of experimental pancreatitis is due to VPAC1 receptor-mediated inhibition of cytokine production. Pancreas 30:62–70
Sawa H, Ueda T, Takeyama Y, Yasuda T, Shinzeki M, Matsumura N, Nakajima T, Kuroda Y (2008) Expression of toll-like receptor 2 and 4 in intestinal mucosa in experimental severe acute pancreatitis. Hepatogastroenterology 55:2247–2251
Lankisch PG, Ihse I (1987) Bile-induced acute experimental pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol 22:257–260
Jasani B, Schmid KW (1993) Immunocytochemistry in diagnostic histopathology, 1st edn. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
Zhang XP, Ye Q, Jiang XG, Ma ML, Zhu FB, Zhang RP, Cheng QH (2007) Preparation method of an ideal model of multiple organ injury of rat with severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 13:4566–4573
Xu GF, Lu Z, Gao J, Li ZS, Gong YF (2006) Effect of ecoimmunonutrition supports on maintenance of integrity of intestinal mucosal barrier in severe acute pancreatitis in dogs. Chin Med J (Engl) 119:656–661
Liu ZH, Peng JS, Li CJ, Yang ZL, Xiang J, Song H, Wu XB, Chen JR, Diao DC (2009) A simple taurocholate-induced model of severe acute pancreatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 15:5732–5739
Ryan CM, Schmidt J, Lewandrowski K, Compton CC, Rattner DW, Warshaw AL, Tompkins RG (1993) Gut macromolecular permeability in pancreatitis correlates with severity of disease in rats. Gastroenterology 104:890–895
Ammori BJ, Leeder PC, King RF et al (1999) Early increase in intestinal permeability in patients with severe acute pancreatitis: correlation with endotoxemia, organ failure, and mortality. J Gastrointest Surg 3:252–262
Juvonen PO, Alhava EM, Takala JA (2000) Gut permeability in patients with acute pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol 35:1314–1318
Ding LA, Li JS, Li YS, Zhu NT, Liu FN, Tan L (2004) Intestinal barrier damage caused by trauma and lipopolysaccharide. World J Gastroenterol 10:2373–2378
Kazantsev GB, Hecht DW, Rao R, Fedorak IJ, Gattuso P, Thompson K, Djuricin G, Prinz RA (1994) Plasmid labeling confirms bacterial translocation in pancreatitis. Am J Surg 167:201–207
Xiping Z, Ruiping Z, Binyan Y, Li Z, Hanqing C, Wei Z, Rongchao Y, Jing Y, Wenqin Y, Jinjin B (2010) Protecting effects of a large dose of dexamethasone on spleen injury of rats with severe acute pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 25:302–308
Zhang X, Chen L, Luo L, Tian H, Feng G, Cai Y, Xu R, Wang K, Wang Z (2008) Study of the protective effects of dexamethasone on ileum mucosa injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 37:e74–e82
Xiping Z, Li C, Miao L, Hua T (2007) Protecting effects of dexamethasone on thymus of rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Mediator inflamm 2007:72361
Smalley SG, Barrow PA, Foster N (2009) Immunomodulation of innate immune responses by vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP): its therapeutic potential in inflammatory disease. Clin Exp Immunol 157:225–234
Colin VS, Wu X, Nguyen C, Dai C, Vallance BA, Buchan AM, Boyer L, Jacobson K (2009) Vasoactive intestinal peptide ameliorates intestinal barrier disruption associated with Citrobacter rodentium-induced colitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 297:G735–G750
de Campos T, Deree J, Martins JO, Loomis WH, Shenvi E, Putnam JG, Coimbra R (2008) Pentoxifylline attenuates pulmonary inflammation and neutrophil activation in experimental acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 37:42–49
Bruewer M, Luegering A, Kucharzik T, Parkos CA, Madara JL, Hopkins AM, Nusrat A (2003) Proinflammatory cytokines disrupt epithelial barrier function by apoptosis-independent mechanisms. J Immunol 171:6164–6172
Rahman SH, Ammori BJ, Holmfield J, Larvin M, McMahon MJ (2003) Intestinal hypoperfusion contributes to gut barrier failure in severe acute pancreatitis. J Gastrointest Surg 7:26–36
Wang X, Gong Z, Wu K, Wang B, Yuang Y (2003) Gastrointestinal dysmotility in patients with acute pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:57–62
Wang YL, Zheng YJ, Zhang ZP, Su JY, Lei RQ, Tang YQ, Zhang SD (2009) Effects of gut barrier dysfunction and NF-kappaB activation on aggravating mechanism of severe acute pancreatitis. J Dig Dis 10:30–40
Delgado M, Ganea D (2001) Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide inhibit nuclear factor-kappa B-dependent gene activation at multiple levels in the human monocytic cell line THP-1. J Biol Chem 276:369–380
Chrivia JC, Kwok RP, Lamb N, Hagiwara M, Montminy MR, Goodman RH (1993) Phosphorylated CREB binds specifically to the nuclear protein CBP. Nature 365:855–859
Johnson GB, Brunn GJ, Platt JL (2004) Cutting edge: an endogenous pathway to systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)-like reaction through Toll-like receptor-4. J Immunol 172:20–24
Hietaranta A, Mustoneu H, Puolakkainen P, Haapiainen R, Kemppainen E (2004) Proinflammatory effects of pancreatic elastase are mediated through TLR-4 and NF-κB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 323:192–196
Li Z, Xia X, Zhang S, Zhang A, Bo W, Zhou R (2008) Up-regulation of Toll-like receptor 4 was suppressed by emodin and baicalin in the setting of acute pancreatitis. Biomed Pharmacother 63:120–128
Acknowledgments
We thank the support of the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhongkai, L., Jianxin, Y. & Weichang, C. Vasoactive intestinal peptide promotes gut barrier function against severe acute pancreatitis. Mol Biol Rep 39, 3557–3563 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1129-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1129-z