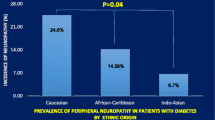
Abstract
Vascular factors beside metabolic problems are involved in both etiopathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy, and more remarkably, later in “repair” phase, that governs the net balance between neuro-regenerative/degenerative reactions. Regarding ischemic nature of diabetic neuropathy that highlights necessity of blood vessels re-establishment during tissue healing, VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) has been recently the subject of extensive investigations in diabetic neuropathy (DNU). This growth factor possesses angiogenic potentials in addition to the hemodynamic functions. The distribution of VEGF gene polymorphisms at positions −7*C/T, −1001*G/C, −1154*G/A and −2578*C/A were analysed by ARMS–PCR in 248 type 1 diabetic British-Caucasian subjects (81 DNU+, 167 DNU−). We have found that distribution of a VEGF gene polymorphism at promoter region (−7*C/T) was significantly different between diabetic subjects with vs. without neuropathy and the allele (C) conferred susceptibility to DNU (P = 0.02; OR = 1.78, 95% CI 1.0–3.1). The present study indicates that polymorphism of the VEGF gene at position −7*C/T might be implicated in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy as it may harbour some functional/regulatory potential in VEGF gene expression. However, this requires further studies in order to better understand its phenotypic impact and to investigate the prognostic value of this polymorphism in diabetic neuropathy as a chronic complication of diabetes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vague P, Brunetti O, Valet AM, Attali I, Lassmann-Vague V, Vialettes B (1988) Increased prevalence of neurologic complications among insulin dependent diabetic patients of Algerian origin. Diabetes Metab 14:706–711
Vague P, Dufayet O, Coste T, Moriscot C, Jannot MF, Raccah D (1997) Association of diabetic neuropathy with Na/K ATPase gene polymorphism. Diabetologia 40:506–511
Vague P, Dufayet O, Lamotte MF, Mouchot C, Raccah D (1997) Genetic factors, Na K ATPase activity and neuropathy in diabetics. Bull Acad Natl Med (French) 181:1811–1821
Heesom AE, Millward A, Demaine AG (1998) Susceptibility to diabetic neuropathy in patients with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus is associated with a polymorphism at the 5′ end of the aldose reductase gene. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 64:213–216
Feldman EL, Stevens MJ, Thomas PK, Brown MB, Canal N, Greene DA (1994) A practical two-step quantitative clinical and electrophysiological assessment for the diagnosis and staging of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 17:1281–1289
Aiello LP, Wong JS (2000) Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in diabetic vascular complications. Kidney Int Suppl 77:S113–S119
Caldwell RB, Bartoli M, Behzadian MA, El-Remessy AE, Al-Shabrawey M, Platt DH, Caldwell RW (2003) Vascular endothelial growth factor and diabetic retinopathy: pathophysiological mechanisms and treatment perspectives. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 19:442–455
Khamaisi M, Schrijvers BF, De Vriese AS, Raz I, Flyvbjerg A (2003) The emerging role of VEGF in diabetic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18:1427–1430
Leinninger GM, Vincent AM, Feldman EL (2004) The role of growth factors in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Peripher Nerv Syst 9:26–53
Schratzberger P, Walter DH, Rittig K, Bahlmann FH, Pola R, Curry C, Silver M, Krainin JG, Weinberg DH, Ropper AH, Isner JM (2001) Reversal of experimental diabetic neuropathy by VEGF gene transfer. J Clin Invest 107:1083–1092
Price SA, Dent C, Duran-Jimenez B, Liang Y, Zhang L, Rebar EJ, Case CC, Gregory PD, Martin TJ, Spratt SK, Tomlinson DR (2006) Gene transfer of an engineered transcription factor promoting expression of VEGF-A protects against experimental diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 55:1847–1854
Jin KL, Mao XO, Greenberg DA (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor: direct neuroprotective effect in in vitro ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10242–10247
Duh E, Aiello LP (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor and diabetes: the agonist versus antagonist paradox. Diabetes 48:1899–1906
Tilton RG, Kawamura T, Chang KC, Ido Y, Bjercke RJ, Stephan CC, Brock TA, Williamson JR (1997) Vascular dysfunction induced by elevated glucose levels in rats is mediated by vascular endothelial growth factor. J Clin Invest 99:2192–2202
Tilton RG (2002) Diabetic vascular dysfunction: links to glucose-induced reductive stress and VEGF. Microsc Res Tech 57:390–407
Ido Y, Chang KC, Lejeune WS, Bjercke RJ, Reiser KM, Williamson JR, Tilton RG (2001) Vascular dysfunction induced by AGE is mediated by VEGF via mechanisms involving reactive oxygen species, guanylate cyclase, and protein kinase C. Microcirculation 8:251–263
Cooper ME (2001) Interaction of metabolic and haemodynamic factors in mediating experimental diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia 44:1957–1972
Aiello LP, Northrup JM, Keyt BA, Takagi H, Iwamoto MA (1995) Hypoxic regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in retinal cells. Arch Ophthalmol 113:1538–1544
Natarajan R, Bai W, Lanting L, Gonzales N, Nadler J (1997) Effects of high glucose on vascular endothelial growth factor expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J PhysioI 273:H2224–H2231
Murata T, Nagai R, Ishibashi T, Inomuta H, Ikeda K, Horiuchi S (1997) The relationship between accumulation of advanced glycation end products and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human diabetic retinas. Diabetologia 40:764–769
Treins C, Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Murdaca J, Van Obberghen E (2001) Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by advanced glycation end products. J Biol Chem 276:43836–43841
Williams B, Gallacher B, Patel H, Orme C (1997) Glucose-induced protein kinase C activation regulates vascular permeability factor mRNA expression and peptide production by human vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro. Diabetes 46:1497–1503
Caldwell RB, Bartoli M, Behzadian MA, El-Remessy AE, Al-Shabrawey M, Platt DH, Liou GI, Caldwell RW (2005) Vascular endothelial growth factor and diabetic retinopathy: role of oxidative stress. Curr Drug Targets 6:511–524
Ferrara N (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev 25:581–611
Dvorak HF, Brown LF, Detmar M, Dvorak AM (1995) Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor, microvascular hyperpermeability, and angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 146:1029–1039
Antonetti DA, Barber AJ, Khin S, Lieth E, Tarbell JM, Gardner TW (1998) Vascular permeability in experimental diabetes is associated with reduced endothelial occludin content: vascular endothelial growth factor decreases occludin in retinal endothelial cells. Penn State Retina Research Group. Diabetes 47:1953–1959
Unemori EN, Ferrara N, Bauer EA, Amento EP (1992) Vascular endothelial growth factor induces interstitial collagenase expression in human endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol 153:557–562
Ferrara N, Carver-Moore K, Chen H, Dowd M, Lu L, O’Shea KS, Powell-Braxton L, Hillan KJ, Moore MW (1996) Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation of the VEGF gene. Nature 380:439–442
Mu H, Zhang XM, Liu JJ, Dong L, Feng ZL (2009) Effect of high glucose concentration on VEGF and PEDF expression in cultured retinal Müller cells. Mol Biol Rep 36(8):2147–2151
Teng Y, Cui H, Yang M, Song H, Zhang Q, Su Y, Zheng J (2009) Protective effect of puerarin on diabetic retinopathy in rats. Mol Biol Rep 36(5):1129–1133
Tesfaye S, Malik R, Ward JO (1994) Vascular factors in diabetic neuropathy. Diabetologia 37:847–854
Stevens MJ, Feldman EL, Greene DA (1995) The aetiology of diabetic neuropathy: the combined roles of metabolic and vascular defects. Diabetes Med 12:566–579
Schratzberger P, Schratzberger G, Silver M, Curry C, Kearney M, Magner M, Alroy J, Adelman LS, Weinberg DH, Ropper AH, Isner JM (2000) Favorable effect of VEGF gene transfer on ischemic peripheral neuropathy. Nat Med 6:405–413
Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus (1997) Diabetes Care 20:1183–1197
The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group (1993) The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes in the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 329:977–986
UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group (1998) Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 352:837–853
Gao XY, Kuang HY, Zou W, Liu XM, Lin HB, Yang Y (2009) The timing of re-institution of good blood glucose control affects apoptosis and expression of Bax and Bcl-2 in the retina of diabetic rats. Mol Biol Rep 36(7):1977–1982
Seaquist ER, Goetz FC, Rich S, Barbosa J (1989) Familial clustering of diabetic kidney disease. Evidence for genetic susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med 320:1161–1165
The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group (1997) Clustering of long-term complications in families with diabetes in the diabetes control and complications trial. Diabetes 46:1829–1839
Renner W, Kotschan S, Hoffmann C, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Pilger E (2000) A common 936 C/T mutation in the gene for vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with vascular endothelial growth factor plasma levels. J Vasc Res 37:443–448
Watson CJ, Webb NJ, Bottomley MJ, Brenchley PE (2000) Identification of polymorphisms within the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene: correlation with variation in VEGF protein production. Cytokine 12:1232–1235
Shahbazi M, Fryer M, Pravica V, Brogan IJ, Ramsay HM, Hutchinson IV, Harden PN (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor gene polymorph isms are associated with acute renal allograft rejection. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:260–264
Wang T, Hu K, Ren J, Zhu Q, Wu G, Peng G (2010) Polymorphism of VEGF-2578C/A associated with the risk and aggressiveness of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in a Chinese population. Mol Biol Rep 37(1):59–65
Onen IH, Konac E, Eroglu M, Guneri C, Biri H, Ekmekci A (2008) No association between polymorphism in the vascular endothelial growth factor gene at position −460 and sporadic prostate cancer in the Turkish population. Mol Biol Rep 35(1):17–22
Sfar S, Saad H, Mosbah F, Chouchane L (2009) Combined effects of the angiogenic genes polymorphisms on prostate cancer susceptibility and aggressiveness. Mol Biol Rep 36(1):37–45
Marsh S, Nakhoul FM, Skorecki K, Rubin A, Miller BP, Leibu R, Levy NS, Levy AP (2000) Hypoxic induction of vascular endothelial growth factor is markedly decreased in diabetic individuals who do not develop retinopathy. Diabetes Care 23:1375–1380
Chaturvedi N, Fuller JH, Pokras F, Rottiers R, Papazoglou N, Aiello LP, EUCLID Study Group (2001) Circulating plasma vascular endothelial growth factor and microvascular complications of type 1 diabetes mellitus: the influence of ACE inhibition. Diabet Med 18:288–294
Acknowledgement
The authors wish to thank Christine Halford and Mike Frazer and all the Manchester Diabetes Centre staff for their assistance in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tavakkoly-Bazzaz, J., Amoli, M.M., Pravica, V. et al. VEGF gene polymorphism association with diabetic neuropathy. Mol Biol Rep 37, 3625–3630 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0013-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0013-6